Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Biologics are widely used and effective treatments for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but generally biologics are avoided when patients have active infections on the day of administration.
In Japan, nurses are not authorized to assess whether patients have active infections or not. In our hospital, doctors in charge of the pre-administration assessments conventionally checked patient’s status by taking history and physical examinations on the day of intravenous biologics, but it does not seem to be time efficient. We implemented new method in which nurses systematically screen according to pre-determined questionnaires on infections before doctors see patients. Our aim of this study is to reveal effectiveness of this new method of assessments.
Methods:
We retrospectively review charts of patients with RA who received intravenous biologics at our hospital in Tokyo, Japan from June 2016 to April 2018. We investigated basic demographics, kinds of biologics and other treatments, underlying diseases, numbers and sites of serious infection(SI), and opportunistic infections. SI was defined as infections requiring intravenous antibiotics, hospitalization, or resulting in death. We compared numbers of infections in the new method with those in conventional one. Univariate analysis and Chi-square test were performed.
We also calculated the number of scheduled administrations and evaluated results of screening by nurse and doctor’s assessment.
Results:
We identified 360 cases in total. There are 189 and 171 patients who received intravenous biologics from June 2016 to May 2017 with conventional assessment and from June 2017 to April 2018 with new-style assessment.
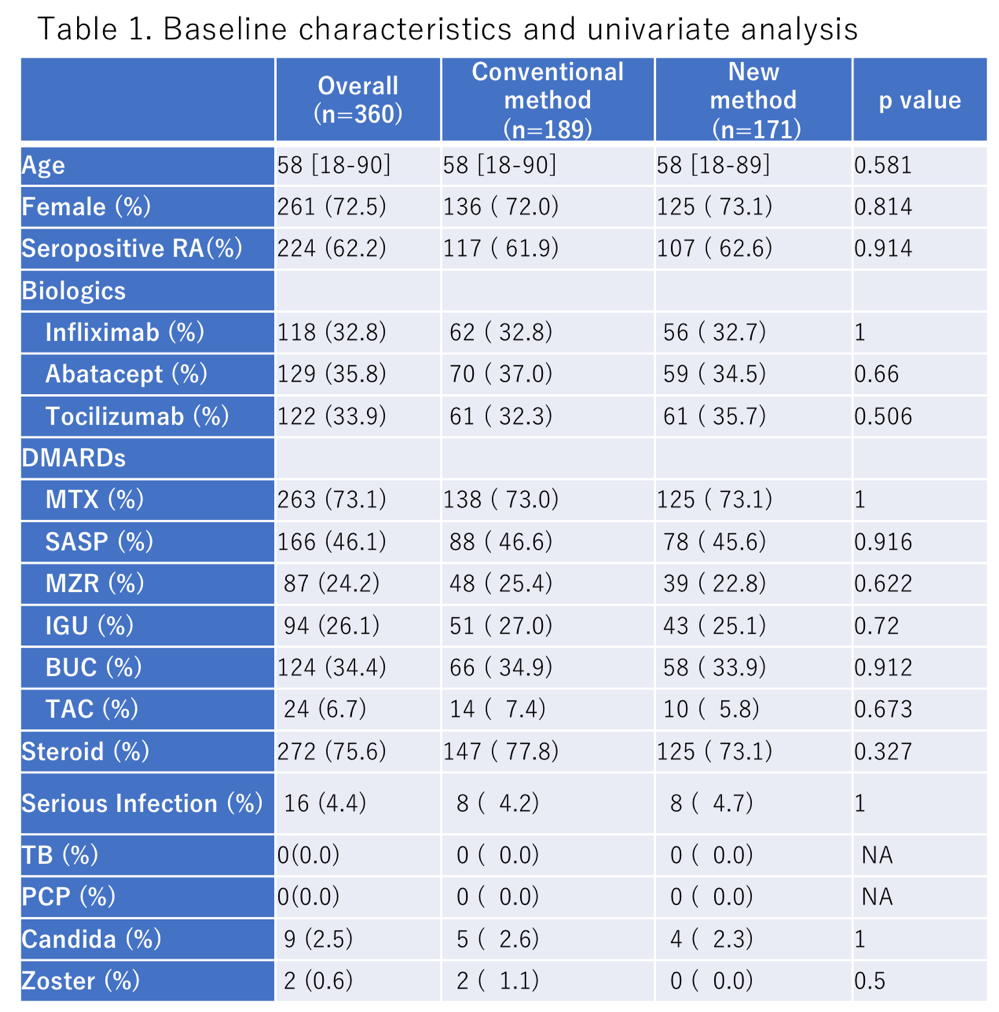
The baseline characteristics are shown in table 1. Though there are no significant differences in the number of SI between new and conventional methods, the rate of SI was 4.4% and lower than that reported in previous studies.
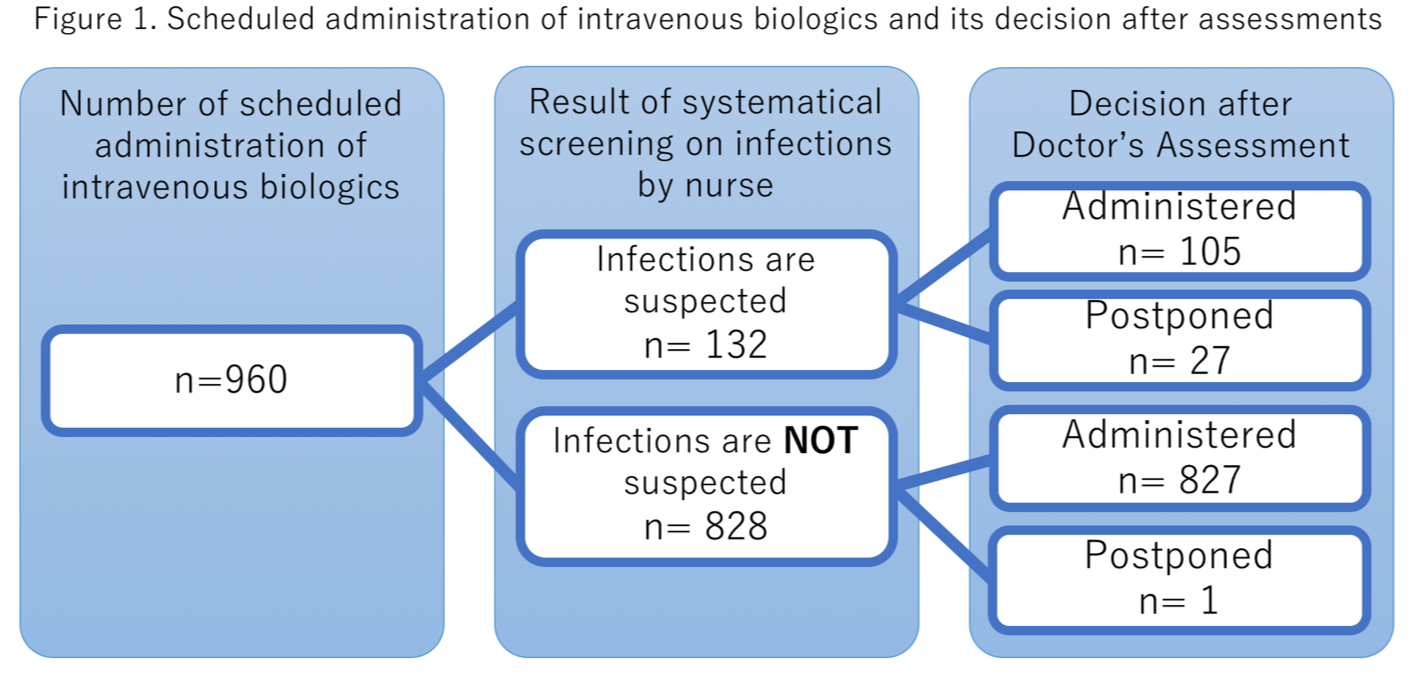
The number of scheduled administration of biologics and its decision after assessments by nurse and doctors are shown in figure 1. There was just 1 case in which doctors postponed biologics even the patient was assessed not to have active infections by nurse.
Conclusion:
Systematical screening by nurse with pre-determined questionnaires is very sensitive so that doctors can carefully see cases in which infections are suspected by the screening. Our new-method of pre-administration assessments can contribute to time-efficient practice without any increasing risk of SI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fukui S, Suda M, Sawada H, Ikeda Y, Watanabe M, Koido A, Kawato R, Suyama Y, Shimizu H, Yanaoka H, Rokutanda R, Tamaki H, Tsuda T, Yamaguchi KI, Kishimoto M, Okada M. Effect of New Method for Pre-Administration Assessment of Intravenous Biologics on Infections in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-new-method-for-pre-administration-assessment-of-intravenous-biologics-on-infections-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-new-method-for-pre-administration-assessment-of-intravenous-biologics-on-infections-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/