Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: To evaluate the effects of subcutaneously-administered blisibimod on renal and inflammation biomarkers in patients with SLE during the phase 2b clinical trial PEARL-SC (NCT01162681) and the ensuing open-label extension (OLE) study (NCT01305746).
Methods: 547 patients with serologically-active SLE and SELENA SLEDAI ≥6 were randomized to receive placebo or blisibimod. Per SELENA-SLEDAI definitions, 76 subjects (13.9%) had renal involvement at baseline. In the PEARL-SC study, subjects received blinded study drug for up to 52 weeks (with a median of 37 weeks) or until the last subject completed 6 months of therapy. A total of 382 subjects enrolled in the OLE study and received blisibimod. Here we report the effects of blisibimod in subjects who initiated blisibimod therapy in the PEARL study (N=277), evaluating changes on renal and inflammation biomarkers in the combined PEARL and OLE studies through March 2013. In addition, we report blisibimod effects on renal biomarkers in 2 renal subgroups defined as (i) baseline proteinuria equivalent ≥0.5 g/24hr (determined from random spot urinary protein:creatinine ratio, N=41), or (ii) baseline proteinuria equivalent to ≥1g/24hr (N=25).
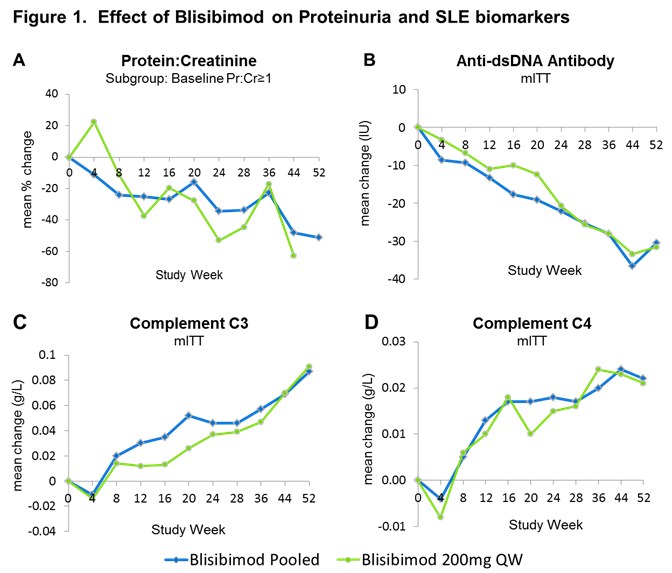
Results: Compared with baseline, decreases in proteinuria were observed with blisibimod from Week 12 through Week 52 in the subgroup of subjects with proteinuria equivalent ≥1 g/24hr at enrollment (Figure 1A). Similarly decreases in proteinuria were observed in subjects with proteinuria equivalent ≥0.5 g/24hr through Week 44. When compared with response in the patients randomized to receive placebo in PEARL-SC, there was a tendency toward greater decreases in mean GFR in the patients receiving placebo compared with blisibimod at Week 24 in both renal subgroups, eg mean ΔGFR =1.4 and -3.0 mL/min [N=36,37], for blisibimod and placebo respectively in the ≥0.5 g/24hr subgroup.
Consistent with a durable pharmacological effect, decreases in anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibodies, and increases in complement C3 and C4 compared with baseline were observed through 52 weeks of blisibmod therapy (Figure 1B, C and D).
Blisibimod was safe and well-tolerated at all dose levels with no meaningful imbalances in serious adverse events or infections between blisibimod and placebo in the PEARL-SC study, and continued to be well-tolerated through the OLE study.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that blisibimod induces pharmacological effects on proteinuria and SLE biomarkers that are consistent with BAFF-mediated inhibition of B cells and plasma cells, without adversely impacting the risk of infection in patients with SLE. These data support further evaluation of blisibimod in patients with SLE and other B cell-mediated diseases.
Disclosure:
R. A. Furie,
Anthera Pharmaceuticals,
9;
M. Thomas,
None;
A. Chu,
Anthera Pharmaceuticals,
3,
Anthera Pharmaceuticals,
1;
R. S. Martin,
Anthera Pharmaceuticals,
3,
Anthera Pharmaceuticals,
1;
C. Hislop,
Anthera Pharmaceuticals,
1,
Anthera Pharmaceuticals,
3,
Anthera Pharmaceuticals,
1;
M. A. Scheinberg,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-chronic-treatment-with-blisibimod-an-inhibitor-of-b-cell-activating-factor-on-renal-and-inflammation-biomarkers-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-observations-from-the-p/