Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
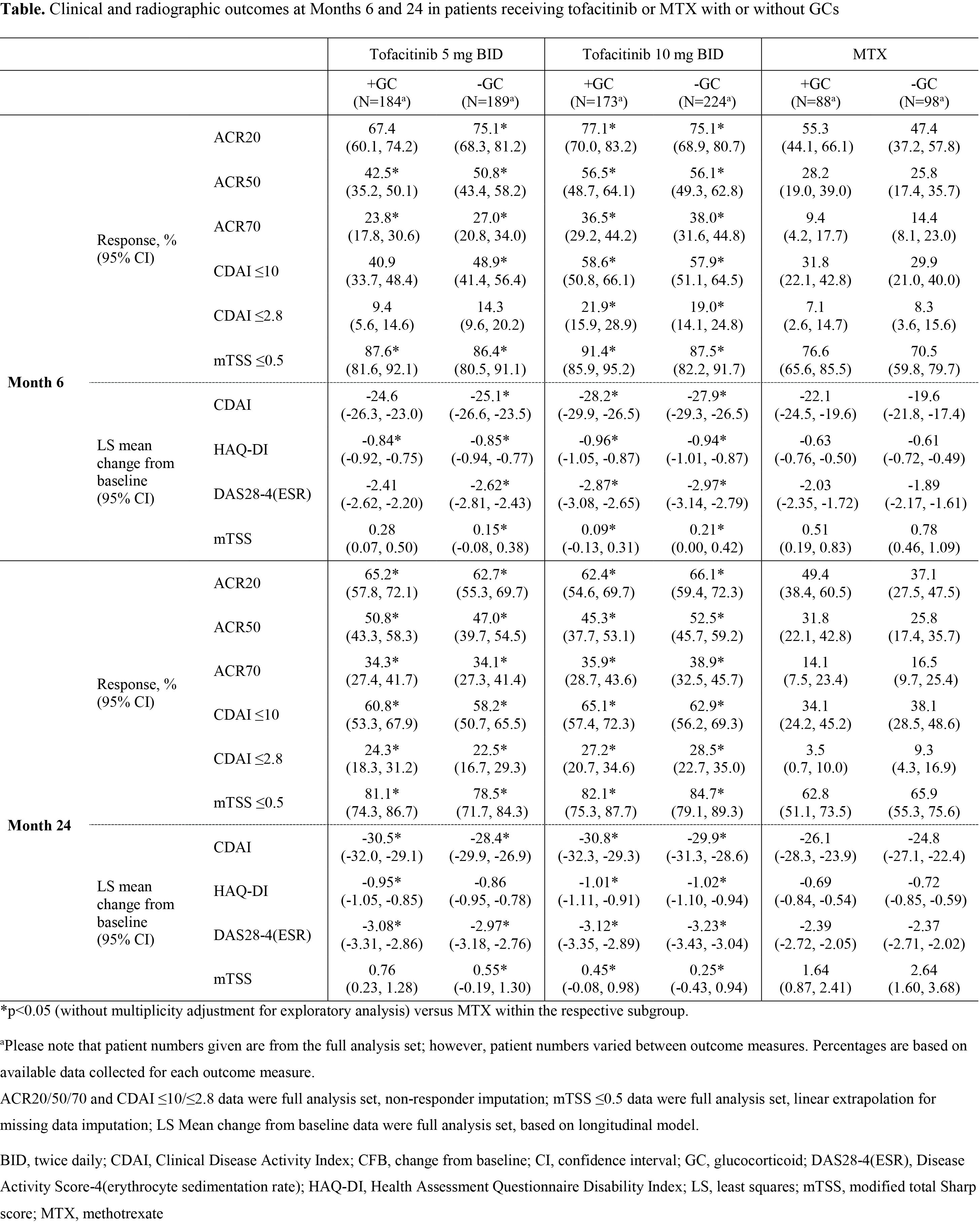
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. Patients (pts) with RA often receive concomitant treatment with glucocorticoids (GCs) to control inflammatory symptoms. The purpose of this analysis was to investigate whether the presence or absence of GCs has an effect on the clinical and radiographic efficacy of tofacitinib or MTX administered as monotherapy in MTX-naïve pts with RA.
Methods: ORAL Start (NCT01039688) was a 2-year, randomized Phase 3 clinical trial in which 956 MTX-naïve pts with RA received either tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID), tofacitinib 10 mg BID, or MTX titrated to 20 mg/week over 8 weeks. Pts receiving GCs (≤10 mg/day of prednisone or equivalent) prior to enrollment were required to remain on a stable dose throughout the study. All pts were required to meet the ACR classification criteria for the diagnosis of RA. Primary results have been reported previously. Endpoints evaluated in this analysis at Months 6 and 24 included ACR20/50/70 response rates, the proportion of pts achieving low disease activity and remission as measured by Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) ≤10 and ≤2.8, respectively, the proportion of pts with no radiographic progression as defined by a change from baseline of ≤0.5 in modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS), and least squares mean (LSM) change from baseline in CDAI, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), Disease Activity Score (DAS28-4[ESR]), and mTSS. This was an exploratory post-hoc analysis without multiplicity adjustment.
Results: Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were similar between treatment groups and among those receiving treatment with and without GCs. For assessments measured at Months 6 and 24, tofacitinib was more effective as monotherapy than MTX, regardless of GC status (Table). At Months 6 and 24, the proportions of pts achieving ACR20/50/70, CDAI ≤10, CDAI ≤2.8, and change in mTSS ≤0.5 were numerically similar between pts receiving tofacitinib with and without GCs, and between pts receiving MTX with and without GCs (Table). A similar trend was observed for LSM change from baseline in CDAI score, HAQ-DI, and DAS28-4(ESR) (Table). LSM change from baseline in mTSS was numerically similar in pts receiving tofacitinib with or without GCs, but showed a trend to be reduced (indicating less radiographic progression) in pts receiving MTX with GCs compared with those receiving MTX without GCs (Table).
Conclusion: GCs in low doses did not appear to impact clinical efficacy or inhibit radiographic progression when administered with tofacitinib monotherapy, and had a limited effect, if any, when given with MTX monotherapy. These findings might reflect the pt population, who had active disease at study entry despite receiving GCs and therefore may not be generalizable to pts starting GCs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Charles-Schoeman C, van der Heijde D, Burmester G, Nash P, Zerbini CAF, Connell CA, Fan H, Kwok K, Bananis E, Fleischmann R. Effect of Glucocorticoids on Clinical and Radiographic Efficacy Outcomes in Methotrexate-Naive Patients with RA Receiving Tofacitinib or Methotrexate Monotherapy: Analysis of Data from a Phase 3 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-glucocorticoids-on-clinical-and-radiographic-efficacy-outcomes-in-methotrexate-naive-patients-with-ra-receiving-tofacitinib-or-methotrexate-monotherapy-analysis-of-data-from-a-phase-3-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-glucocorticoids-on-clinical-and-radiographic-efficacy-outcomes-in-methotrexate-naive-patients-with-ra-receiving-tofacitinib-or-methotrexate-monotherapy-analysis-of-data-from-a-phase-3-trial/