Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: EQUATOR (NCT03101670) was a 16-week, Phase 2, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial of filgotinib for PsA. At Week 16, placebo-treated patients could switch to filgotinib and those on filgotinib could continue treatment for up to an additional 304 weeks in an open-label extension (OLE) study (EQUATOR2; NCT03320876). This prespecified analysis at Week 52 of the OLE assessed the effect of filgotinib on clinical enthesitis after 52 weeks of treatment in the OLE.
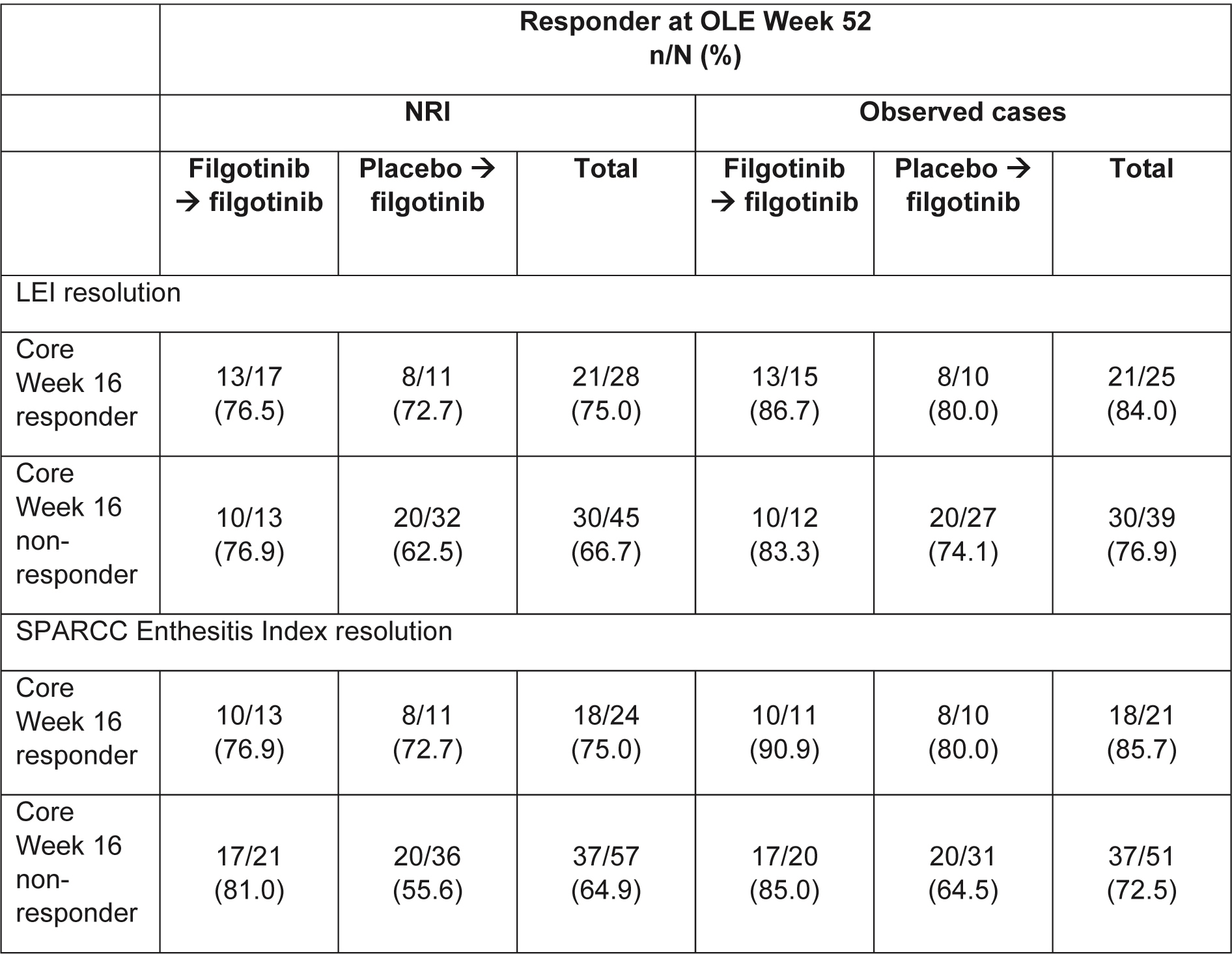
Methods: In EQUATOR, patients with active moderate-to-severe PsA (≥5 swollen joints and ≥5 tender joints, fulfilling Classification for PsA [CASPAR] criteria) were randomized 1:1 to receive oral filgotinib 200 mg or placebo once daily (QD) for 16 weeks. At Week 16, patients could continue into the OLE, receiving filgotinib 200 mg QD. The effects on Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) Enthesitis Index and Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI) resolution were assessed in patients with core baseline enthesitis (SPARCC or LEI >0) up to and including Week 52 of EQUATOR2 (≤68 weeks in total), using observed case (OC) and non-responder imputation (NRI) analyses.
Results: In EQUATOR, 131 patients were randomized, of which 76 and 85 had LEI >0 and SPARCC >0 at baseline, respectively. At OLE Week 52, 79.7% and 67.1% of all patients with LEI >0 at baseline (regardless of treatment in the core 16-week trial) achieved LEI resolution (i.e. LEI=0) in the OC and NRI analyses, respectively (Figure 1), and 76.4% and 64.7% of those with SPARCC >0 at baseline, achieved SPARCC Enthesitis Index resolution (i.e. SPARCC=0) in the OC and NRI analyses, respectively (Figure 2). Comparing patients originally assigned filgotinib versus placebo, the proportion of patients with clinical resolution at Week 16 of the core EQUATOR trial was 51.5% and 25.6%, respectively, for LEI, and 35.1% and 22.9%, respectively, for SPARCC (NRI analysis; Figures 1 and 2). At OLE Week 52, the proportion of patients with clinical resolution had increased in both the filgotinib and placebo groups from core Week 16 (Figures 1 and 2). Of filgotinib-treated patients who achieved clinical resolution of enthesitis (LEI or SPARCC) at core Week 16 of EQUATOR, 76.5% (13 out of 17) and 76.9% (10 out of 13) also achieved responses at Week 52 of the OLE for LEI and SPARCC, respectively, in the NRI analysis (Table). Of filgotinib-treated patients who did not achieve clinical resolution of enthesitis (LEI or SPARCC) at core Week 16, 76.9% (10 out of 13) and 81.0% (17 out of 21) had responded by Week 52 for LEI and SPARCC, respectively, in the NRI analysis (Table).
Conclusion: Data from this 52-week OLE interim analysis suggest that further improvement in enthesitis can be expected with filgotinib 200 mg QD beyond 16 weeks of treatment in patients with pre-existing enthesitis. The majority of patients were able to maintain and/or achieve clinical resolution of enthesitis by Week 52. These findings should be confirmed in the further extension of this trial and in future Phase 3 trials.
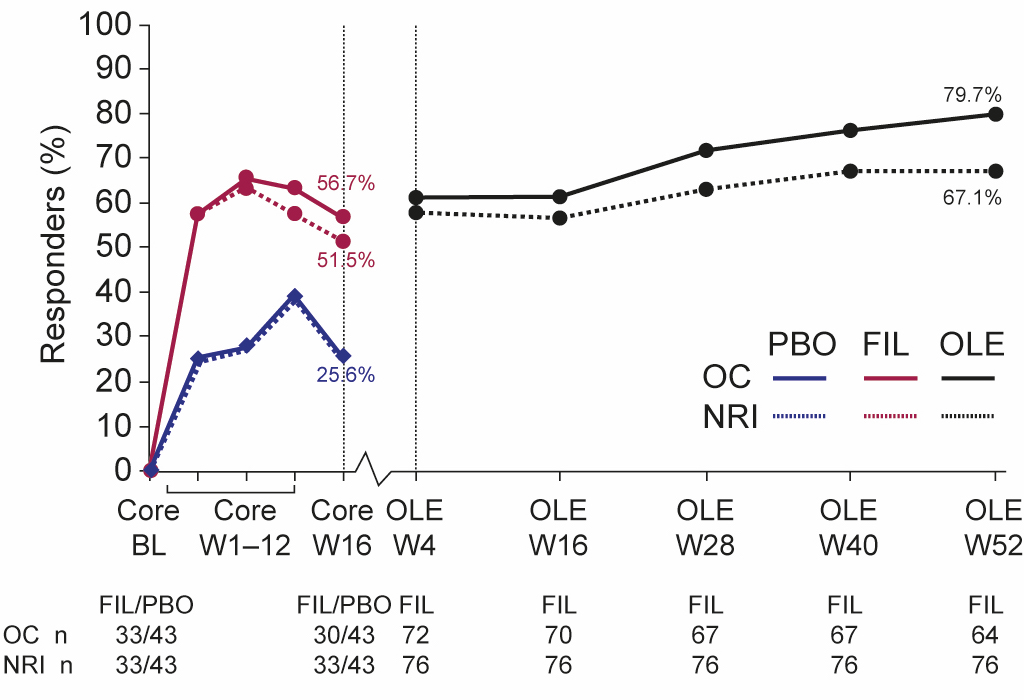 Figure 1. Proportion of LEI responders over time. BL, baseline; FIL, filgotinib; LEI, Leeds Enthesitis Index; NRI, non-responder imputation; OC, observed cases; OLE, open-label extension; PBO, placebo; W, week. Note: The percentage of responders in the placebo group up to core Week 16 was the same in the OC and NRI analyses
Figure 1. Proportion of LEI responders over time. BL, baseline; FIL, filgotinib; LEI, Leeds Enthesitis Index; NRI, non-responder imputation; OC, observed cases; OLE, open-label extension; PBO, placebo; W, week. Note: The percentage of responders in the placebo group up to core Week 16 was the same in the OC and NRI analyses
 Figure 2. Proportion of SPARCC responders over time. BL, baseline; FIL, filgotinib; NRI, non-responder imputation; OC, observed cases; OLE, open-label extension; PBO, placebo; SPARCC, Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada; W, week
Figure 2. Proportion of SPARCC responders over time. BL, baseline; FIL, filgotinib; NRI, non-responder imputation; OC, observed cases; OLE, open-label extension; PBO, placebo; SPARCC, Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada; W, week
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Coates L, Van den Bosch F, Helliwell P, Gladman D, Gilles L, Gheyle L, Trivedi M, Alani M, Besuyen R. Effect of Filgotinib on the Complete Resolution of Enthesitis in Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) Patients: 52-week Results from EQUATOR2 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-filgotinib-on-the-complete-resolution-of-enthesitis-in-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-patients-52-week-results-from-equator2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-filgotinib-on-the-complete-resolution-of-enthesitis-in-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-patients-52-week-results-from-equator2/