Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Real-world (RW) data on the effectiveness of tofacitinib in patients (pts) with PsA are limited. This study summarized disease activity and pt‑reported outcome measures in pts with PsA initiating tofacitinib as monotherapy vs in combination with oral small molecules (OSMs) in a RW setting.
Methods: Pts with PsA enrolled in the CorEvitas PsA/SpA Registry who initiated tofacitinib either as monotherapy or in combination with OSMs (MTX, leflunomide, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, or apremilast) from December 2017-October 2023 were identified. Pts were included if a baseline and 6-month follow-up visit (with ±3-month window) were available. The proportions of pts at 6 months who remained on monotherapy/combination therapy, who discontinued, or who added an OSM treatment, were evaluated. Changes from baseline (∆) were measured at 6±3 months for: Disease Activity Index for PsA (DAPSA), clinical DAPSA low disease activity (cDAPSA LDA), minimal disease activity (MDA), body surface area (BSA)=0%, and HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI). For binary endpoints, 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using normal approximation to binomial proportions were provided. Continuous endpoints at month 6 were analyzed as ∆ with an analysis of covariance model that included treatment and baseline value as covariates. Least squares (LS) means (standard error) and adjusted LS means/odds ratios (95% CI) are presented.
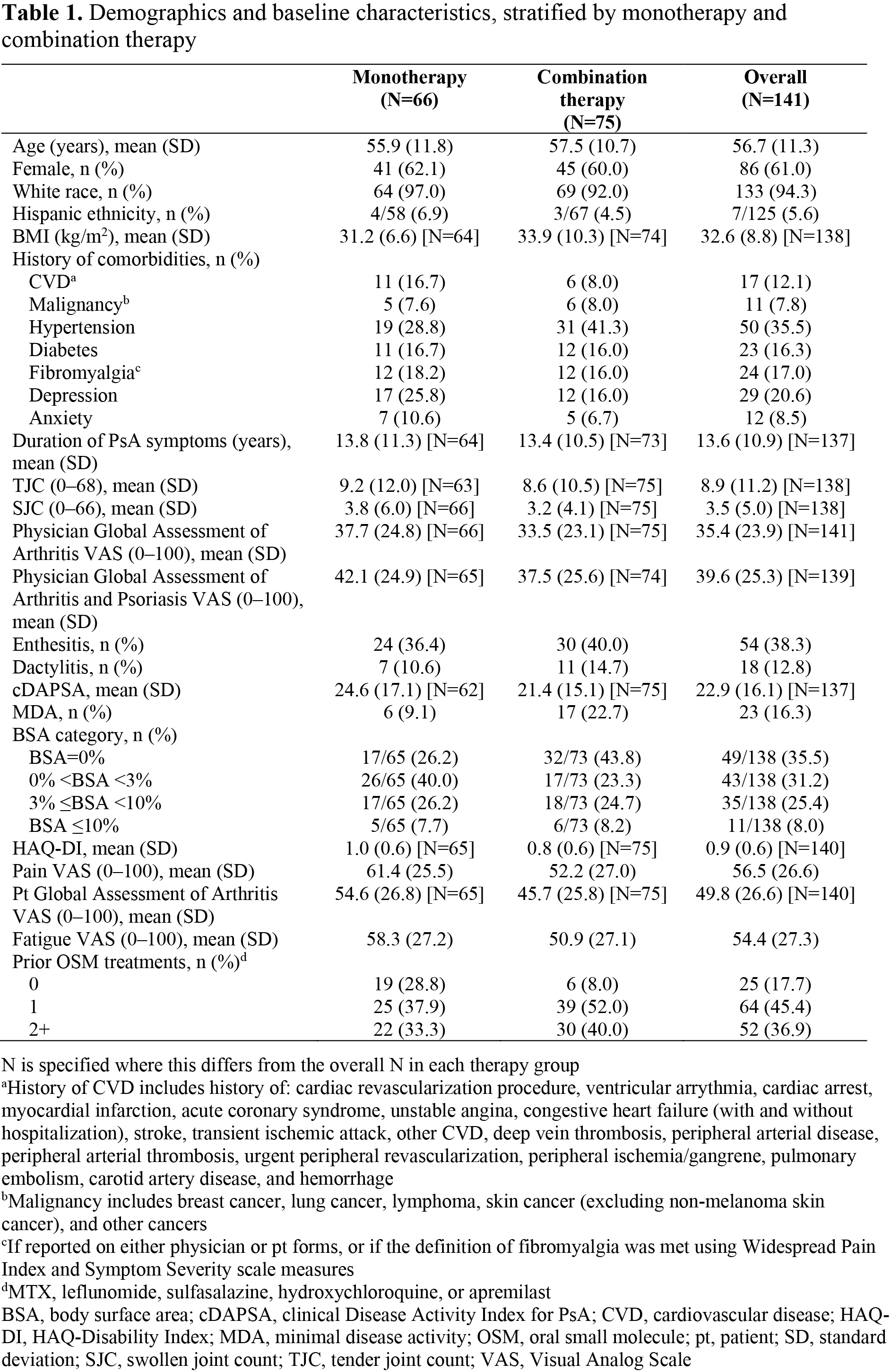
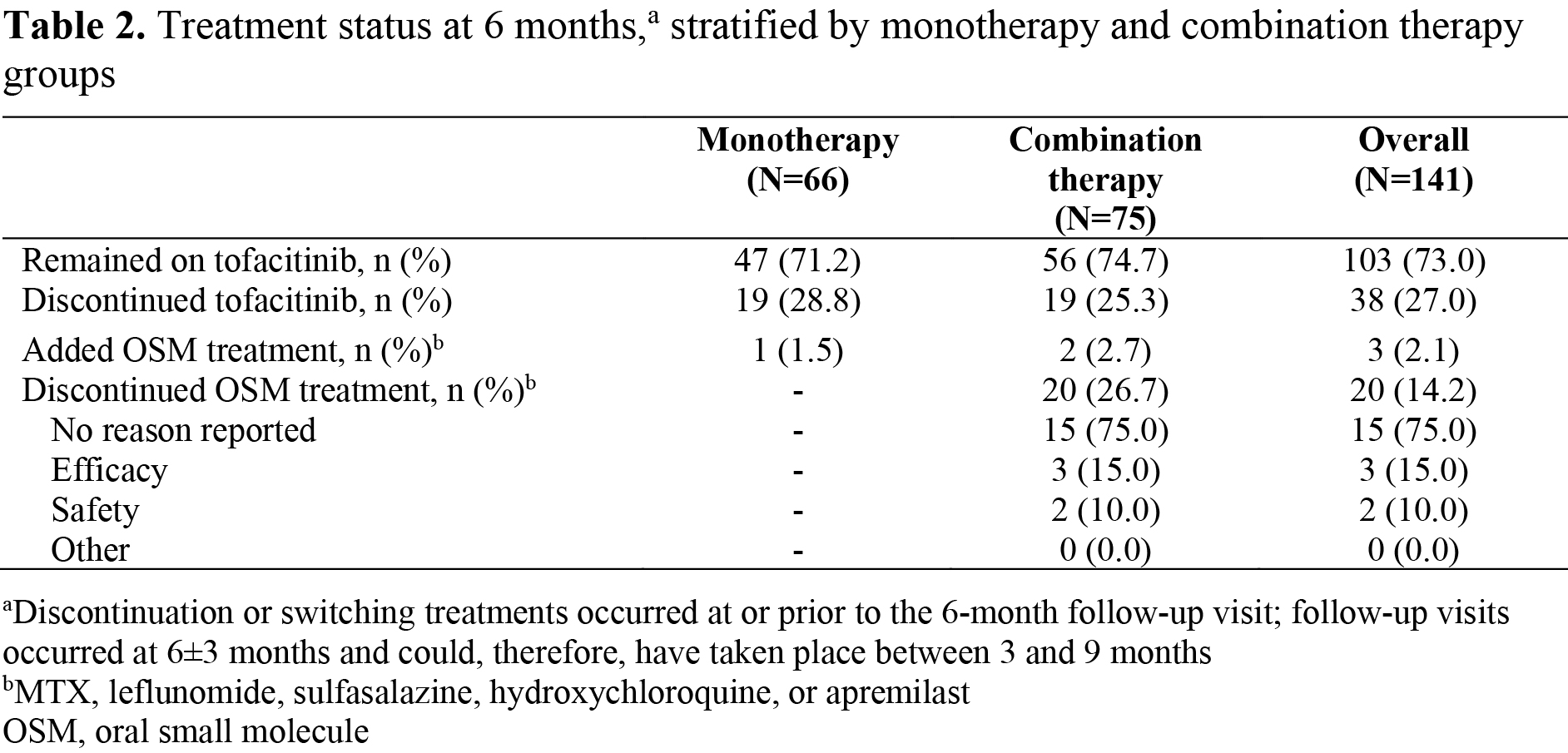
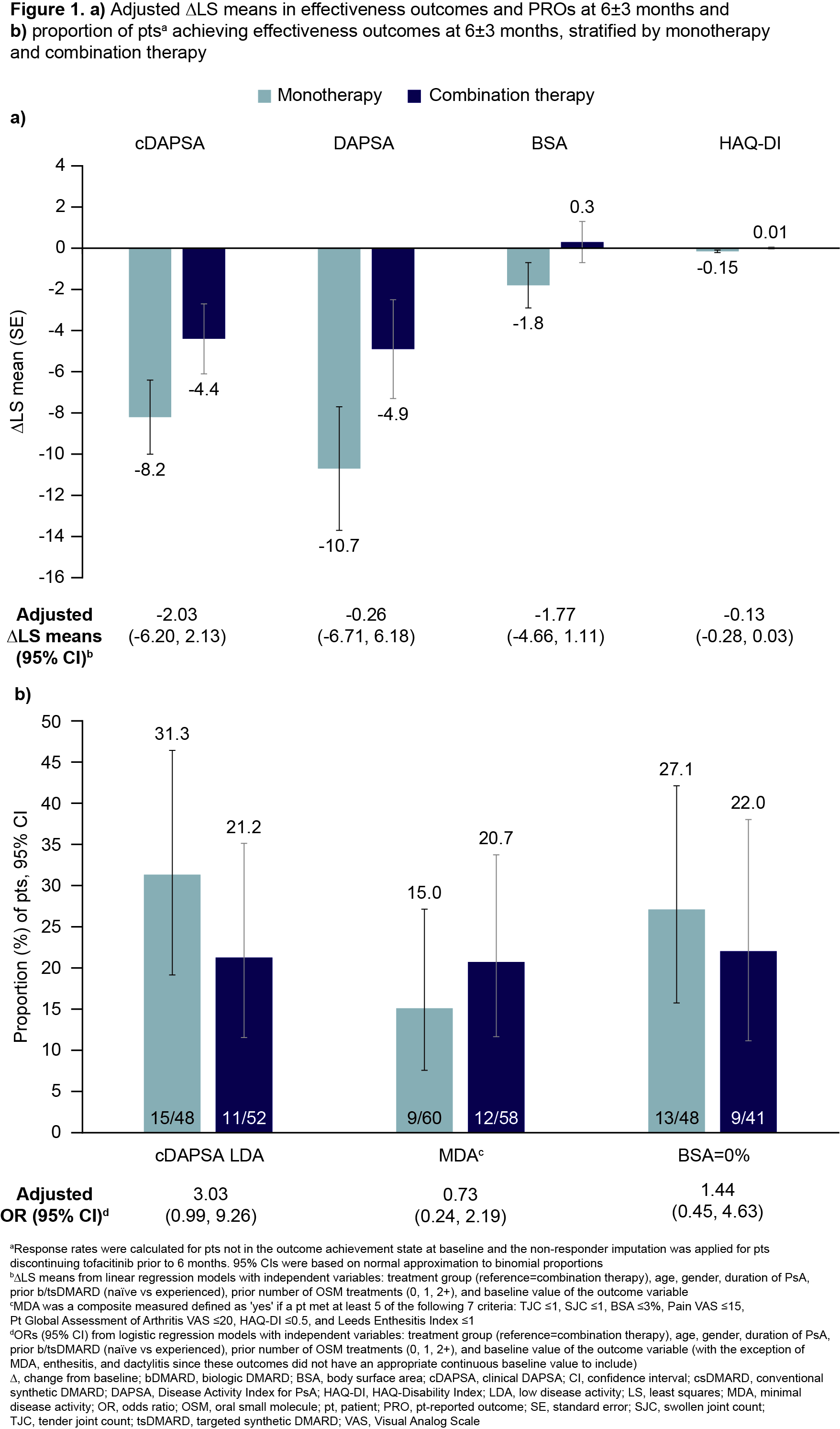
Results: In total, 141 pts initiated tofacitinib (66/141 as monotherapy; 75/141 as combination therapy). At baseline, 61.0% of pts were female, 94.3% were white, mean (standard deviation) age was 56.7 (11.3) years, and mean duration since PsA diagnosis was 8.7 years. More monotherapy users were OSM treatment-naïve and had higher mean Pt Global Assessment of Arthritis, compared with combination therapy users (Table 1). At 6±3 months, 71.2% of monotherapy initiators remained on tofacitinib, 28.8% discontinued tofacitinib, and 1.5% added an OSM treatment. Corresponding data for combination therapy users were 74.7%, 25.3%, and 2.7%, respectively; 26.7% of combination therapy initiators discontinued OSMs at/prior to 6 months (Table 2). Across treatment groups, improvements in many outcomes were observed at 6±3 months; there were no significant differences in LS means (Figure 1a). At 6±3 months, 31.3% of monotherapy initiators achieved cDAPSA LDA, 15.0% achieved MDA, and 27.1% had BSA=0%. Corresponding data for combination therapy users were 21.2%, 20.7%, and 22.0%, respectively (Figure 1b). Differences between groups were not significant.
Conclusion: In this RW population of pts with PsA who initiated tofacitinib, approximately half initiated as monotherapy. Both monotherapy and combination therapy users demonstrated improvements across effectiveness outcomes with no statistical differences after adjustment. This analysis illuminates the use of tofacitinib in a broad population of initiators and underscores its effectiveness both as monotherapy and in combination with other OSMs.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer and registry by CorEvitas, LLC. Medical writing support provided by Caitlin Duncan, PhD, CMC Connect; funded by Pfizer.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogdie A, Middaugh N, Blachley T, Bourgeois T, Ling Y, Mundayat R, Fallon L, Masri K, Mease P. Effectiveness of Tofacitinib Monotherapy versus Combination Therapy in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from the CorEvitas Psoriatic Arthritis/Spondylarthritis Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-tofacitinib-monotherapy-versus-combination-therapy-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-the-corevitas-psoriatic-arthritis-spondylarthritis-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-tofacitinib-monotherapy-versus-combination-therapy-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-the-corevitas-psoriatic-arthritis-spondylarthritis-registry/