Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID have been shown in long-term extension (LTE) studies up to 105 months. We assessed the impact of tofacitinib dose changes on efficacy and safety in patients (pts) who increased dose (step-up), and pts who decreased dose (step-down), vs pts who remained on the same dose when entering LTE studies.
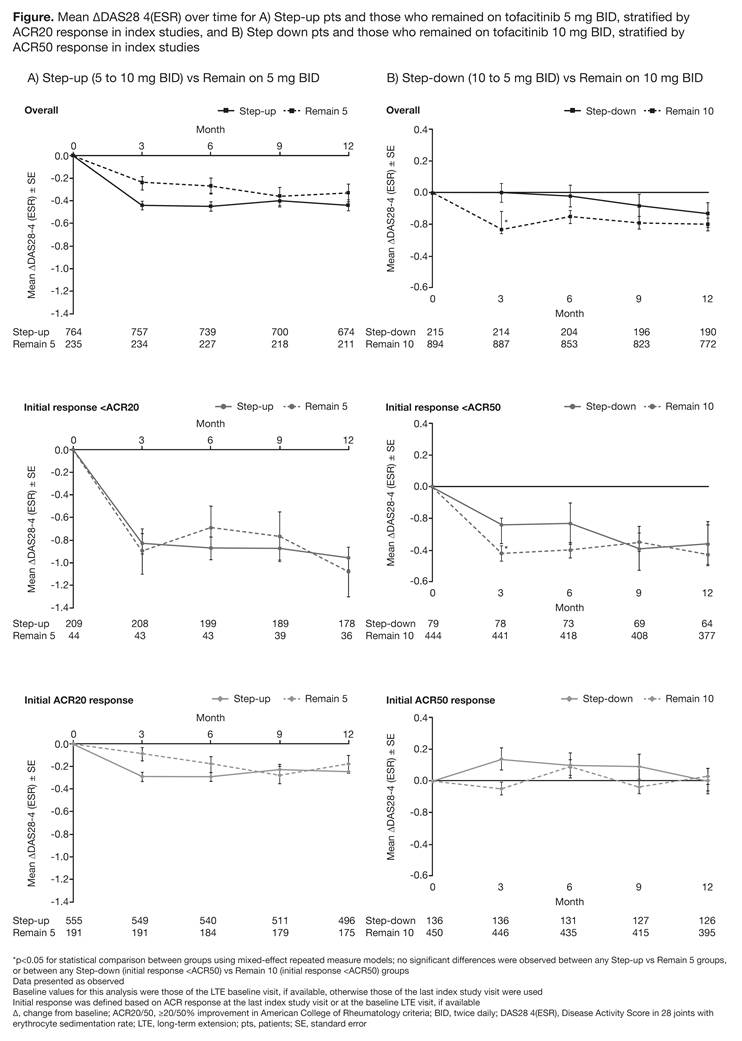
Methods: In this exploratory, post-hoc analysis, data were pooled from 2 open-label LTE studies (NCT00413699 [ongoing; database not locked at January 2016 data-cut]; NCT00661661) of RA pts who had participated in Phase (P) 1/2/3 tofacitinib index studies and had ≥81 days of tofacitinib exposure (to allow ≥2 assessments) in each period (P1/2/3 index, LTE). Dose changes from index study dose were either mandated by protocol (upon LTE entry) or at the investigator’s discretion (during LTE). This analysis only included pts who remained on their initial/changed dose once in the LTE. Pts were analyzed in 4 groups: 5 mg BID [index]→10 mg BID [LTE] (Step-up; N=833); 5 mg BID [index]→5 mg BID [LTE] (Remain 5; N=248); 10 mg BID [index]→10 mg BID [LTE] (Remain 10; N=951); 10 mg BID [index]→5 mg BID [LTE] (Step‑down; N=234). To determine whether initial efficacy (last index study assessment) may affect response following dose change on LTE entry, sub-groups for the Step-up and Remain 5 groups were defined based on initial ACR20 response, and sub-groups for the Step-down and Remain 10 groups were defined based on initial ACR50 response. Efficacy was assessed up to Month 12 in the LTE based on ΔDAS28-4(ESR). Exposure-adjusted event rates (pts with event/100 pt-yrs) are presented for the most common AEs for the entire LTE study exposure.
Results: No statistically significant differences in ΔDAS28‑4(ESR) were observed between the Step-up and Remain 5 groups (Figure), whether or not they had an initial ACR20 response. In general, no significant differences in ΔDAS28‑4(ESR) were observed between the Step‑down and Remain 10 groups (Figure), whether or not they had an initial ACR50 response. The rates and types of adverse events (AEs) were similar across all groups (Table).
Conclusion: In RA pts, the safety profile was similar regardless of dose change. Step-up from tofacitinib 5 to 10 mg BID, or step-down from 10 to 5 mg BID did not affect efficacy over 12 months vs remaining on the same dose, and was not influenced by initial response. Conclusions are limited by small pt numbers in some groups, the open-label design, and inclusion of pts in the LTE who show tolerability for tofacitinib and drug retention.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mueller R, Schulze-Koops H, Furst DE, Cohen SB, Kwok K, Maniccia A, Wang L, Akylbekova E, von Kempis J. Effect of a Step-up or Step-Down in Tofacitinib Dose on Efficacy and Safety in Long-Term Extension Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-a-step-up-or-step-down-in-tofacitinib-dose-on-efficacy-and-safety-in-long-term-extension-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-a-step-up-or-step-down-in-tofacitinib-dose-on-efficacy-and-safety-in-long-term-extension-studies/