Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Janus kinases (JAKs) play an important role in intracellular signaling for multiple cytokines in the pathogenesis of RA. Baricitinib is an oral, selective JAK 1 and 2 inhibitor which has been shown to be effective in the treatment of RA in several clinical trials. This meta-analysis aims to aggregate currently available data to assess the overall efficacy and safety of baricitinib in RA.
Methods:
We searched PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane CENTRAL from inception through 05/25/17 without language restriction. Our eligibility criteria included human placebo-controlled RCTs in adults (≥ 18 years of age) that evaluated efficacy and safety outcomes of barcitinib in RA patients. We excluded meeting abstracts without full text publication. We used RevMan 5.3 to perform meta-analysis between groups on baricitinib 4mg per day and placebo using random effect model calculating odds ratio (OR) as well as 95% confidence interval (CI). I2 statistic was used to identify heterogeneity between studies, and values of more than 50 was used to indicate significant heterogeneity. We measured efficacy using ACR20/50/70 and DAS28-CRP response criteria and safety with adverse events.
Results:
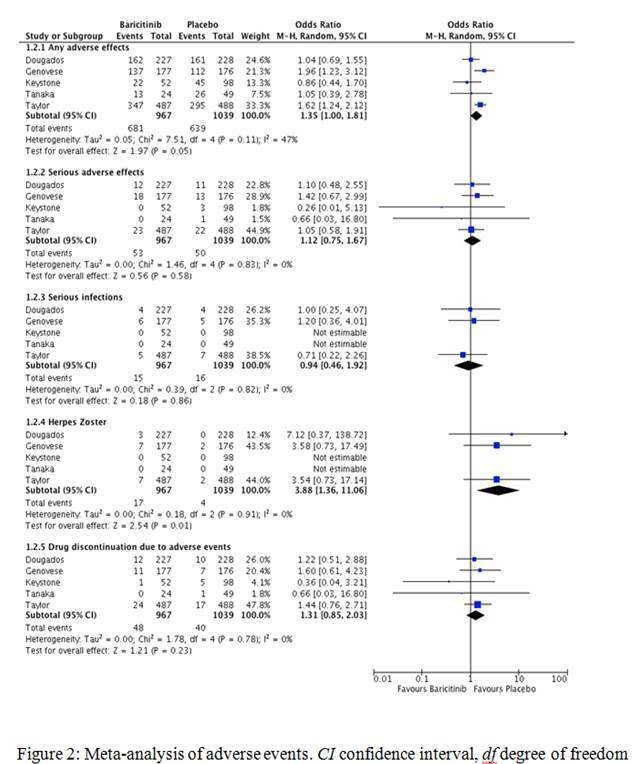
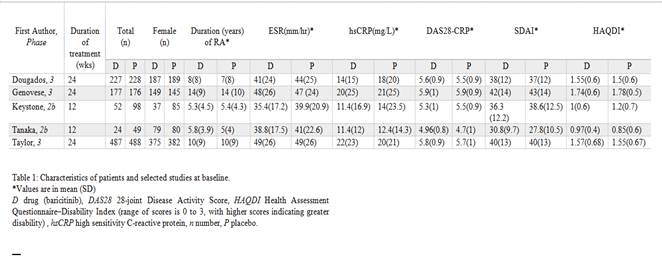
Five studies with a total of 2006 patients (967 on baricitinib and 1039 on placebo) were included for meta-analysis. The maximum study duration was 24 weeks. Baricitinib demonstrated greater efficacy in achieving ACR20/50/70 responses compared to placebo (66.7 vs 36.6%, OR 3.33, 95% CI 2.18-5.07, I2 75%, P<0.00001; 44.1 vs 17.8%, OR 3.56, 95% CI 2.77-4.58, I2 20%, P<0000.1 and 24.4 vs 6.5%, OR 4.62, 95% CI 2.96-7.19, I2 40%, P<0.00001 respectively). There was a small increase in any adverse events in the baricitinib group (70.4 vs 61.5%, OR 1.35, 95% CI 1-1.81, I2 47%, P=0.05), however, no increase in serious adverse events (5.5 vs 4.8%, OR 1.12, 95% CI 0.75-1.67, I2 0%, P=0.58) or serious infections (1.5 vs 1.5%, OR 0.94, 95% CI 0.46-1.92, I2 0%, P=0.86) when compared to placebo.
Conclusion:
Baricitinib is effective in treatment of RA, and did not appear to have significant safety concerns during the first six months of treatment. However, the long term safety profile of this drug should be evaluated by future clinical trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kunwar S, Collins CE, Constantinescu F. Efficacy and Safety of Baricitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-baricitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-baricitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/