Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Mavrilimumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor-α, has demonstrated efficacy and safety in disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-inadequate responder (IR) patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).1 Few head-to-head studies in tumor necrosis factor antagonist (aTNF)-IR assess alternative aTNFs vs. other agents; this Phase IIb exploratory study (NCT01715896) evaluates the efficacy and safety of mavrilimumab and golimumab in aTNF-IR and DMARD-IR pts.
Methods: This 24-week study enrolled pts with active RA (28-joint Disease Activity Score [DAS28]–C-reactive protein [CRP]/erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR] ≥3.2); ≥4 swollen joints; inadequate response to ≥1 DMARDs and/or 1–2 aTNFs receiving concomitant methotrexate (MTX; 7.5–25.0 mg/week). Pts received subcutaneous mavrilimumab 100 mg every other week (eow), based on data from the Phase IIa study,2 or golimumab 50 mg alternating with placebo eow. Key endpoints were ACR20/50/70 responses, DAS28–CRP <3.2 and <2.6, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index improvement >0.22 at Week 24 and safety/tolerability. Treatment estimates for mavrilimumab and golimumab are presented with standard errors.
Results: Pts were randomized to mavrilimumab or golimumab (1:1) (Table). Data for pts receiving mavrilimumab 100 mg eow and golimumab 50 mg at Week 24 are shown for the aTNF-IR, DMARD-IR and overall strata (Table). The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) for mavrilimumab 100 mg and golimumab 50 mg were nasopharyngitis (5.7%, 1.5%), headache (4.3%, 2.9%), upper respiratory tract infection (4.3%, 2.9%), viral upper respiratory tract infection (4.3%, 2.9%), and hepatic enzyme increase (4.3%, 2.9%), respectively. Related serious TEAEs were pneumocystis pneumonia (n=1) and lung disorder (n=1) [both in golimumab-treated pts]. No deaths were reported and no significant pulmonary safety signals were identified.
Conclusion: In this exploratory study, mavrilimumab 100 mg eow and golimumab 50 mg demonstrated efficacy and an acceptable safety profile in DMARD-IR and aTNF-IR pts. The study was not powered to demonstrate statistical significance between mavrilimumab and golimumab. As mavrilimumab 100 mg eow has previously been shown to have suboptimal efficacy compared with 150 mg eow in DMARD-IR pts (EARTH EXPLORER 1),1 additional studies are needed to establish the benefit of a higher dose in pts with moderate to severe RA and inadequate response to aTNF agents. References: 1Burmester G, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;66:S1231. 2Burmester G, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:1445–1452. ^Joint senior authors. First presented at EULAR 2016. 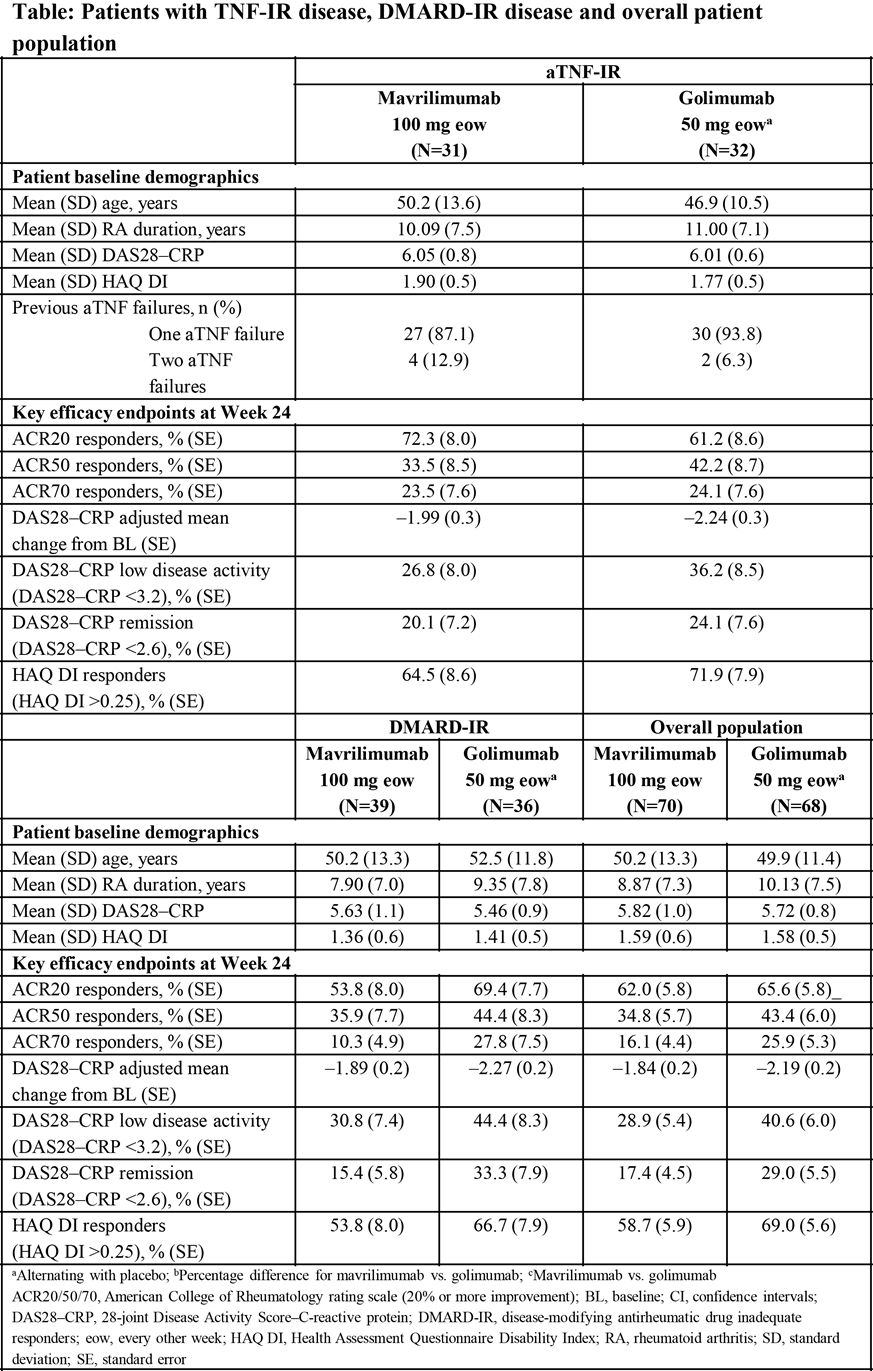
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weinblatt M, McInnes I, Kremer J, Miranda P, Vencovský J, Godwood A, Albulescu M, Close^ D, Burmester^ G. EARTH EXPLORER 2, a Phase IIb Exploratory Study Evaluating Efficacy and Safety of Mavrilimumab, a Fully Human Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor-Alpha Monoclonal Antibody, and the Tumor Necrosis Factor Antagonist Golimumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/earth-explorer-2-a-phase-iib-exploratory-study-evaluating-efficacy-and-safety-of-mavrilimumab-a-fully-human-granulocyte-macrophage-colony-stimulating-factor-receptor-alpha-monoclonal-antibody/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/earth-explorer-2-a-phase-iib-exploratory-study-evaluating-efficacy-and-safety-of-mavrilimumab-a-fully-human-granulocyte-macrophage-colony-stimulating-factor-receptor-alpha-monoclonal-antibody/
