Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In spondyloarthritis (SpA), the lipid profile changes due to the systemic inflammatory response. Theoretically, the proinflammatory state is associated with a decrease in total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TG) than expected, and an increase in these lipid levels after anti-inflammatory therapies, such as tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) inhibitor. This study aimed to assess the influence of long-term treatment with TNF-α inhibitor on lipid profile and atherogenic index (AI) in patients with SpA.
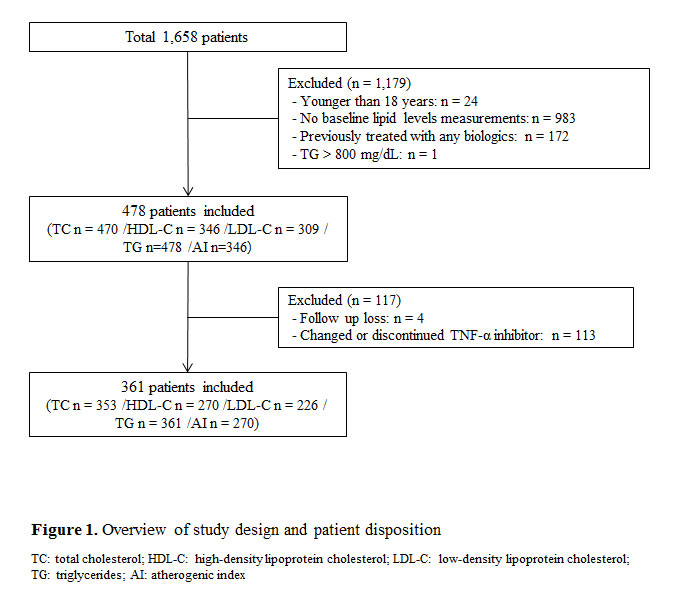
Methods: Lipid data and AI of SpA patients treated with TNF-α inhibitor were analysed from the Korean College of Rheumatology Biologics (KOBIO) registry between 2012 and 2017. Patients exposed at least for one year to SpA approved dosage regimens of etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab or golimumab as first line treatment were included. The baseline lipid profile and AI were compared with between 0 – 12 months, 12 – 18 months, 18 – 24 months, > 24 months. AI was derived according to the logarithmic (TG/HDL-C).
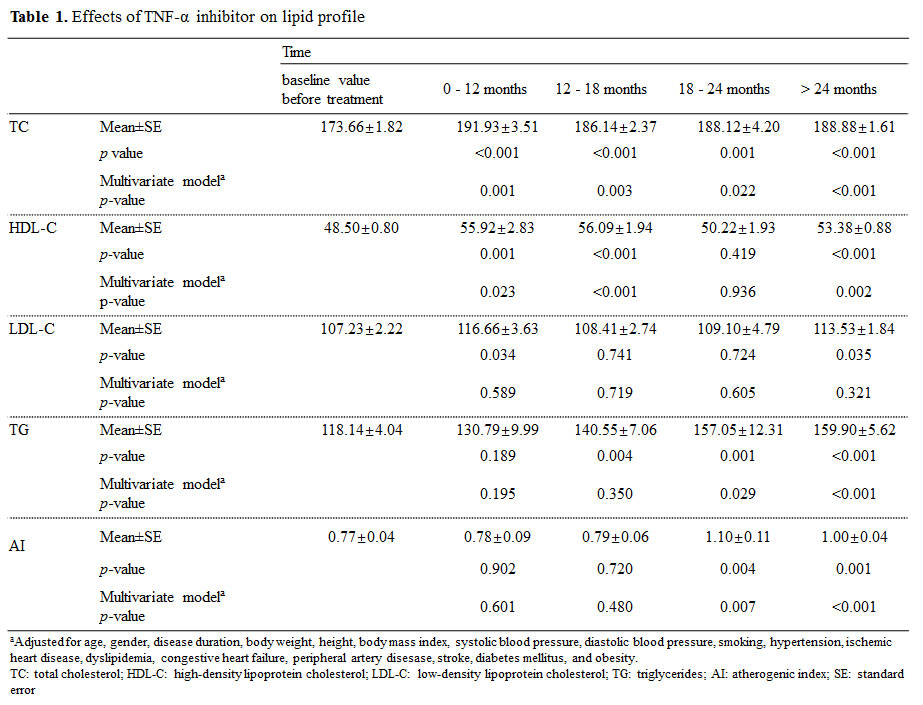
Results: The records of 361 patients (male 279, female 82) were reviewed. Mean follow-up duration was 2.25 ± 0.03 year (0.24 – 5.66 years) and baseline Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) was 6.0 ± 0.1. Treatment with TNF-α inhibitor was associated with increased levels of TC (173.66 ± 1.82 mg/dL at baseline, 191.93 ± 3.51 mg/dL; p = 0.001 at 0 – 12 months, and 188.88 ± 1.61 mg/dL; p < 0.001 at > 24 months), HDL-C (48.50 ± 0.80 mg/dL at baseline, 55.92 ± 2.83 mg/dL; p = 0.023 at 0 – 12 months, and 53.38 ± 0.88 mg/dL; p= 0.002 at > 24 months) and TG (118.14 ± 4.04 mg/dL at baseline, 157.05 ± 12.31 mg/dL; p = 0.029 at 18 – 24 months, and 159.90 ± 5.62 mg/dL; p < 0.001 at > 24 months), but no significant change in LDL-C. After treatment, AI increased from 0.77 ± 0.04 at baseline to 1.00 ± 0.04 (p < 0.001) at > 24months.
Conclusion: In patients with SpA, long-term treatment of TNF-α inhibitor was associated with increased TC, HDL-C, and TG levels and AI, whereas it presented no effect on LDL-C levels. Increased HDL-C may have beneficial effects, but evaluation of cardiovascular event rates during long-term treatment is needed to further characterize these findings and their possible clinical implications.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yeo J, Seo M, Ryu H, Choi H, Baek H. Effect of Long-term Treatment with TNF-α Inhibitor on Lipid Profile in Spondyloarthritis: Data from Nationwide Korean College of Rheumatology Biologics (KOBIO) Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-long-term-treatment-with-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitor-on-lipid-profile-in-spondyloarthritis-data-from-nationwide-korean-college-of-rheumatology-biologics-kobio-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-long-term-treatment-with-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitor-on-lipid-profile-in-spondyloarthritis-data-from-nationwide-korean-college-of-rheumatology-biologics-kobio-registry/