Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II: Measurements (0739–0763)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) is an intracellular kinase that mediates signaling by cytokines, such as IL-23, IL-12, and IFNα/β, involved in the pathogenesis of PsA and other immune-mediated diseases. Deucravacitinib is a novel, oral selective inhibitor of TYK2 via the TYK2 nonconserved regulatory domain. Phase 2 results showed deucravacitinib was efficacious and well tolerated versus placebo (PBO) in patients (pts) with active PsA. The Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PsAID) questionnaire is a validated instrument designed to specifically assess the impact of PsA on health-related quality of life from the pt’s perspective and is available as separate versions for clinical practice (PsAID-12) and clinical trials (PsAID-9)1 This analysis compared the effect of deucravacitinib vs PBO on PsAID-12 and PsAID-9 responses and assessed the relationships between PsAID scores and clinical and pt-reported outcome (PRO) measures.
Methods: In this 1-year, double-blind, Phase 2 trial (NCT03881059), pts with active PsA were randomized 1:1:1 to deucravacitinib 6 mg or 12 mg once daily (QD), or PBO for 16 weeks (Wk). PsAID-12 and PsAID-9, other PROs, and clinical response outcomes were assessed at baseline (BL) and Wk 16. Mean changes from BL in PsAID-12 and PsAID-9 total scores at Wk 16 were determined for each treatment group as well as by response outcomes (ie, achievement of response at Wk 16 for PROs and select clinical response outcomes). Spearman correlations between PsAID-12 and PsAID-9 scores and clinical and PRO measures were also assessed .
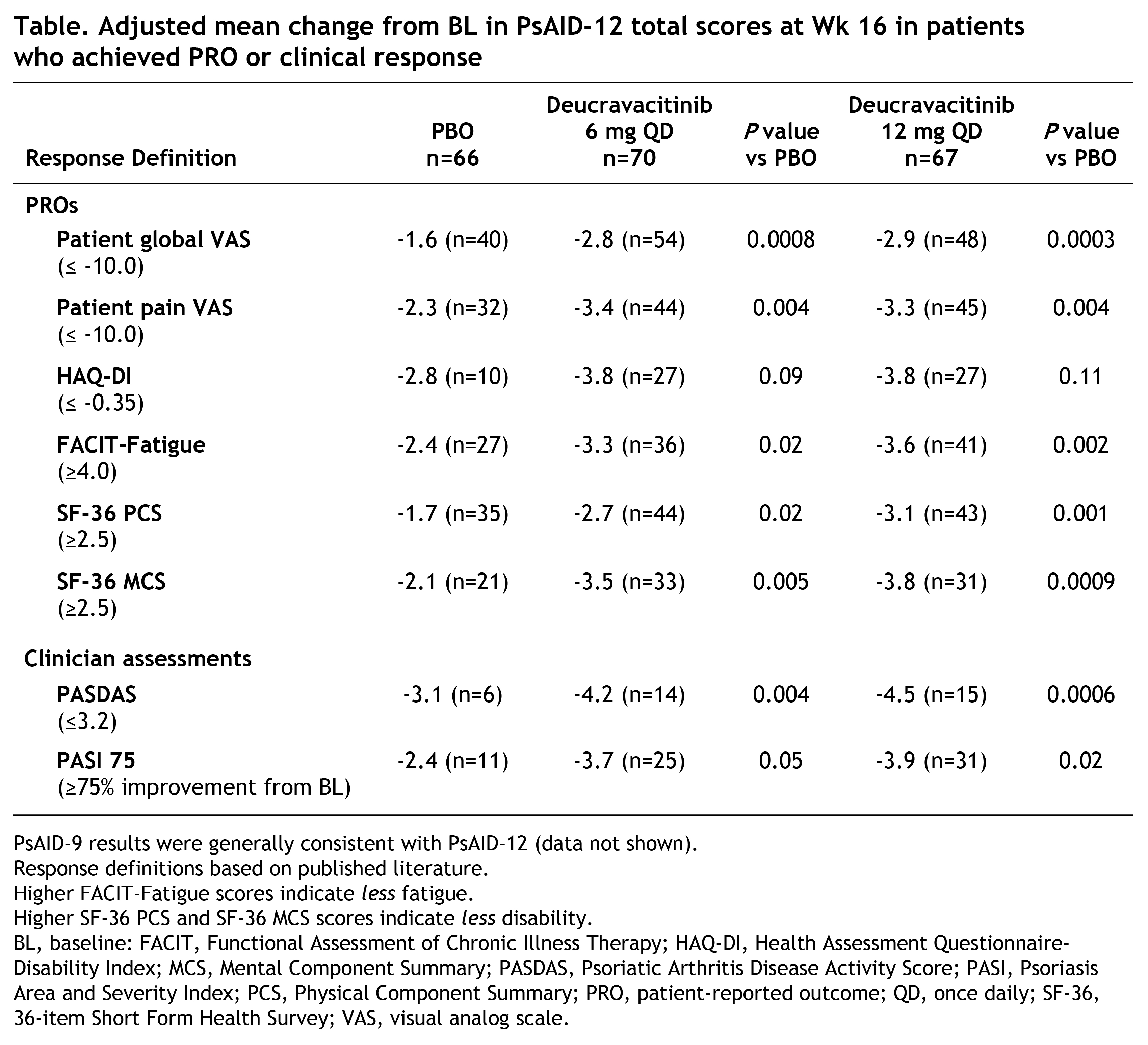
Results: Of 203 pts randomized, 180 (89%) completed 16 Wks of treatment (deucravacitinib 6 mg QD, 63/70 [90%]; deucravacitinib 12 mg QD, 59/67 [88%]; PBO, 58/66 [88%]). Demographic and BL disease characteristics were similar across groups. Mean age was 49.8 years and median PsA duration since diagnosis was 4.5 years. Adjusted mean changes from BL in PsAID-12 and PsAID-9 scores at Wk 16 were significantly greater in the deucravacitinib groups vs PBO (Figure). Significant improvements with deucravacitinib vs PBO were also observed in pts who achieved response for PROs and for Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity Score low disease activity and ≥75% improvement from BL in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index response (Table). In contrast, adjusted mean changes from BL were generally similar with deucravacitinib vs PBO in nonresponders. Spearman correlation analysis revealed significant correlations at BL and Wk 16 between PsAID-12 and PsAID-9 scores and clinical and PRO measures (P< 0.0001).
Conclusion: With deucravacitinib vs PBO, PsAID-12 and PsAID-9 scores were significantly improved vs BL at Wk 16. Both PsAID scores detected additional improvements among pts achieving response for multiple other PROs and select clinical outcome measures.
Reference: 1. Gossec L et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:1012-9.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gossec L, Coates L, Ogdie-Beatty A, Mease P, Lehman T, Nowak M, Wei L, Ye J, Choi J, Zhuo J, Becker B. Effect of Deucravacitinib on the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease Questionnaires 12 and 9: Analysis of a Phase 2 Study of Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-deucravacitinib-on-the-psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-questionnaires-12-and-9-analysis-of-a-phase-2-study-of-active-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-deucravacitinib-on-the-psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-questionnaires-12-and-9-analysis-of-a-phase-2-study-of-active-psoriatic-arthritis/