Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologic agents are effective in treating patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA); however, some patients either fail to respond or lose response over time. This study assessed the direct and indirect economic burden among RA patients who had inadequate responses to initial biologic therapy compared with treatment responders.
Methods: Data from 1/1/1998-3/31/2014 were used from a large de-identified, privately insured claims database, which included work loss from a subset of reporting companies. Study sample consisted of patients with ≥1 claim for a biologic DMARD (bDMARD) approved for treatment of RA and ≥2 RA diagnoses in the claim history, with continuous eligibility for 6 months before (baseline) and 12 months after (study period) the date of the first bDMARD claim (index date). Patients were classified as responders and non-responders based on a validated, claim-based algorithm. All-cause and RA-related healthcare resource use and costs, work loss, and indirect costs during the study period were compared for bDMARD responders vs. non-responders. Multivariable regressions were used to adjust for baseline characteristics. As different treatments were approved over time and the pattern of costs and resources use may have changed, subgroup analyses of resource use and direct costs were conducted for patients with index dates in 1998-2007 and in 2008-2013.
Results: This study included 7,540 eligible RA patients, with 2,527 bDMARD responders and 5,013 non-responders; 407 responders and 723 non-responders had work loss data. Compared with responders, non-responders had significantly higher adjusted rates of resource use, including inpatient admissions (incidence rate ratio [IRR]=1.94), outpatient visits (IRR=1.19), emergency department visits (IRR=1.53), and number of prescription fills (IRR=1.09) (all p-values < 0.001). Non-responders had significantly higher adjusted all-cause and RA-related medical costs compared with responders (all-cause: $12,868 vs. $9,621, RA-related: $5,740 vs. $4,495, adjusted p-values<0.001) (Figure 1). Results for subgroup analyses of resource use and direct costs by index date were consistent with the full sample. Non-responders also had significantly more days of work loss compared with responders (22.1 vs. 16.7 days, IRR=1.21, adjusted p-value=0.007) and higher indirect costs ($3,548 vs. $2,890, adjusted p-value = 0.002).
Conclusion: Two-thirds of RA patients had inadequate responses to their initial bDMARD. These non-responders faced a significantly higher burden, including increased healthcare resource use, direct medical costs, and work loss compared to responders. Figure 1. Medical costs of biologic non-responders vs. responders 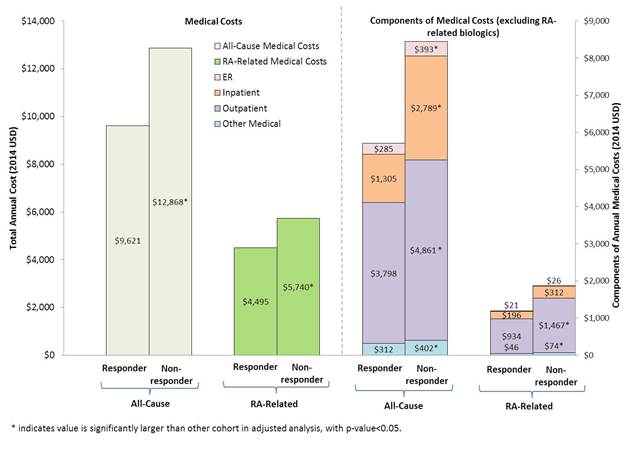
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Tundia N, Song Y, Macaulay D, Fuldeore M. Economic Burden of Non-Responders to Biologic DMARD Treatments in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/economic-burden-of-non-responders-to-biologic-dmard-treatments-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/economic-burden-of-non-responders-to-biologic-dmard-treatments-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
