Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose To evaluate the effects of infliximab (Ifx) dose increase in active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, presenting different serum infliximab concentrations.
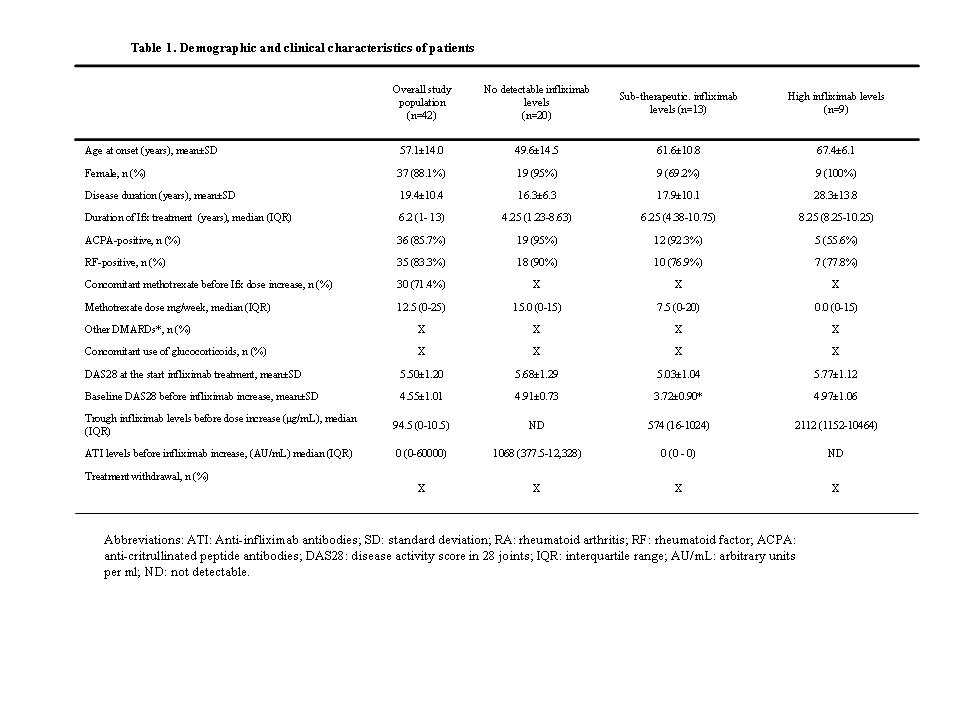
Methods Retrospective study including 42 RA patients treated with increased Ifx following insufficient response (DAS28 > 3.2). Serum concentrations of Ifx and antibodies to Ifx (ATI) were recorded together with DAS28 and EULAR clinical response parameters throughout a year prior (T1) and after increasing dose (T2: immediately post-increase, T3: 6 months after T1 and T4:1 year after T1). Analyses were carried out with three patient groups defined by Ifx serum concentration prior to treatment enhancement: no detectable levels, (NL), low levels (LL< 1.1 µg/ml) or high levels (HL≥1.1 µg/ml). This cut-off was chosen empirically, based on most patients with Ifx levels >1.1 µg/ml experienced clinical improvement in our cohort.
Results The demographic characteristics are shown in the Table 1. Twenty patients (47.6%) were classified in NL, while 13 (30.9%) and 9 (31.4%) showed LL and HL respectively. Due to drug interference with ELISA, ATI were only detected in NL patients. DAS28 improved immediately after increasing Ifx dosage, from baseline (4.55±1.01 vs 3.95±1.22; p<0.05 after Bonferroni correction), but the improvement did not persist at 1 year (3.98±1.22; p=0.075 after Bonferroni correction). The change in DAS28 from baseline (deltaDAS28) followed a similar pattern (-0.63±1.18 at T2 to 1.17±1.45 at T4 (p<0.001))(Figure 1). Overall, 5 (13.2%) patients achieved a good response by EULAR response after the first dose increase, whereas 18 (47.4%) patients had no response. At T4, 3 (10.7%) patients showed a good response and 18 (64.3%) remained non-responders.
Conclusion These results suggest that the effectiveness of Ifx dose increase after therapeutic failure is limited, independently of pre increase serum trough infliximab concentrations.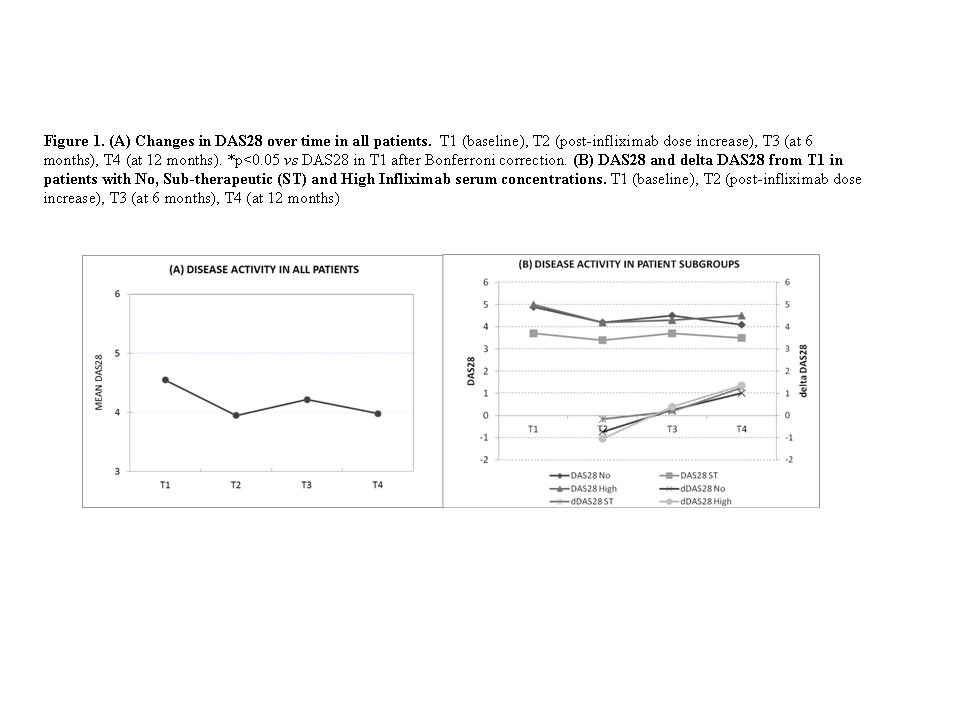
Disclosure:
A. Balsa,
Pfizer Inc,
9;
C. Plasencia-Rodriguez,
Pfizer Inc,
2;
M. G. Bonilla,
None;
A. Villalba,
None;
D. Peiteado,
None;
S. Garcia-Carazo,
None;
L. Nuño,
None;
T. Jurado,
None;
E. Martín-Mola,
None;
D. Pascual-Salcedo,
Pfizer Inc,
2.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-infliximab-dose-increase-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-at-different-trough-concentrations/
