Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Contradictory data has been reported on the effectiveness of a second and third line of TNFi in early axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). The objective of the study was to evaluate the effectiveness of TNFi after a first switch, in real life conditions, over 5 years of follow-up in this population.
Methods: Observational prospective French cohort (DESIR) with 5 years of follow-up, including 708 TNFi-naïve early axSpA patients. Study visits were scheduled every 6 months in the first two years and then yearly up to 5 years. Treatment (TNFi or other) was at the discretion of the treating rheumatologist’s. The characteristics of patients who received a second and a third TNFi were compared to those who never switched. Effectiveness of the first, second and third TNFi was firstly defined by their drug survival, estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method, and compared with the log-rank test. Secondly, we evaluated treatment effect of the second TNFi by the probability to reach an ASAS40 response in both groups (second TNFi vs. responders to the first TNFi), after at least 10months of exposure. To overcome prescriptions bias repeatedly occurring over time, we have applied an iterative method based on inverse propensity score (PS) weighting using a marginal structural model, that allows the integration of the repeated weights derived from the propensity score at each visit (i.e the probability to receive the treatment at each visit). The structural model used for this analysis was a PS-weighted cox regression, to estimate the probability to present an ASAS40 response after at least 10months of treatment.
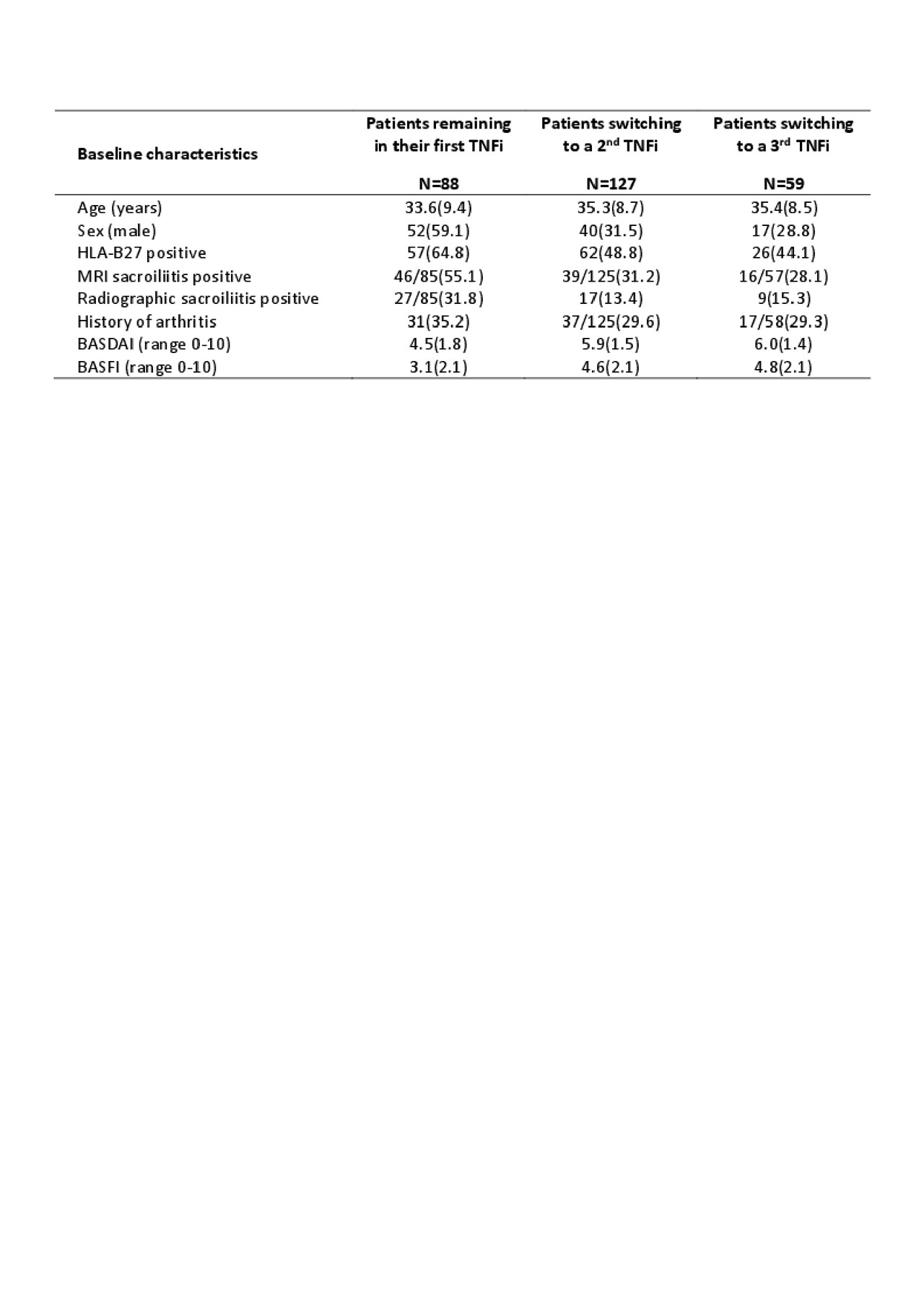
Results: of the 708 patients included in the analysis, 258 (36.4%) patients initiated a first TNFi during the 5y of follow-up. Of these, 127/258 (49.2%) switched to a second TNFi, and among them, 59/127 (46.5%) switched to a third TNFi. Patients who switched to a second or a third TNFi were more frequently older, predominantly females, HLA-B27 negative, with MRI and radiographic sacroiliitis negative, without history of peripheral arthritis, and with higher BASFI and BASDAI scores at baseline of the DESIR cohort (see table). Estimated median drug survival for the first, second and third TNFi was 21.7months [95%CI 17.6-33.6], 18.8months [95%CI 15.1-24.4] and 25.0months [95%CI 11.8-NA] respectively. Drug survival was significantly extended for the first TNFi compared to the second one (p=0.004), but no differences were observed between the 2nd and the 3rd TNFi. Identically, when taking into account the time-varying propension to perform a switch, likelihood of an ASAS40 response was lower for the second TNFi than for the first one (HR=2.4[95%CI 1.9-3.0] vs HR=3.3[95%CI 2.9-3.8] respectively), but remained clinically significant.
Conclusion: Our study suggests a lower but clinically significant TNFi effectiveness after a first switch in real-life conditions in early axial spondyloarthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pons M, Chevret S, Briot K, D’Agostino M, Roux C, Dougados M, Moltó A. Effectiveness of TNFi After a First Switch in Patients with Early Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Longitudinal Analysis of the DESIR Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-tnfi-after-a-first-switch-in-patients-with-early-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-longitudinal-analysis-of-the-desir-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-tnfi-after-a-first-switch-in-patients-with-early-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-longitudinal-analysis-of-the-desir-cohort/