Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: As part of the update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of axSpA, we performed a systematic literature review to assess the efficacy and safety of biological (b) and targeted synthetic (ts) DMARDs in patients with axSpA published since the last SLR in 2009.
Methods: We searched in Medline, EMBASE, and Cochrane Central databases (2009-2016), supplemented by searches in 2014-2015 EULAR and ACR abstracts, for randomized clinical trials (RCT) and controlled CTs, including long-term extensions, strategy trials, and observational studies (only for safety assessment and as long as a comparator group was included). Interventions were any bDMARD, tsDMARD and biosimilar. All relevant efficacy and safety outcomes were included and meta-analyses performed whenever appropriate.
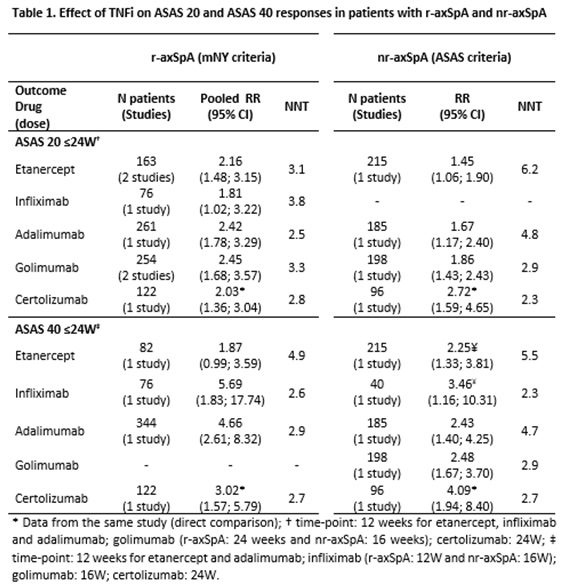
Results: Of 10,244 articles and 428 conference abstracts screened, 76 papers and 26 abstracts fulfilled the inclusion criteria. A Cochrane review confirmed the efficacy and safety of etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab and golimumab in patients with r-axSpA. In addition, we found large treatment-effects both in r-axSpA and nr-axSpA for these drugs and also for certolizumab pegol (table 1). For nr-axSpA, results were better among those with objective signs of inflammation (either sacroiliitis on MRI or CRP) before treatment start (table 2). Secukinumab has shown good efficacy results in two large phase 3 RCTs [ASAS 20 pooled RR (95% CI) at week 16: 2.1 (1.7; 2.7) for 150 mg; NNT: 3.1] and overall good safety data. Ustekinumab, apremilast and tofacitinib have shown good (preliminary) results in phase 2/proof of concept trials; Rituximab, IL-6 antagonists (tocilizumab and sarilumab) and abatacept failed to do so. Infliximab biosimilar (CT-P13) proved to be as effective and safe as the infliximab originator. Although long-term observational safety data are still scarce, no new safety signals were identified.
Conclusion: New evidence strengthens the efficacy and safety of TNFi both in patients with r-axSpA and nr-axSpA. Secukinumab is the first drug targeting a new pathway showing efficacy and safety in axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sepriano A, Regel A, van der Heijde D, Braun J, Baraliakos X, Landewé R, van Den Bosch F, Ramiro S. Efficacy and Safety of Biological Therapy and Target Synthetic Dmards: A Systematic Literature Review Informing the 2016 Update of the ASAS/EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-biological-therapy-and-target-synthetic-dmards-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-the-2016-update-of-the-asaseular-recommendations-for-the-management-of-axial-spondyloar/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-biological-therapy-and-target-synthetic-dmards-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-the-2016-update-of-the-asaseular-recommendations-for-the-management-of-axial-spondyloar/