Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is a novel oral Janus kinase inhibitor being investigated as a targeted immunomodulator and disease-modifying therapy for RA. In RA patients (pts), suppression of total (TC), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels during inflammation has been described. Tofacitinib has shown significant efficacy in reducing RA disease activity and inflammation in Phase 2/3 studies, during which a proportion of pts displayed increases in cholesterol levels. This Phase 1 study aimed to understand the mechanisms for suppression of cholesterol levels in active RA pts compared with healthy controls, and to investigate changes in cholesterol and lipoprotein kinetics following 6 weeks of tofacitinib treatment in RA pts.
Methods: Baseline lipid profiles and cholesterol and lipoprotein kinetics were assessed in 36 RA pts and 33 matched healthy controls (of similar age, race, sex, and menopausal status) and were repeated in RA pts after treatment with oral tofacitinib 10 mg twice daily for 6 weeks. Fasting blood samples were collected for apolipoprotein (Apo) and lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations, HDL and LDL particle size, and biomarkers of HDL dysfunction. In vivo cholesterol and lipoprotein kinetics were assessed with a 22‑hour infusion of [13C]cholesterol and [13C]leucine.
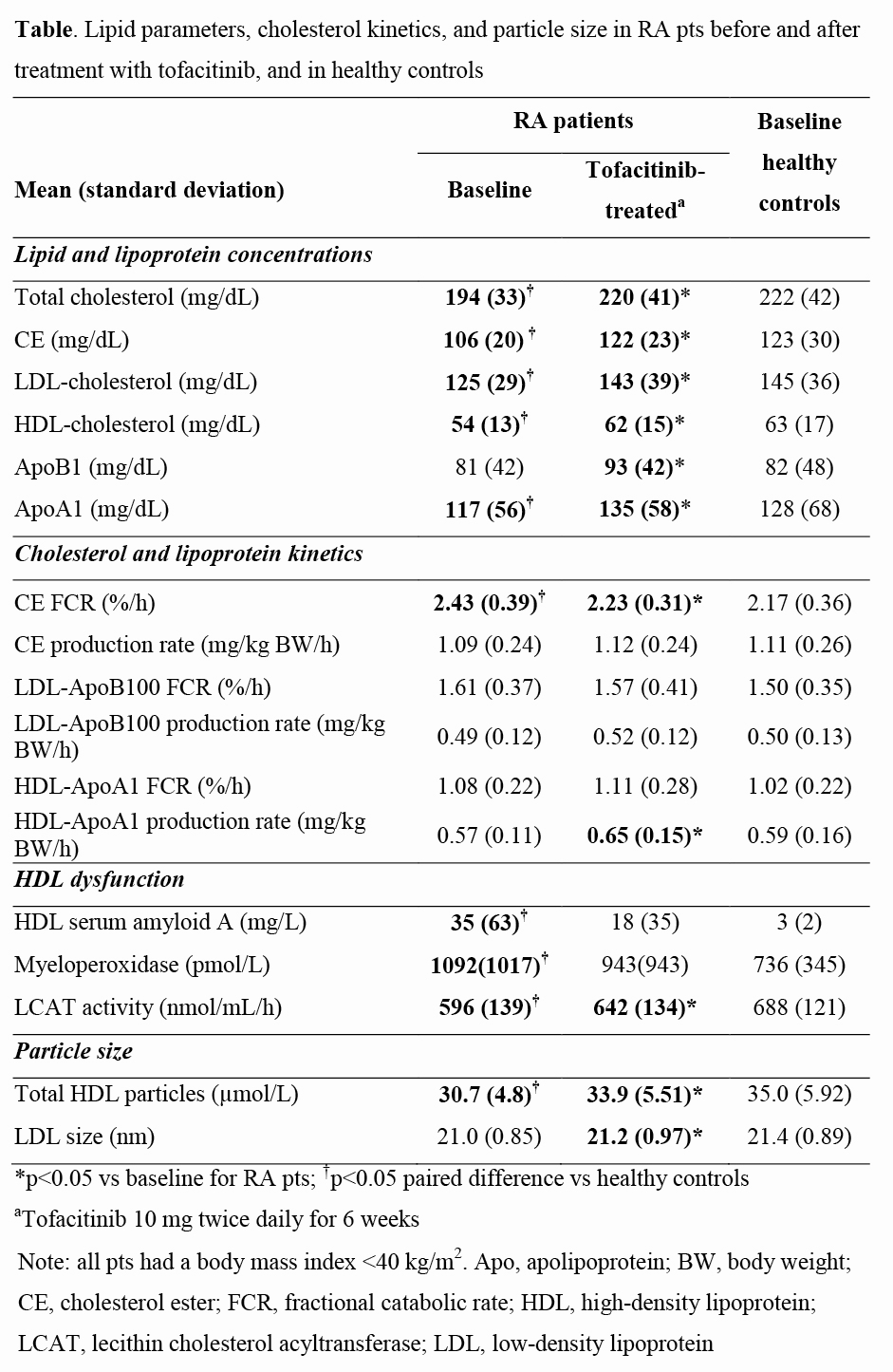
Results: At baseline, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, TC and ApoA1 concentrations in RA pts were lower than in controls (Table). The cholesterol ester (CE) fractional catabolic rate (FCR) was significantly greater in RA pts vs controls without differences in cholesteryl ester transfer protein mass/activity or CE production rate. HDL-ApoA1 and LDL-ApoB100 FCR were similar between the groups. HDL biomarkers indicated HDL dysfunction in RA pts compared with controls as shown by higher HDL‑associated serum amyloid A and myeloperoxidase, and lower in vitro lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase activity/mass. After tofacitinib therapy, the HDL‑ApoA1 production rate was increased. Additionally, the CE FCR and cholesterol levels approached levels of controls with increases in plasma ApoA1 and ApoB concentrations. Increased CE FCR in the absence of changes in HDL-ApoA1 or LDL‑ApoB100 FCR suggests increased selective CE uptake by scavenger receptor Class B Type 1 in RA pts, which was normalized by tofacitinib. Total HDL particle number and LDL size increased, and markers of HDL dysfunction improved after tofacitinib.
Conclusion: This is the first study to assess cholesterol and lipoprotein kinetics in pts with active RA and matched healthy controls. The data suggest that low cholesterol levels in RA pts with active disease may be explained by increases in CE catabolism. Treatment with tofacitinib decreased CE catabolism and normalized cholesterol levels to those of healthy controls while improving markers of HDL function, including increased HDL‑ApoA1 production.
Disclosure:
C. Charles-Schoeman,
Pfizer Inc.,
2,
Pfizer Inc.,
5,
Pfizer Inc.,
9;
R. Fleischmann,
Pfizer Inc.,
2,
Pfizer Inc.,
5;
J. Davignon,
None;
H. Schwartz,
None;
S. Turner,
KineMed, Inc.,
1,
KineMed, Inc.,
3;
C. Beysen,
Kinemed,
1,
Kinemed,
3;
M. Milad,
Pfizer, Inc.,
1,
Milad Pharmaceutical Consulting LLC,
5,
Milad Pharmaceutical Consulting LLC,
9;
Z. Luo,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
J. Bradley,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
I. Kaplan,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
R. Riese,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
A. Zuckerman,
Pfizer Inc.,
1,
Pfizer Inc.,
3;
I. B. McInnes,
Pfizer Inc.,
2,
Pfizer Inc.,
5.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-tofacitinib-on-lipid-profiles-and-cholesterol-and-lipoprotein-kinetics-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/