Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patient-reported outcomes are, in addition to other efficacy and safety related outcomes, important reflections of effectiveness and adverse effects of a therapy. The Outcomes Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials (OMERACT) initiative therefore strongly endorses to monitor also health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) studies. In the U-Act-Early strategy trial, initiation of tocilizumab (TCZ) has been proven more efficacious for reducing disease activity when compared to a step-up methotrexate strategy in disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARD)-naïve patients with early RA. Here we report the effect of the strategies in this treat-to-target trial on HRQoL, as measured by the five dimensional EuroQol (EQ-5D) questionnaire.
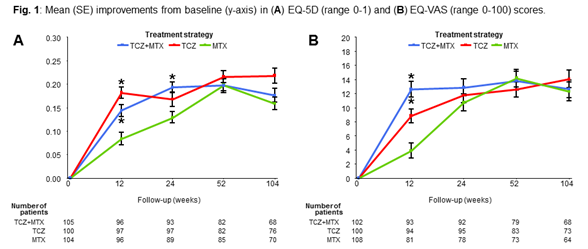
Methods: In U-Act-Early, 317 early RA patients were randomized (1:1:1) to initiate methotrexate (MTX), TCZ or TCZ+MTX therapy and were treated to target until sustained remission (disease activity score assessing 28 joints (DAS28) <2.6 with ≤4 swollen joints for ≥24 weeks) was achieved. Hydroxychloroquine, as part of the initial treatment regimen, was added if remission was not achieved. If after 12 additional weeks the target still was not reached, patients switched to a subsequent treatment regimen: those in the TCZ arm or in the MTX arm switched to TCZ+MTX therapy; patients who started with TCZ+MTX switched to standard of care. We used a linear mixed model to analyze the differences between groups in change from baseline over time in EQ-5D utility scores (anchored at “0” (dead) and “1” (perfect health)) and the corresponding visual analogue scale (EQ-VAS, range 0-100). ANCOVA was used for between-group comparisons of scores at week 12, 24, 52 and 104.
Results: Significant greater improvements over time were found in EQ-5D scores in patients in the TCZ+MTX arm, compared to the MTX arm (p=0.02), but not compared to the TCZ arm (p=0.09, Fig. 1). No significant differences were found over time between the strategies in EQ-VAS scores (p≥0.14). When evaluating between-group differences at specific time-points, improvements were significantly greater at week 12 in both TCZ strategies in EQ-5D (TCZ+MTX vs MTX, p=0.04; TCZ vs MTX, p=0.01) and EQ-VAS scores (TCZ+MTX vs MTX, p<0.01; TCZ vs MTX, p=0.04), when compared to the MTX strategy. After 24 weeks, significance only remained in the EQ-5D score in favor of the TCZ+MTX strategy (TCZ+MTX vs MTX, p<0.01).
Conclusion:
Initiating a treat-to-target TCZ-based strategy in DMARD-naïve patients with early RA resulted in significant improvements in HRQoL when compared to initiation of step-up MTX therapy, in line with current standards.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Teitsma XM, Jacobs JW, Welsing PM, Pethö-Schramm A, Borm ME, van Laar JM, Lafeber FP, Bijlsma JWJ. Effect of Treat-to-Target Tocilizumab- and Methotrexate-Based Strategies on Health-Related Quality of Life in Newly Diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Results of the U-Act-Early Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-treat-to-target-tocilizumab-and-methotrexate-based-strategies-on-health-related-quality-of-life-in-newly-diagnosed-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-results-of-the-u-act-early-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-treat-to-target-tocilizumab-and-methotrexate-based-strategies-on-health-related-quality-of-life-in-newly-diagnosed-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-results-of-the-u-act-early-trial/