Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Fibromyalgia, Soft Tissue Disorders, Regional and Specific Clinical Pain Syndromes Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Abstract
Background/Purpose: Chronic non-specific widespread pain (CWP) including fibromyalgia (FM) is characterized by widespread pain, reduced pain threshold and multiple tender points on examination, causing disability and decreased quality of life. Vitamin D has been proposed as an associated factor in CWP. This meta-analysis aimed to explore the benefit of vitamin D supplementation in the management of CWP.
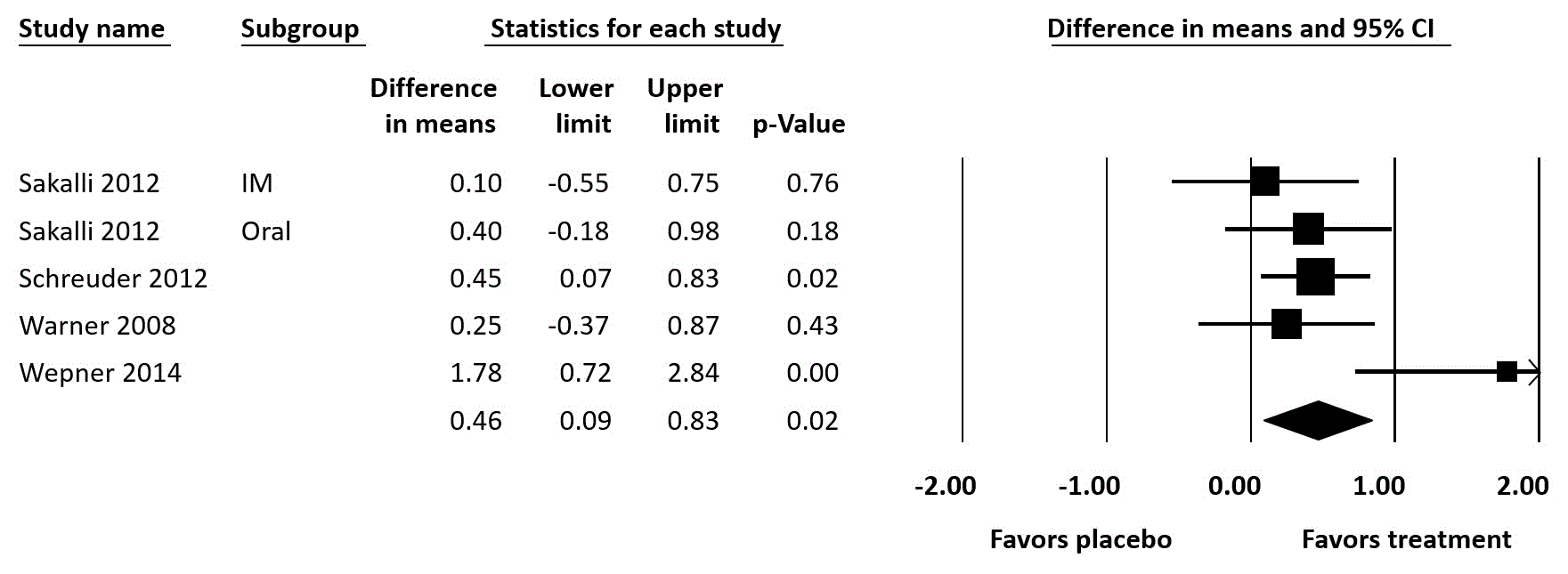
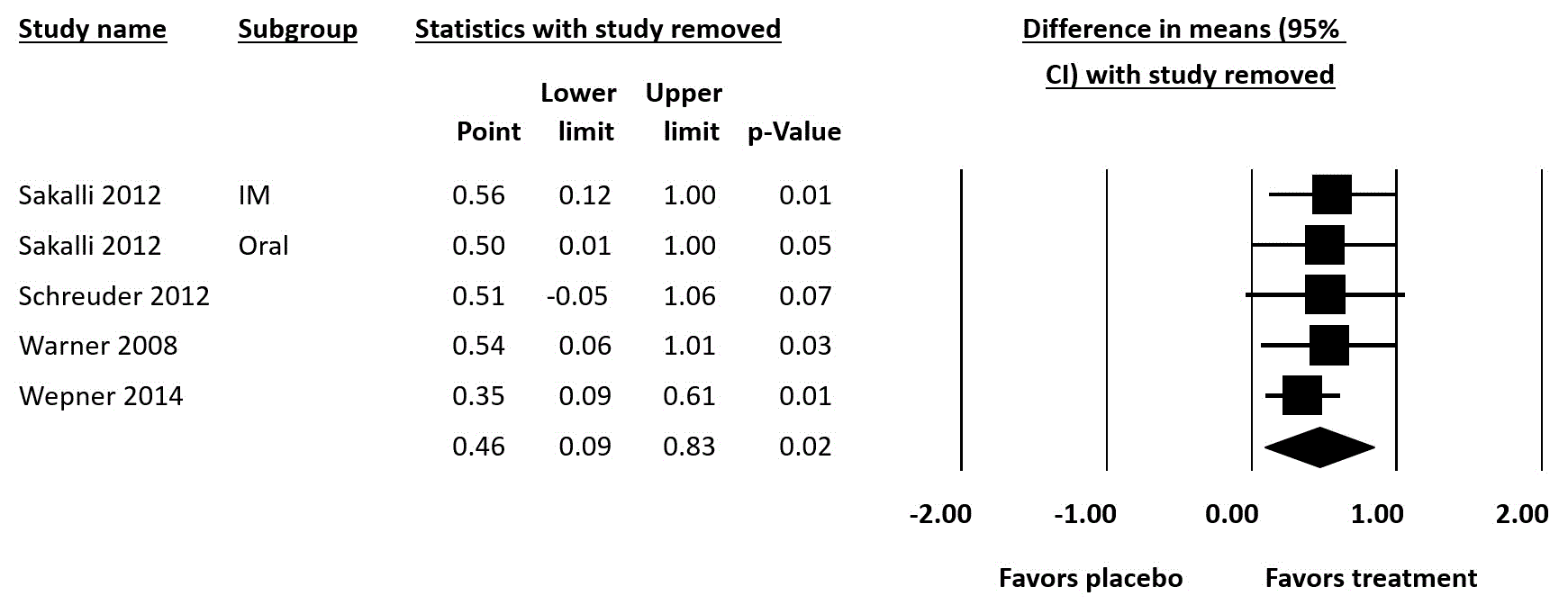
Methods: A comprehensive search of the CENTRAL, MEDLINE and EMBASE databases was performed from inception through January 2017. The inclusion criterion was the randomized clinical trials’ evaluating the effects of vitamin D treatment in adult subjects with CWP or fibromyalgia. CWP was defined as chronic recurrent musculoskeletal pain without secondary causes; fibromyalgia patients met the American College of Rheumatology criteria for fibromyalgia. Study outcome was assessed using visual analog scale (VAS) of pain intensity. Pooled mean difference (MD) of VAS and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated using a random-effect meta-analysis. Meta-regression analysis using random-effects model was performed to explore the effects of change in vitamin D in the treatment group on difference in mean of VAS. Sensitivity analysis was performed to evaluate the robustness of results. The between-study heterogeneity of effect-size was quantified using the Q statistic and I2.
Results: Data were extracted from 4 randomized control trials involving 287 subjects. Pooled result demonstrated a significant lower VAS in CWP patients who received vitamin D treatment compared with those who received placebo (MD=0.46; 95% CI: 0.09 – 0.89, I2 = 48%). Meta-regression analysis revealed no significant relationship between the changes of vitamin D and VAS with a coefficient = 0.04 (95% CI: -0.01 to 0.08), p=0.10.
Conclusion: In this meta-analysis, we conclude that vitamin D supplementation is able to decrease pain scores and improve pain despite no significant change in VAS after increasing serum vitamin D level. Further study needs to be conducted in order to explore the improvement of functional status, quality of life, and the pathophysiological change that improves chronic widespread pain.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yong WC, Sanguankeo A, Upala S. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation in Chronic Widespread Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-vitamin-d-supplementation-in-chronic-widespread-pain-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-vitamin-d-supplementation-in-chronic-widespread-pain-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/