Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Methotrexate (MTX) is currently the most frequently used drug in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). MTX co-medication can improve the therapeutic benefit of adalimumab (ADA) in biologic-naïve RA patients. However, the impact of concomitant MTX has not been fully characterized in patients pretreated with biologics. Similarly, the influence of adding MTX to established ADA monotherapy has not been fully characterized.
Methods
We analyzed data from a large German multicenter, prospective, observational study of patients with active RA who are treated with ADA during routine clinical care. The effect of therapy on mean DAS28 scores was evaluated at baseline (month 0) and at months 3, 6, and 12 for patients receiving continuous ADA monotherapy, continuous ADA + MTX combination therapy, and MTX added to ADA therapy at 6 months (ADA monotherapy for the first 6 months and ADA + MTX combination therapy for months 6–12). Subgroup analyses for ADA monotherapy vs ADA + MTX were performed on biologic-naïve versus biologic-experienced patients. Stepwise forward and backward regression analyses were performed for identifying significant predictors.
Results
Combination therapy with ADA + MTX resulted in lower mean DAS28 scores at month 12 and a significant reduction in DAS28 scores from baseline than ADA monotherapy (Table). DAS28 improvements in patients who began the observation period on ADA monotherapy and added MTX at month 6 were similar to those receiving ADA + MTX continuously for 12 months. Subgroup analysis by prior biologic therapy indicated that both biologic-naïve and biologic-experienced patients achieved lower mean DAS28 scores with ADA + MTX than with ADA monotherapy (p<0.0001). However, patients treated previously with biologics did not show as much improvement in DAS28 scores as biologic-naïve patients, irrespective of MTX use.
Conclusion
Adding MTX to ADA monotherapy at month 6 resulted in DAS28 decreases similar to those observed with continuous ADA + MTX therapy, although patient numbers were small. Both biologic-naïve and biologic-experienced patients achieved lower DAS28 scores with ADA + MTX than with ADA monotherapy. These findings support the addition of MTX to ADA therapy for all patient populations.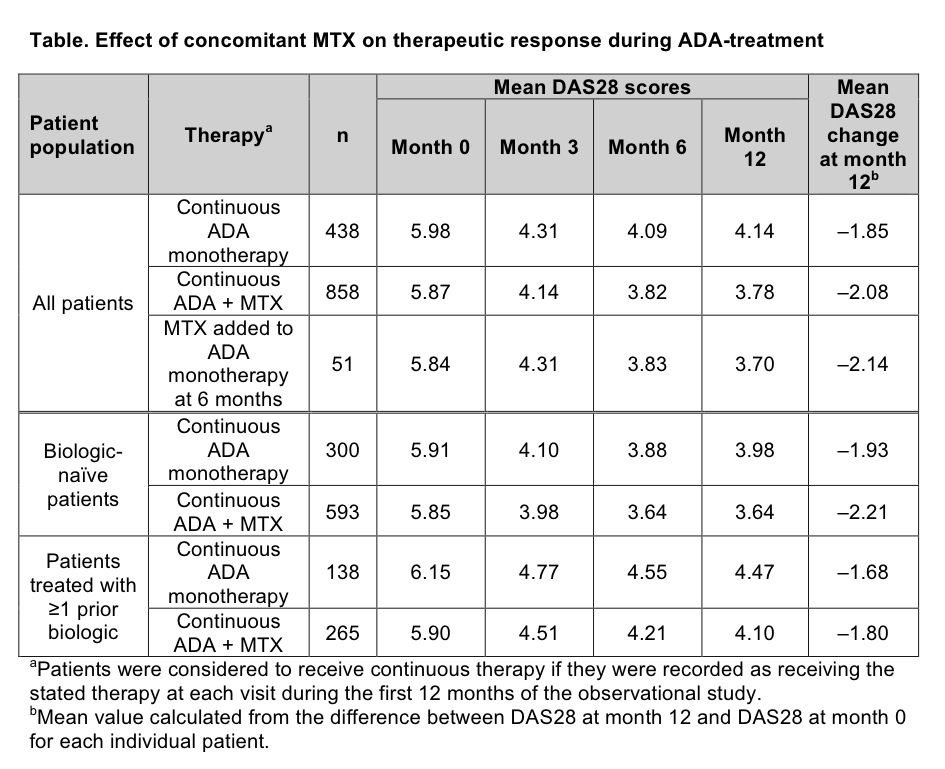
Disclosure:
M. Schmalzing,
AbbVie,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Actelion Pharmaceuticals US,
5,
BMS,
5,
Chugai,
5,
UCB,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
F. Behrens,
AbbVie,
5,
Chugai,
8,
Chugai,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
5;
E. C. Scharbatke,
AbbVie,
5,
Chugai,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5;
M. Koehm,
AbbVie,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
2;
B. Wittig,
AbbVie,
3;
G. Greger,
AbbVie,
3;
H. Burkhardt,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
AbbVie,
5,
UCB,
5,
BMS,
5,
Chugai,
5;
H. P. Tony,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-methotrexate-on-anti-tnf-treatment-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-in-depth-analysis-of-a-prospective-observational-study-with-adalimumab/
