Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Myositis associated autoantibodies (MAA) in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) demonstrate unique phenotypic features. In some autoimmune disorders, autoantibody levels correlate with disease activity and are reduced after B cell depletion (BCD). Our aim was to determine the effect of BCD on the serum levels of 3 common MAAs (anti-Jo-1, -TIF1g, -SRP) and to assess whether quantitative changes in MAA levels correlate with IIM core-set measures (CSM) [manual muscle testing (MMT), muscle enzyme, physician global, patient/parent global, extramuscular disease activity and HAQ].
Methods: Treatment-resistant IIM subjects (n=200) received rituximab in a 44-week clinical trial, the Rituximab in Myositis (RIM) Study. CSM were evaluated monthly and serial serum samples were collected. Anti-Jo-1 (n=25), -SRP (n=25) and -TIF1g (n=23) levels were measured using validated ELISAs. Temporal trends in MAA levels and longitudinal relationship between MAA levels and CSM within patients (adjusted for the total immunoglobulin (IgG) levels) was estimated using linear mixed models (SAS v. 9.2). Spearman correlation within each subject longitudinally and median MAA levels and CSM over time were evaluated.
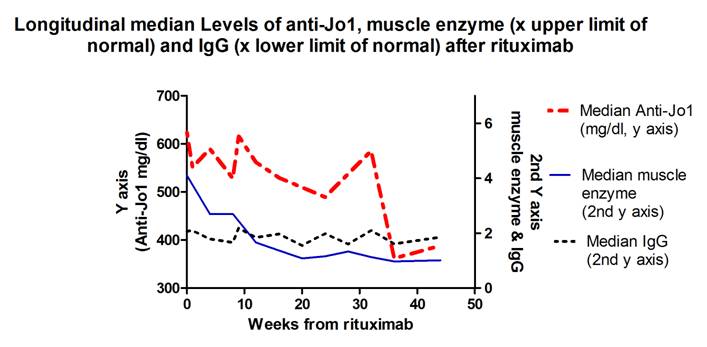
Results: After start of the treatment autoAb levels in Jo-1 subjects decreased by approximately 9 units per week (p<0.001). Anti-Jo-1 levels longitudinally correlated with all CSM (p<0.05) univariately and after adjusting for IgG levels In contrast, anti-TIF1g and anti-SRP levels do not demonstrate systematic trends with time; there was no significant correlation between anti-TIF1g or anti-SRP levels and any CSM. Median (IQR) Anti-TIF1g levels were unchanged between baseline [34 (11–85)] and the last visit [38 (13–94)]. Post-hoc analysis of anti-SRP levels (n=25) revealed intermediate results as 13/25 (52%) anti-SRP subjects dropped their autoAb level while 9 were unchanged. The 13 subjects with a decrease in anti-SRP levels had significantly higher baseline anti-SRP levels compared to the remaining patients [median 81 (12-208) vs. 5(4-50); p=0.02]. Those 13 subjects demonstrated moderate to strong correlations (rho > 0.35) between anti-SRP levels and CSM except for the HAQ (median rho 0.26).
Conclusion: Anti-Jo-1 autoAb levels in IIM patients decreased after BCD with rituximab and longitudinally correlated with changes in all CSM. In contrast, anti-TIF-1g and anti-SRP levels did not change significantly over time and there were no significant correlations with CSM, except a subset of anti-SRP patients with higher baseline levels.. The strong association of anti-Jo-1 levels with clinical outcomes suggests that these autoantibodies may have a direct pathogenic role in IIM that is mitigated by B cell depletion with rituximab and may be a good biomarker for disease activity.
Disclosure:
R. Aggarwal,
None;
C. V. Oddis,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
9;
A. Bandos,
None;
D. Goudeau,
None;
D. Koontz,
None;
Q. Zengbiao,
None;
A. M. Reed,
None;
D. P. Ascherman,
None;
M. C. Levesque,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
2.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-b-cell-depletion-therapy-with-rituximab-on-myositis-associated-autoantibody-levels-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy/