Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects III: Obesity and Other Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: We evaluated the associations between MBDA score and age and between MBDA score and BMI in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These relationships may be important to patient management and clinical decision-making.
Methods: Data in this retrospective study are from CORRONA, a longitudinal RA registry comprising >625 US rheumatologists in 40 states. Patients included must have had an MBDA test performed between 1 month before to 7 days after a CORRONA visit, which was the source of patient characteristics and clinical data. MBDA scores were categorized as low (<30), moderate (30-44), and high (>44). Age was categorized by decade (<40, 40-49, 50-59, 60-69, 70-79, and >80 years). BMI was categorized as ≤25, >25-30, >30-<35, ≥35 kg/m2. Associations between age or BMI and MBDA score were evaluated using the Chi-square and trend tests.
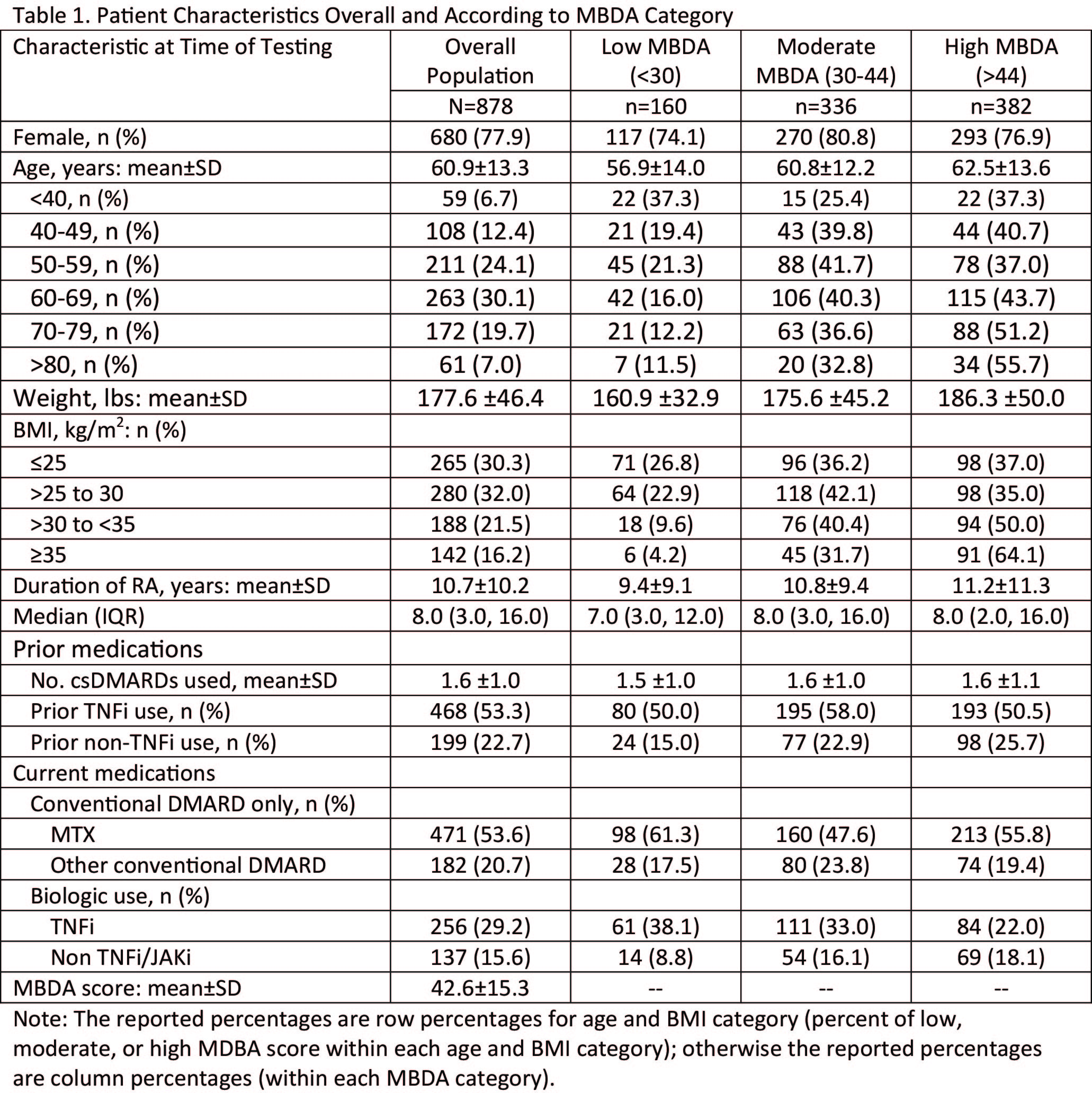
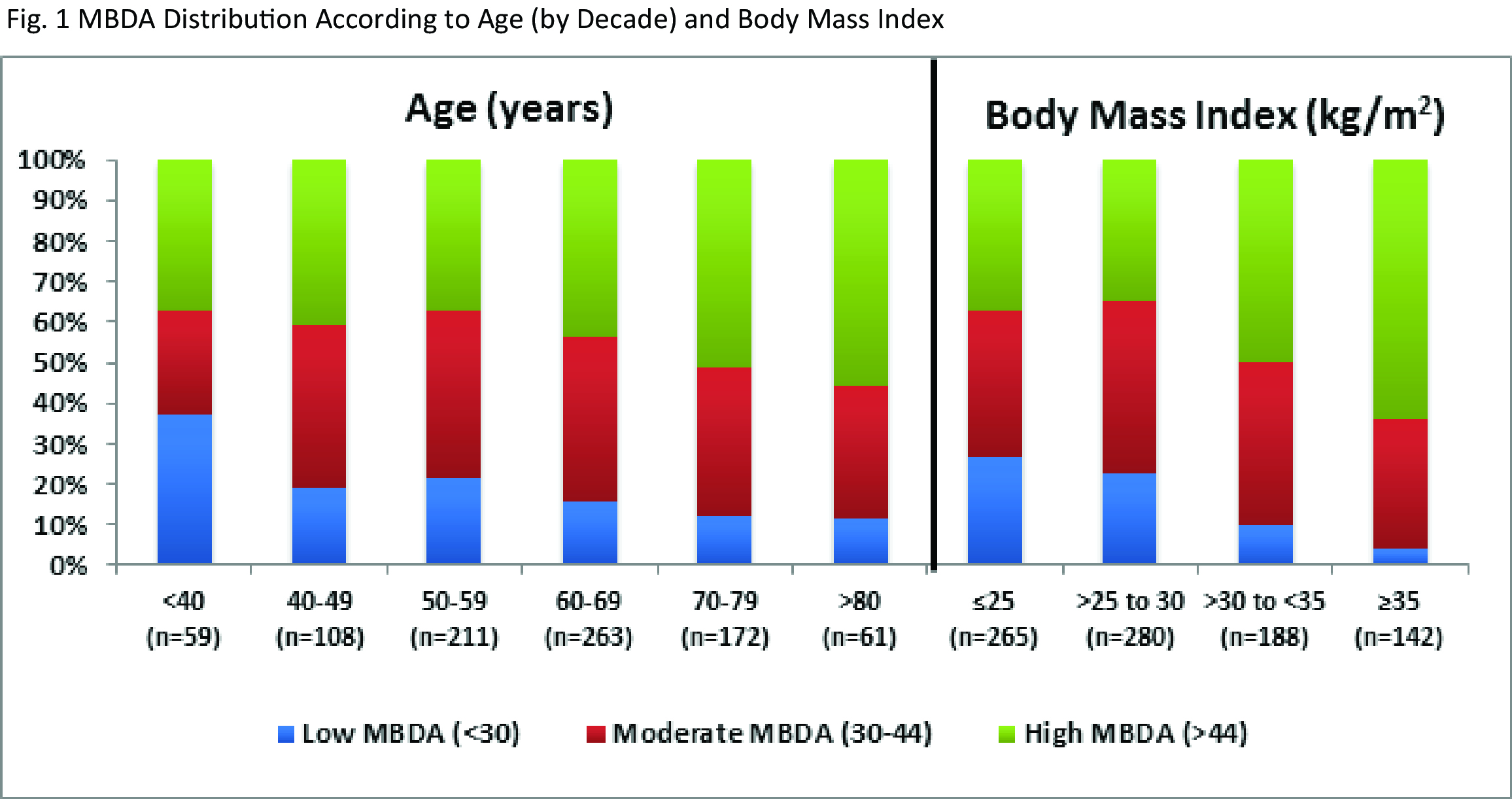
Results: 878 patients were included: 77.9% were female with mean age 60.9 years, mean weight of 177.6 lbs, and mean RA disease duration of 10.7 years. Approximately half of patients (54%) were using methotrexate or other conventional DMARDs (21%), and nearly half (45%) were using a biologic (Table 1). Mean MBDA score was 42.6, with 18% in the low, 38% moderate and 44% high MBDA categories. The distribution of patients across the low, moderate and high MBDA categories was significantly associated with age by decade (Figure 1) both by chi-square test (p=0.001) and trend test (p<0.0001). MBDA category was also significantly associated with BMI (chi-square p=0.001; trend test p<0.0001) (Table 1). Low MBDA scores were observed in 135 of 545 (24.8%) patients with BMI ≤30 and 6 of 142 (4.2%) with MBDA scores ≥35 (Table 1). Conversely, high MBDA scores were observed in 196 of 545 (36.0%) of patients with BMI ≤30 and in 91 of 142 (64.1%) with BMI ≥35 (Table 1).
Conclusion: Age and BMI were each found to have a significant association with the MBDA score. These data suggest inflammatory biomarkers in RA may be affected by non-RA related factors. The magnitude of these effects deserves further evaluation in order to provide guidance on the interpretation of MBDA scores in older patients and those with very high BMI (≥35).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ford K, Chernoff D, Wang X, Sasso EH, Etzel CJ, Pappas DA. Effect of Age and Body Mass Index (BMI) on Multi-Biomarker Disease Activity (MBDA) Score in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-age-and-body-mass-index-bmi-on-multi-biomarker-disease-activity-mbda-score-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-age-and-body-mass-index-bmi-on-multi-biomarker-disease-activity-mbda-score-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/