Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Blau syndrome (BS) is a rare dominantly inherited autoinflammatory disorder associated with mutations in the NOD2 gene. BS is mainly seen in Caucasian patients. Biologic therapy of BS yielded diversity results. We aimed to evaluate clinical features and outcomes of Chinese patients with BS who were treated with TNFα inhibitors.
Methods: A total of four patients with BS were diagnosed and treated with infliximab (IFX) at Peking Union Medical College Hospital during 2015 to 2018, and were followed up for 18 months. All patients were systematically studied for treatment outcomes including the clinical manifestations and inflammatory markers. We also conducted a comprehensive literature review about TNFα inhibitors therapy in BS.
Results: These four BS patients were all Chinese Han, and three of them were women. The mean age of disease onset was 4±3.5 years, and the mean time of diagnosis delay was 19±11 years. All of the 4 patients received IFX plus methotrexate, and had achieved clinical remission of skin lesions and polyarthritis rapidly, and normalization of ESR and CRP, improvements in inflammatory cytokines, patient visual analogue scale, physician global assessment and SF-36 as well, at the first follow-up of 6 months. The disease relapsed in two patients after they lengthened the interval of IFX due to the financial limitation and discontinued methotrexate because of the side effects. According to the 38 English-language publications, 62 patients with BS were presented who underwent TNFα inhibitors therapy, including IFX used in 31, adalimumab in 24 and etanercept in 7. IFX was well tolerated in 27 patients, while 2 still had uveitis, and the other 2 experienced an adverse drug reaction to IFX infusion. Adalimumab was useful in 21 BS patients, although the other 3 didn’t get well controlled. Five BS patients who were given etanercept yielded good responses, but 2 discontinued because of etanercept-induced myelopathy or an exacerbation of arthritis.
Conclusion: Early recognition and effective treatment of BS is very important to avoid the irreversible organ damage such as loss of vision, joint deformities. TNFα inhibitors including IFX may be a promising approach for BS patients who have unsatisfactory response to corticosteroids and traditional DMARDs. Due to the sample limitation of our study, more clinical trials are required.
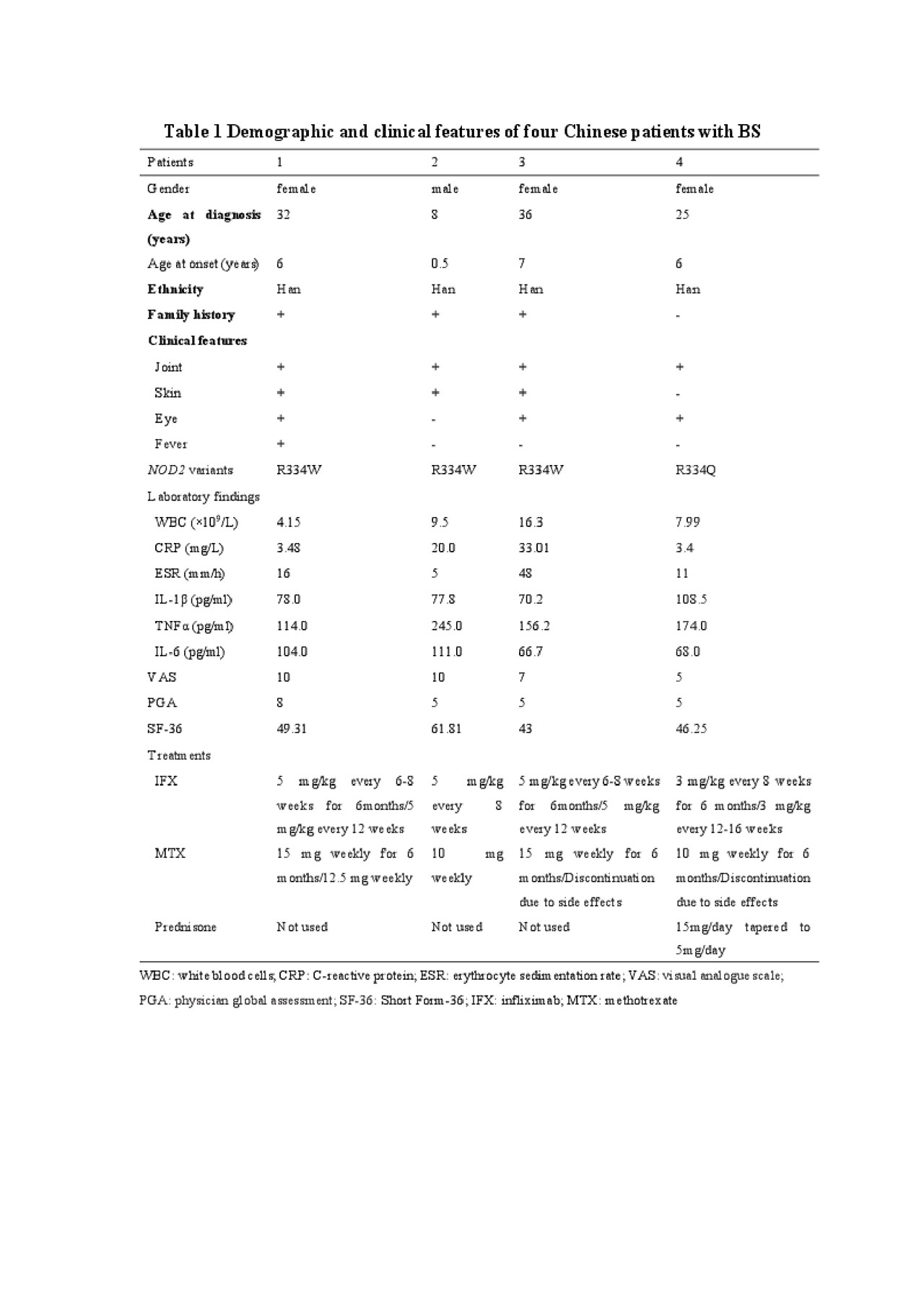
Table 1 Demographic and clinical features of four Chinese patients with BS
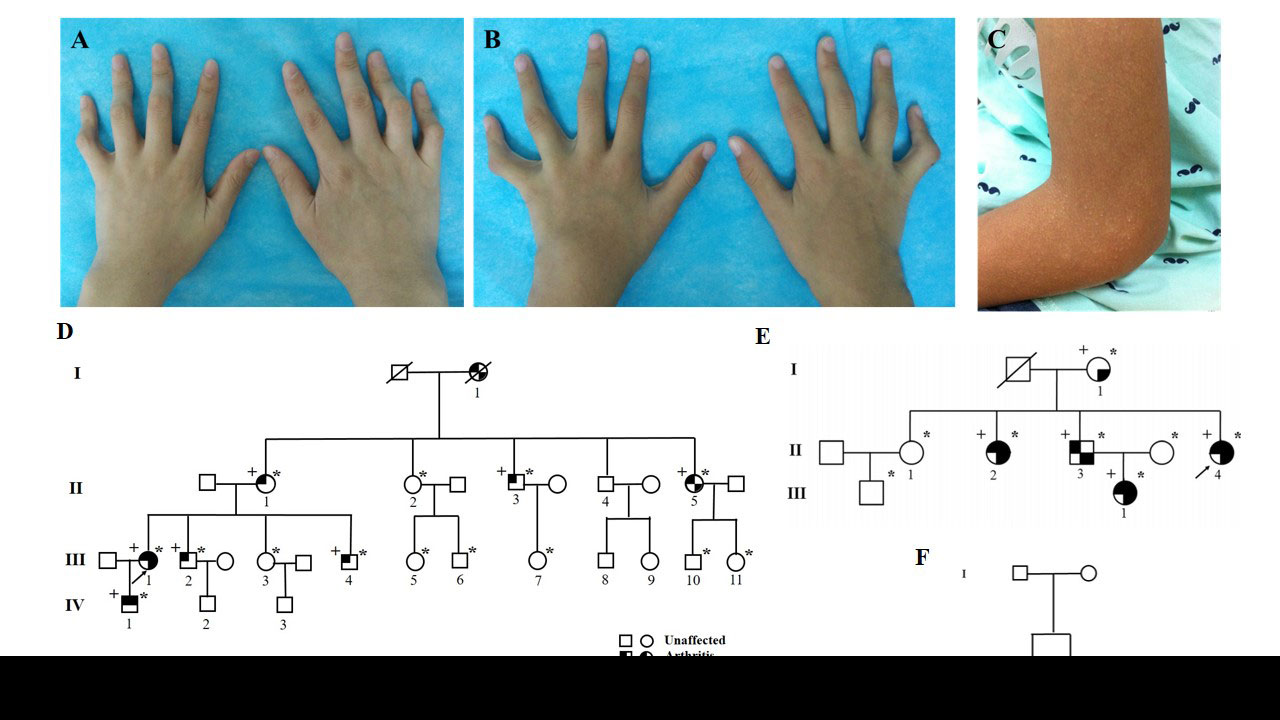
Camptodactyly of patients 1 -A- and 2 -B-; Papules on the upper limbs of patient 2 -C-; Pedigrees of patients 1 and 2 -D-, 3 -E- and 4 -F-.
Overall, WBC, CRP, ESR, IL-1β, IL-6, VAS and PGA decreased, and SF-36 increased at the first follow-up of 6-month. TNFα decreased at the first follow-up for patients 2 and 3, but increased for patients 1 and 4. At the last visit of 18-month, WBC, ESR and CRP remained normal in all except patient 3, whose ESR and CRP increased to above normal range. Among all the patients, serum levels of IL-1β, TNFα and IL-6 were higher than those at the first follow-up, except patient 4. For patients 1 and 2, VAS and PGA reduced further at the last follow-up, while for patients 3 and 4, they slightly increased. CRP: C-reactive protein; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; VAS: visual analogue scale; PGA: physician global assessment; SF-36: Short Form-36.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen J, Luo Y, Zhao M, Wu D, Yang Y, Zhang W, Shen M. Effective Treatment of TNFα Inhibitors in Chinese Patients with Blau Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effective-treatment-of-tnf%ce%b1-inhibitors-in-chinese-patients-with-blau-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effective-treatment-of-tnf%ce%b1-inhibitors-in-chinese-patients-with-blau-syndrome/