Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is hindered by lack of glucocorticoid (GC)-sparing therapies with proven efficacy. A retrospective study showed a higher proportion of patients on IL-6 receptor inhibitors (IL-6Ri) vs conventional synthetic immunomodulators (csIM [methotrexate, leflunomide, and azathioprine]) discontinued GC at 1 year (HR [95% CI] 1.28 [1.02–1.60]). Frailty, associated with aging and inflammation may be accelerated and more prevalent in patients with PMR vs the general population. Prolonged GC treatment may exacerbate frailty, highlighting the need to reduce GC use. IL-6 is involved in the pathogenesis of PMR and frailty; patients with both may particularly benefit from IL-6Ri. The study compared the effectiveness of IL-6Ri vs csIM as second (2L) and third (3L) line treatment for frail patients with PMR.
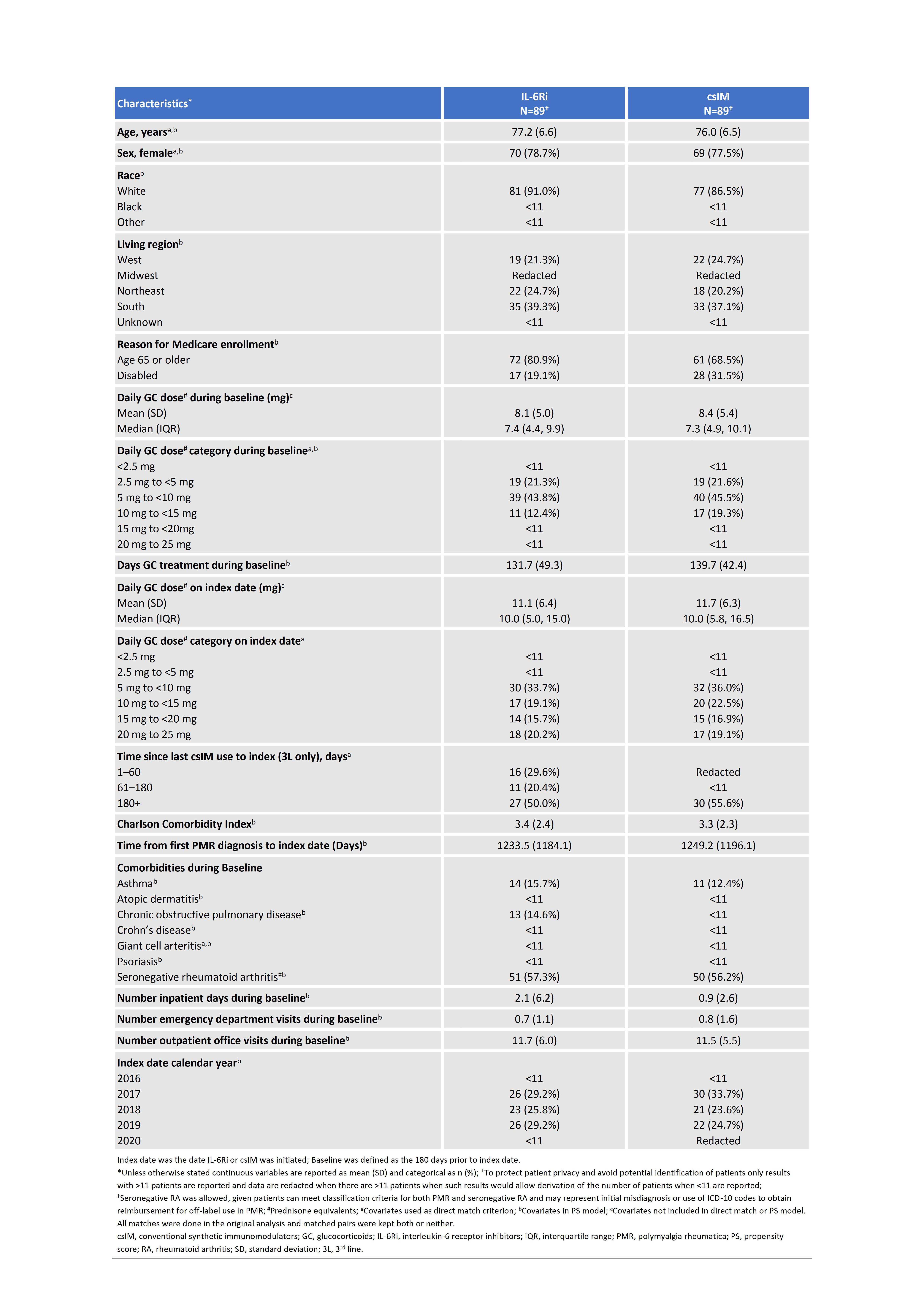
Methods: A subgroup analysis of patients with frailty from a retrospective cohort study comparing the effectiveness of IL-6Ri to csIM as 2L and 3L treatment of patients with PMR identified from 3/2016–6/2019 using Medicare claims data was conducted. IL-6Ri and csIM PMR patients were direct matched on multiple factors and then propensity score (PS) matched pairs were assessed with a validated claims-based frailty index (CFI). CFI is an algorithm to estimate frailty levels by assessing gait speed, grip strength, and the projected 2-year risk of death, institutionalization, disability, hospitalization, and extended skilled nursing facility stay. PS matched pairs of patients with CFI ≥median (0.2), were retained for comparison. The primary outcomes were time to GC discontinuation ( >60-day gap) and time to GC discontinuation or minimal GC dose (≤2 mg/day of prednisone equivalent). Patients were censored at 1 year, 60 days prior to the end of enrollment, death, outcome achievement, stopping csIM/IL-6Ri, or switching csIM/IL-6Ri. Cumulative GC dose was also compared.
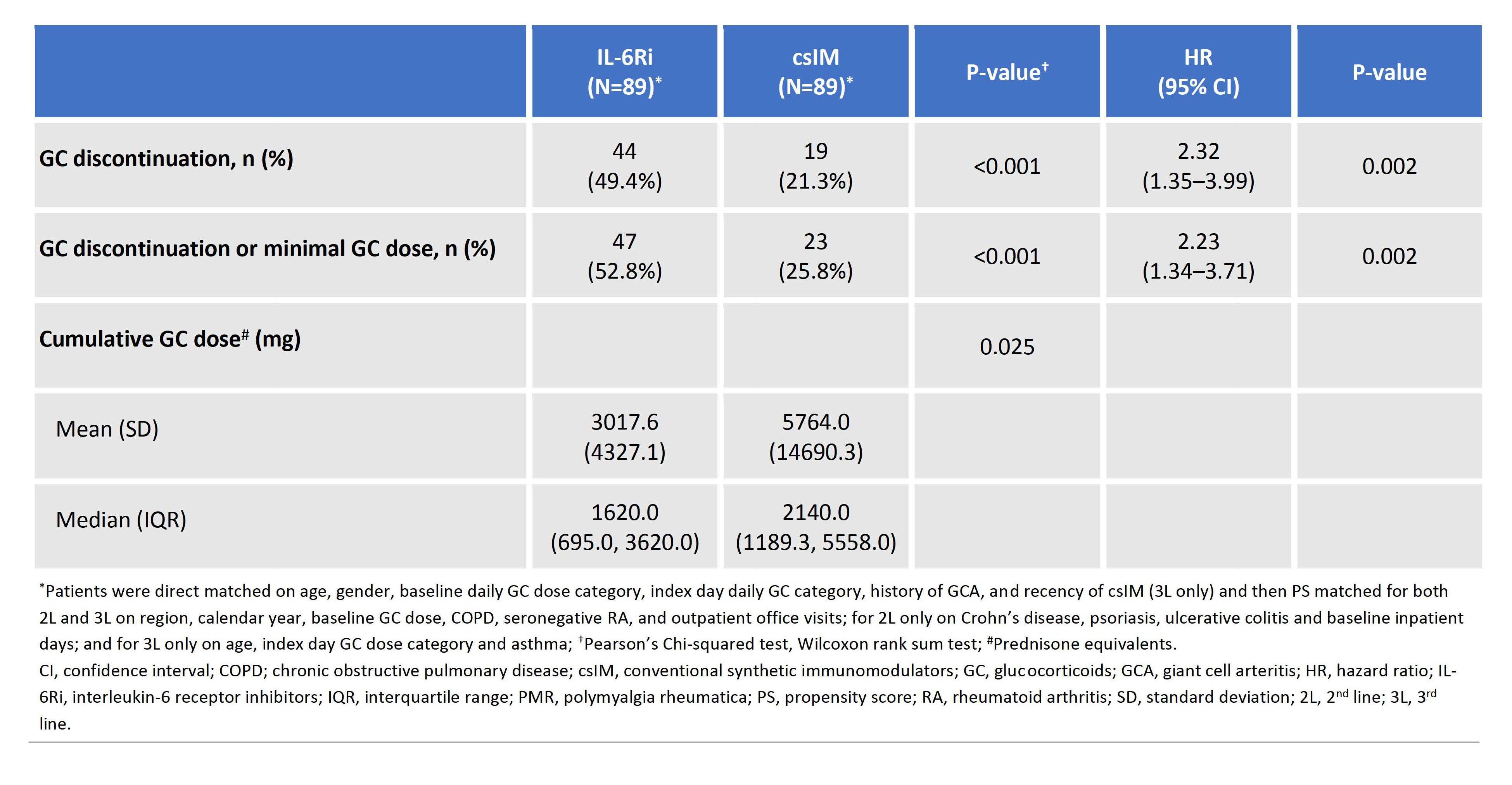
Results: Of 187 2L/228 3L PS matched pairs, 89 (35 [39.3%] 2L/54 [60.7%] 3L) had CFI ≥0.2. The most common csIM in 2L/3L was methotrexate (77.1%)/leflunomide (64.8%), respectively. Patient characteristics were generally balanced though patients on IL-6Ri were less likely to enroll in Medicare due to disability than csIM initiators (19.1% vs 31.5%) and had more inpatient days during baseline (mean [SD] 2.1 [6.2] vs 0.9 [2.6]) (Table 1). IL-6Ri vs csIM initiators were significantly more likely to discontinue GC (HR [95% CI] 2.32 [1.35–3.99], P=0.002) and achieve discontinuation of GC or minimal GC dose (HR [95% CI] 2.23 [1.34–3.71], P=0.002), and had a lower cumulative GC dose (mean [SD], mg; (3017.6 [4327.1] vs 5764.0 [14690.3], P=0.025)) (Table 2). Sensitivity analyses for discontinuation of GC varying the censoring rules by removing censoring for 1 year, stopping or switching csIM or IL-6Ri, and stopping csIM or IL-6Ri resulted in similar findings with HR (95% CI) of 1.88 (1.14–3.10), P=0.013, 2.49 (1.59–3.89), P< 0.001, and 2.71 (1.71–4.29), P< 0.001, respectively.
Conclusion: Compared with csIM, IL-6Ri had a greater GC-sparing effect in frail patients with PMR, suggesting patients with frailty may benefit more from IL-6Ri therapy.
Original presentation: EULAR 2024.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sattui S, Dejaco C, Ford K, Fiore S, Unizony S, Xie F, Curtis J. Effectiveness of Interleukin-6 Receptor Inhibitors versus Conventional Synthetic Immunomodulatory Therapy for Treatment of Frail Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-interleukin-6-receptor-inhibitors-versus-conventional-synthetic-immunomodulatory-therapy-for-treatment-of-frail-patients-with-polymyalgia-rheumatica/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-interleukin-6-receptor-inhibitors-versus-conventional-synthetic-immunomodulatory-therapy-for-treatment-of-frail-patients-with-polymyalgia-rheumatica/