Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There is now an increasing range of drug options in PsA. To inform the update of the EULAR PsA management recommendations (Ref 1), we performed a systematic literature review assessing the efficacy and safety of pharmacological agents in PsA.
Methods: Original articles published since the last EULAR literature review (2015) until 2018 in English were searched in Medline, Embase and Cochrane Library, as well as ACR/EULAR abstracts (2015-2018). For efficacy, randomised controlled trials (RCTs) investigating pharmacological interventions, defined as biological (b)DMARDs, targeted synthetic (ts)/conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs were analysed. The main efficacy outcomes were ACR response criteria, PASI75, enthesitis, physical function and radiographic progression. For safety, also cohorts and case-control studies were analysed with a focus on adverse events, infections, cancer and cardio-vascular events.
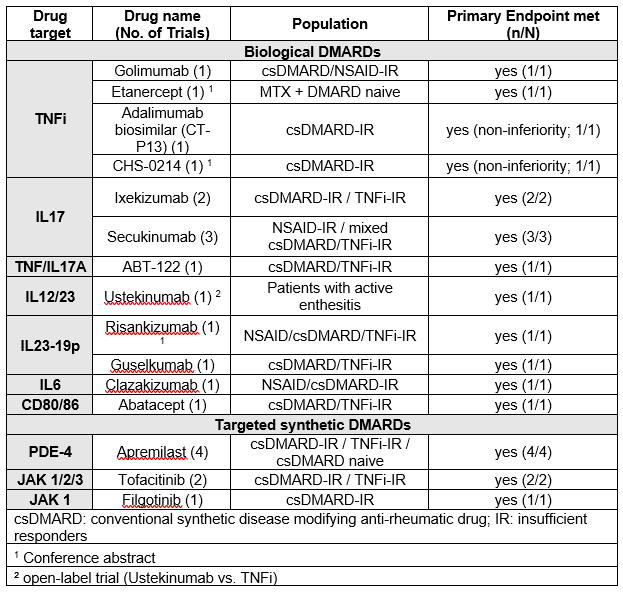
Results: Of 6380 articles (efficacy: 2191, safety: 4189), 76 (68 original articles and 8 abstracts) were analysed. The drugs most investigated over the timeframe of this search were TNFi (5 trials) and IL17i (5 trials) (Table 1). Other drugs with mechanisms not previously published on in this indication were especially IL23-p19 inhibitors and JAK inhibitors (Table 1).
All trials of original drugs, except one open-label study comparing Ustekinumab to TNFi, were placebo-compared trials and met their primary endpoint, ACR20 (Table 1). Figure 1 indicates the variety of responses across disease manifestations. Biosimilar comparison with bio-originator showed non-inferiority.
Safety was evaluated in 32 articles. One article, investigating patients in the ARTIS and DANBIO registries did not show an increased risk of cancer with TNFi compared to TNFi naïve PsA patients and the general population. There was an increased risk of Candida infections and inflammatory bowel disease with IL17 inhibiting agents. Two longitudinal cohorts showed an elevated risk for major adverse cardiac events in PsA. One longitudinal cohort study showed no association of cardiovascular events with any treatment.
Conclusion: New drugs targeting IL17A, IL23-p19, JAK, CD80/86, TNF/IL17A and IL6 demonstrated efficacy for the treatment of PsA with varying responses across different disease domains. Efficacy of TNFi agents and other bDMARDs was confirmed. Investigated biosimilars were non-inferior to their reference products. No new major safety signals were identified, though long-term studies and more registry data are needed. This literature review informed the EULAR updated recommendations for management of PsA.
Ref 1. Gossec L et al. 2019 update of the psoriatic arthritis management recommendations, oral presentation EULAR 2019, 15 June 2019.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kerschbaumer A, Smolen J, Dougados M, de Wit M, Primdahl J, McInnes I, van der Heijde D, Falzon L, Baraliakos X, Gossec L. Efficacy and Safety of Disease-Modifying Drugs in Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): A Systematic Literature Review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-disease-modifying-drugs-in-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-a-systematic-literature-review/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-disease-modifying-drugs-in-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-a-systematic-literature-review/