Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
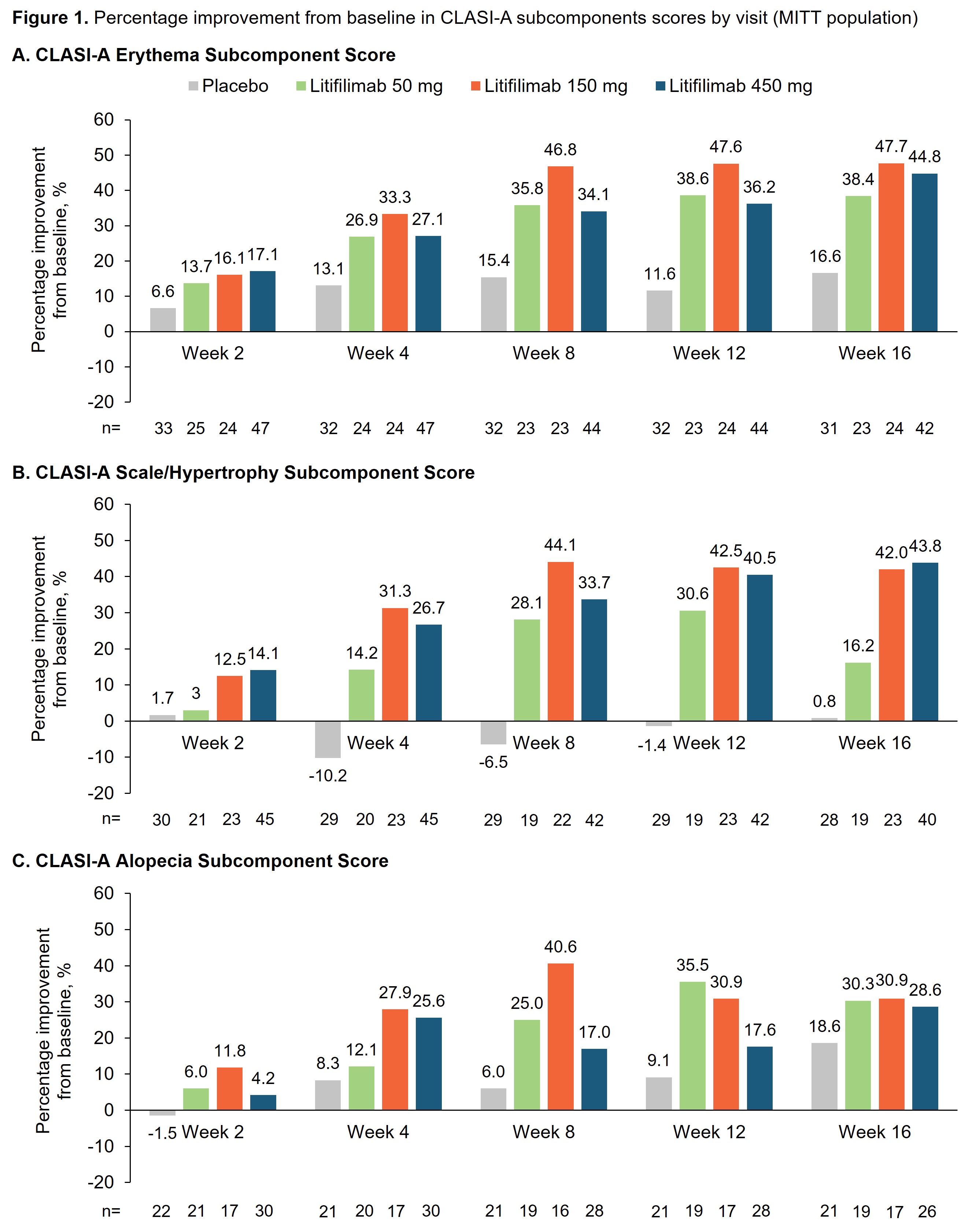
Background/Purpose: In the randomized, placebo-controlled Phase 2 LILAC study of litifilimab (NCT02847598), Part B (participants with active CLE with/without SLE) met its primary endpoint of percentage change from baseline in CLASI-A score at Week 16, with a greater proportion of participants achieving a CLASI-50 response (decrease of ≥50% from baseline in CLASI-A score) with litifilimab than placebo at Week 16.1 The CLASI-A measures disease activity in CLE based on clinical components and anatomical locations. Activity is measured by erythema, scale/hypertrophy, non-scarring alopecia, recent hair loss (preceding 30 days), and mucous membrane lesions.2 We conducted post-hoc analyses to further understand how the individual CLASI-A subcomponents contributed to the change from baseline to Week 16. The PGA–Skin, a physician-reported measure of skin disease activity, was also analyzed.
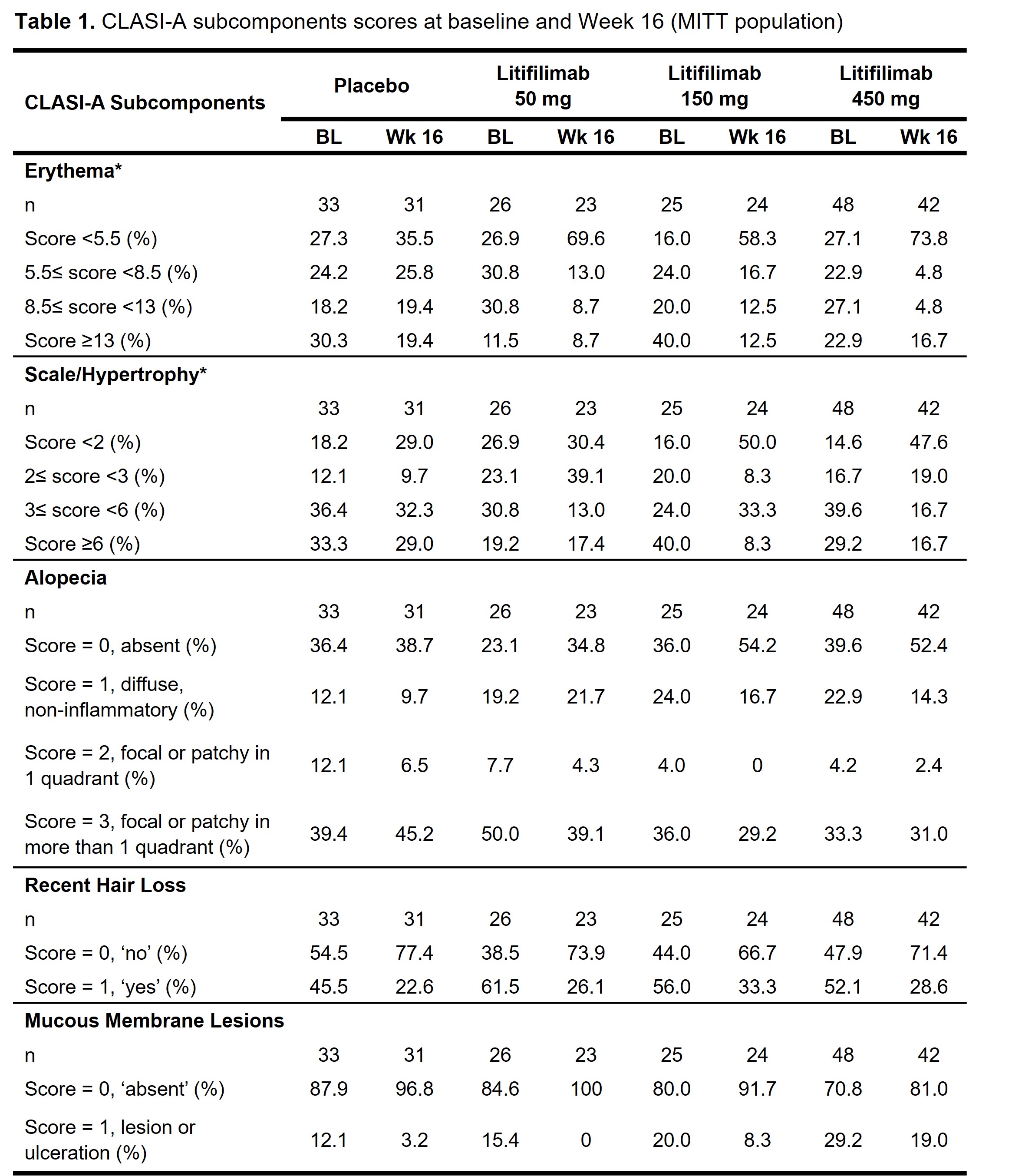
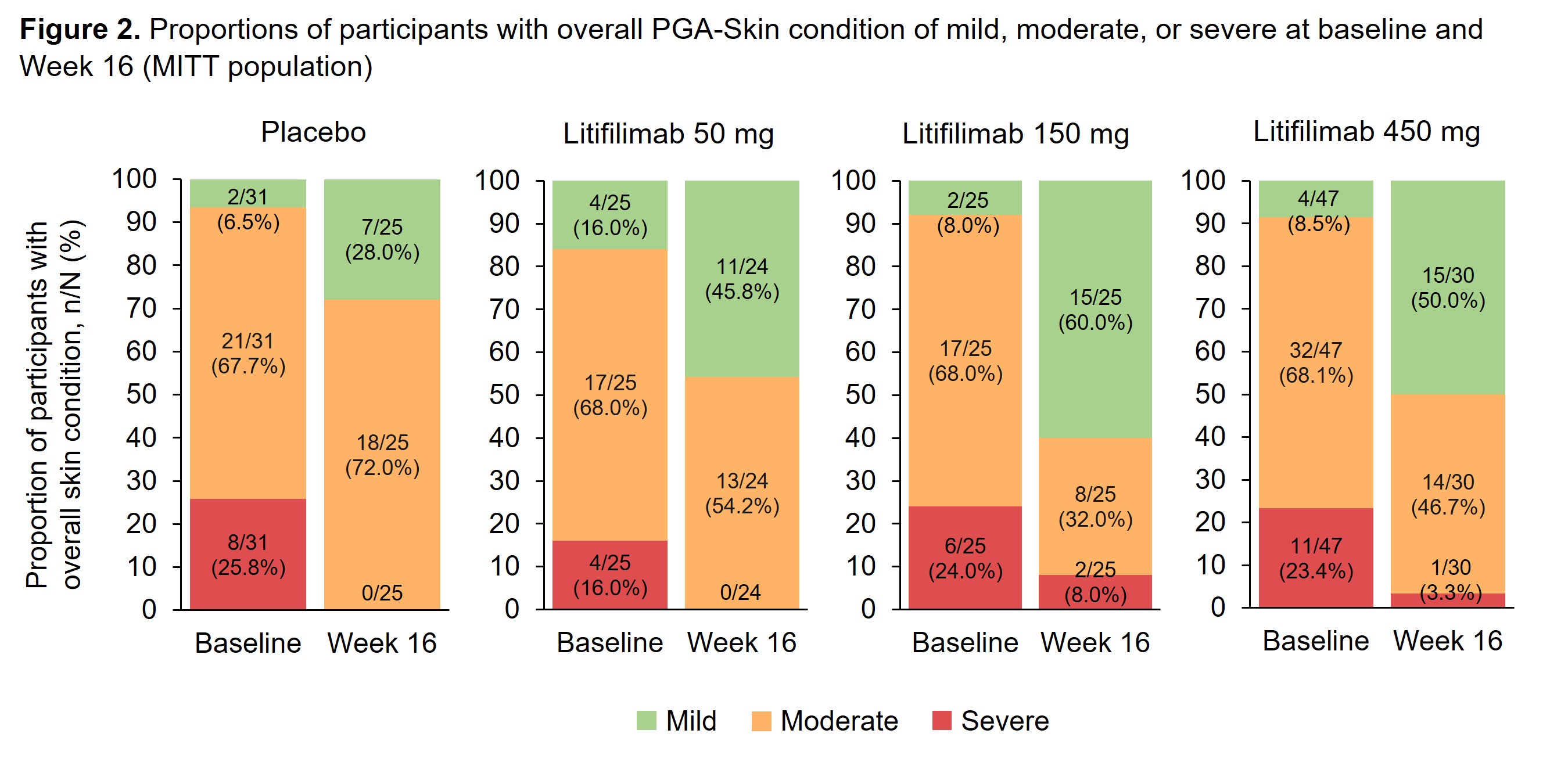
Methods: Study design and baseline participant characteristics for Part B have been reported.1 For the CLASI-A subcomponents analysis, erythema and scale/hypertrophy are presented in 4 categories based on the baseline score quartiles. Alopecia, recent hair loss, and mucous membrane lesions scores are presented as recorded. Overall skin condition, measured by PGA–Skin, was rated as mild, moderate, or severe. For participants who were considered as treatment failures, the worse of baseline or last visit before treatment failure carried forward was used to impute values for all the post-treatment failure visits. Data after the participants’ treatment discontinuation were censored.
Results: The erythema, scale/hypertrophy, and alopecia subcomponents showed greater improvement in the litifilimab groups relative to placebo at all post-baseline visits (Figure 1). At baseline, the proportions of participants with significant activity were: 72.7–84.0% for erythema (score ≥5.5), 73.1–85.4% for scale/hypertrophy (score ≥2), 60.4–76.9% for alopecia (score ≥1), 45.5–61.5% for recent hair loss, and 12.1–29.2% for mucous membrane lesions (Table 1). At Week 16, greater improvements with litifilimab versus placebo were observed consistently across the erythema, scale/hypertrophy, and alopecia subcomponents (Table 1). A minority of participants had mucous membrane lesions at baseline, so no conclusion could be drawn for this subcomponent. In the PGA–Skin analysis at Week 16, 28.0% and 45.8–60.0% of participants in the placebo and litifilimab groups, respectively, were rated with mild disease (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Results from these post-hoc analyses indicated that the CLASI-A subcomponents of erythema, scale/hypertrophy, alopecia, and recent hair loss contributed to the observed overall CLASI-A score improvements at Week 16. In most subcomponents, greater score improvements were observed in the litifilimab-treated participants compared with placebo. Together with the higher proportion of participants with mild overall skin condition in the litifilimab groups at Week 16, these results support the continued development of litifilimab in CLE.
1Werth VP, et al. N Engl J Med 2022;387:321–331
2Albrecht J, et al. J Invest Dermatol 2005;125:889–894
We thank the LILAC investigators and participants for their valuable contributions.
For participants from Part B protocol version 1 who completed treatment up to Week 12 but could not reconsent to protocol version 2, Week 16 data were imputed using the predicted value from the mixed model for repeated measures model of absolute value.
CLASI-A, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index–Activity; MITT, modified intention-to-treat.
A CLASI-A erythema score ≥2 was an enrollment criterion for Part B of the LILAC study.
For participants from Part B protocol version 1 who completed treatment up to Week 12 but could not reconsent to protocol version 2, Week 16 data were imputed using the predicted value from the mixed model for repeated measures model of absolute value.
BL, baseline; CLASI-A, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index–Activity; MITT, modified intention-to-treat; Wk, week.
BL, baseline; MITT, modified intention-to-treat; PGA–Skin, Physician Global Assessment–Skin.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Werth V, Merola J, Li Q, Yang W, Barbey C. Effect of Litifilimab on Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index–Activity (CLASI-A) Subcomponents and Physician Global Assessment–Skin (PGA–Skin) in Patients with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CLE) in a Phase 2 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-litifilimab-on-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-disease-area-and-severity-index-activity-clasi-a-subcomponents-and-physician-global-assessment-skin-pga-skin-in-patie/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-litifilimab-on-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-disease-area-and-severity-index-activity-clasi-a-subcomponents-and-physician-global-assessment-skin-pga-skin-in-patie/