Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab (SEC) provided sustained efficacy, inhibition of radiographic progression, and stable safety profile over 52 Weeks (Wks) in patients (pts) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in the FUTURE 5 study.1,2 Here we report the end-of-study (2-year) results of the effect on radiographic progression of SEC in pts with PsA in the FUTURE 5 study.
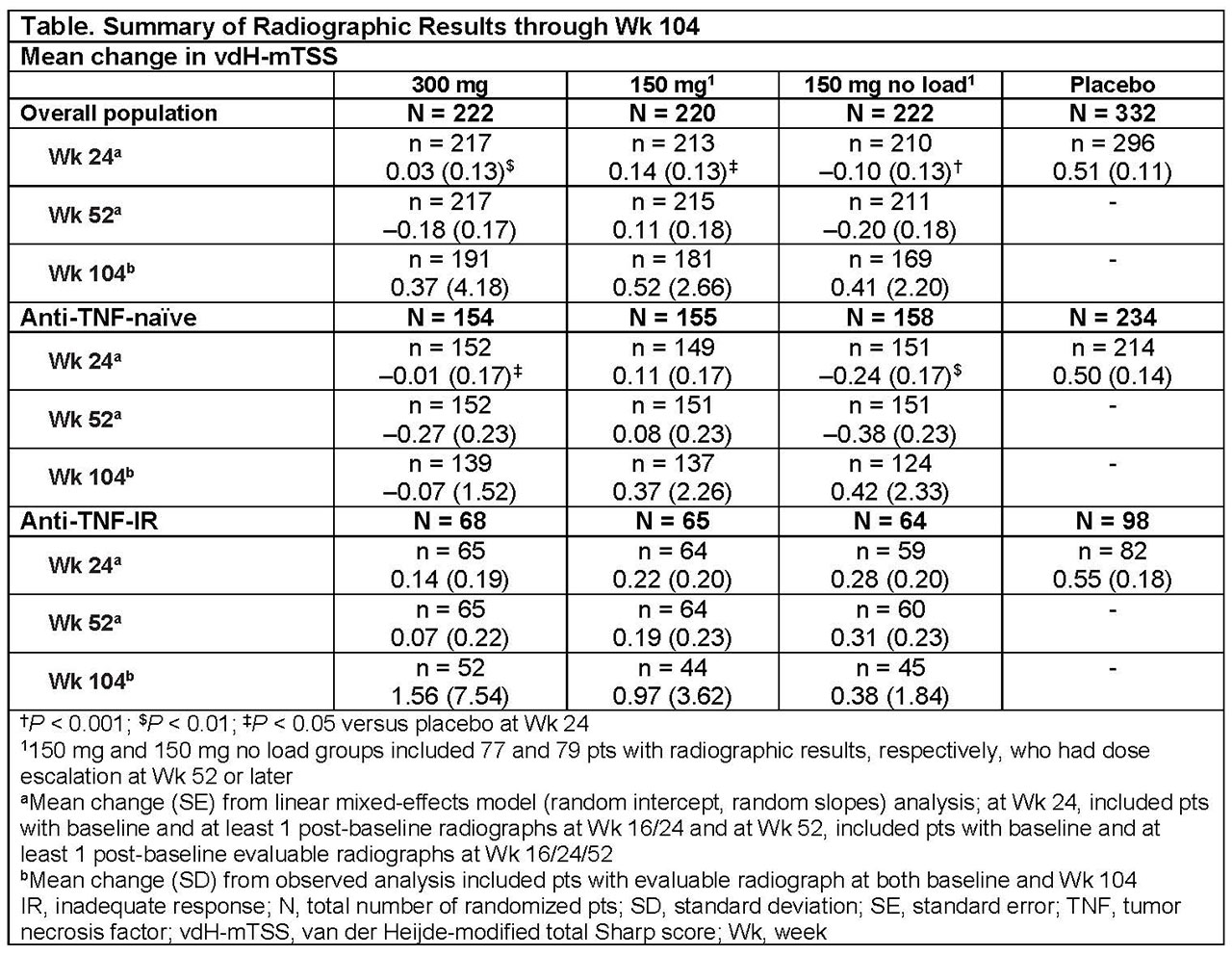
Methods: Adults (N = 996) with active PsA were randomized to subcutaneous SEC 300 mg load (300 mg), 150 mg load (150 mg), 150 mg no load, or placebo at baseline, Wks 1, 2, 3, and 4, and every 4 wks thereafter. Pts could have the SEC dose escalated from 150 mg to 300 mg starting from Wk 52, based on physicians’ judgement. Radiographic progression (mean change in van der Heijde-modified total Sharp score [vdH-mTSS]) was based on hand/wrist/foot radiographs obtained at baseline, Wks 16 (non-responders), 24, 52, and 104, assessed by two blinded readers (plus an adjudicator if required). Radiographic data were analyzed using linear mixed-effects model (random intercept, random slopes) at Wks 24 and 52, and as observed at Wk 104. Data are shown for pts originally randomized to SEC (300 and 150 mg); the 150 mg groups also includes pts who had their dose escalated to 300 mg. Analyses by prior anti-TNF (naïve vs inadequate response/intolerance [IR]; stratification factor) use were also done.
Results: Overall, 85% (300 mg), 82% (150 mg), and 75% (150 mg no load) of pts completed 2 years of treatment. A total of 86 (39%) and 92 (41%) pts had their dose escalated to 300 mg in the 150 mg and 150 mg no load groups, respectively. In overall population, the proportions of pts with no radiographic progression (change from baseline in mTSS ≤0.5) with SEC were 89.5% (300 mg), 82.3% (150 mg), and 81.1% (150 mg no load) at 2 years; the corresponding proportions of pts for change from baseline in mTSS ≤0.0 were: 81.2%, 69.1% and 73.4%, respectively. Radiographic progression was low in SEC-treated pts in the overall population and by prior anti-TNF use over 2 years (Table). Clinical responses were also sustained through 2 years of SEC treatment.
Conclusion: Low radiographic progression was observed over 2 years of treatment with SEC 300 and 150 mg in pts with PsA.
References: 1. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:890-897.
2. Mease PJ, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Landewé R, Rahman P, Tahir H, Singhal A, Böttcher E, Navarra S, Readie A, Mpofu S, Delicha E, Pricop L, van der Heijde D. Effect of Secukinumab on Radiographic Progression Through 2 Years in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: End-of-study Results from a Phase III Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-secukinumab-on-radiographic-progression-through-2-years-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-end-of-study-results-from-a-phase-iii-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-secukinumab-on-radiographic-progression-through-2-years-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-end-of-study-results-from-a-phase-iii-study/