Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), an IL-23p19 inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy in PsA across key Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis (PsO) and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA)-recommended domains1,2. Skin disease and enthesitis have been identified as disease manifestations with earlier response times than others3. In this analysis we: (a) Determined whether early skin and/or entheseal response predicts future response in other PsA domains; (b) Evaluated the trajectory for achieving skin/entheseal responses by 52 weeks (W) in patients (pts) without early responses.
Methods: Pts in the DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 (D1/2) studies were adults with active PsA despite standard therapies. D1 pts had ≥3 swollen and ≥3 tender joints (SJC/TJC) and C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥0.3 mg/dL; D2 pts had SJC ≥5, TJC ≥5, and CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL. 31% of D1 pts received 1-2 prior TNF inhibitors; D2 pts were biologic-naïve. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo. These post hoc analyses included only pooled GUS Q4W and Q8W pts (N=748). Early skin response was defined as PsO Area and Severity Index (PASI) score ≤1 at W16 or skin visual analogue scale (VAS) ≤15mm at W8 among pts with a baseline (BL) PASI score >1 and skin VAS >15mm (first assessment time for both); early entheseal response as Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI) score ≤1 at W8; and categories of early response defined as skin VAS ≤15mm only vs LEI score ≤1 only vs combined skin VAS ≤15mm & LEI score ≤1 vs none at W8. Potential responses at W24 & W52 included achievement of minimal disease activity (MDA), Disease Activity in PsA (DAPSA) low disease activity (LDA) or remission, DAPSA50, and enthesitis/dactylitis resolution. Associations between early skin/entheseal response and W24/W52 response were assessed with crosstabulations and logistic regression.
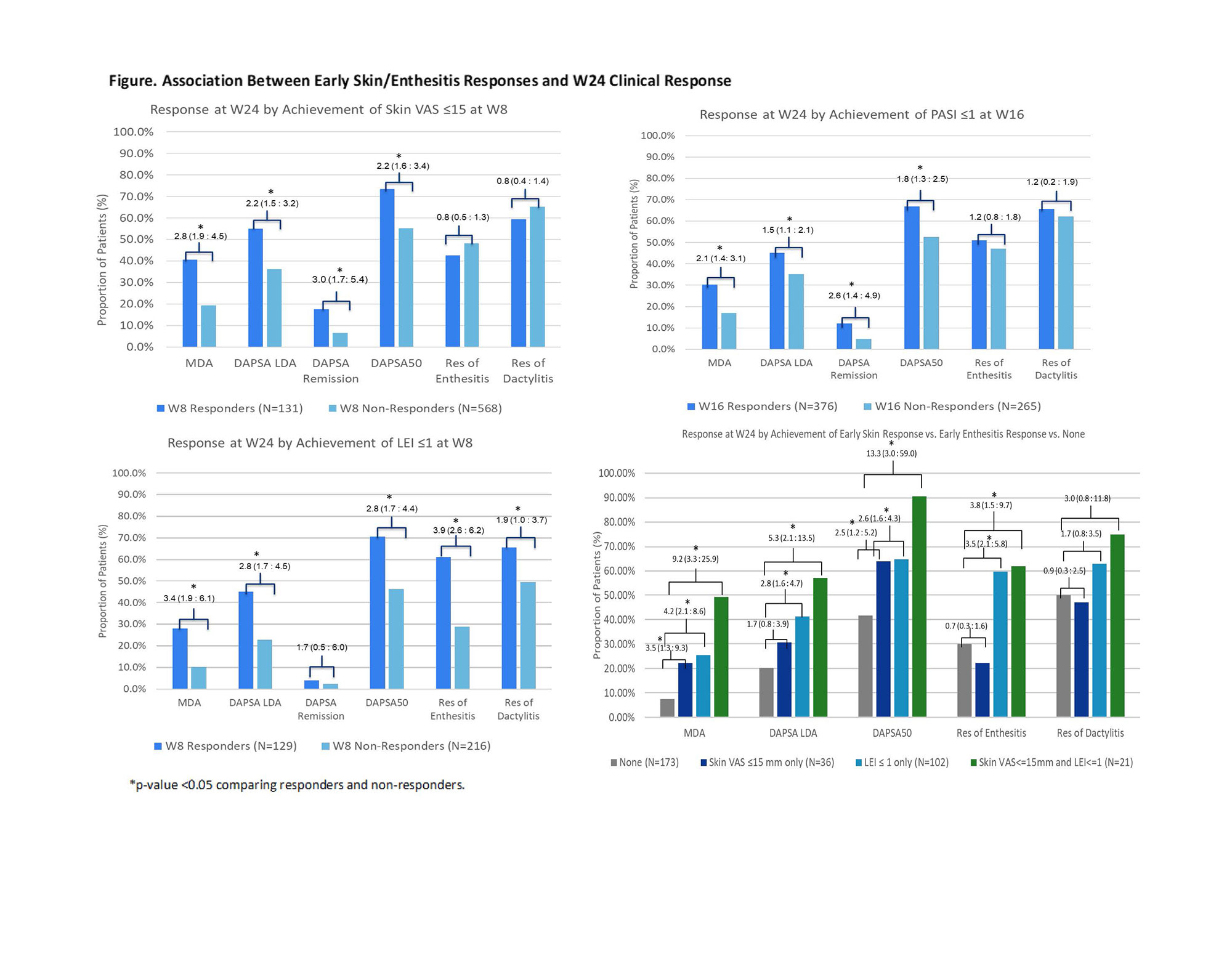
Results: Early skin response associated with greater odds of achieving W24 MDA, DAPSA LDA, DAPSA remission, and DAPSA50, but not enthesitis or dactylitis resolution (Figure). Early entheseal response associated with greater odds of achieving all W24 outcomes, including resolution of enthesitis or dactylitis, with the exception of DAPSA remission; DAPSA remission was achieved by a greater proportion of early responders, though the association was significant only at W52. In pts with both BL PsO and enthesitis, early responders in both domains were even more likely to subsequently demonstrate MDA, DAPSA LDA, DAPSA50, DAPSA remission only at W52, and dactylitis resolution than pts with individual responses. Among pts who did not achieve early responses, approximately half did so by W52.
Conclusion: Early skin and entheseal responses predicted long-term clinical response, including disease remission. A synergistic effect was observed, in which pts with BL PsO and enthesitis exhibiting early response in both domains were more likely to achieve later clinical response. These results highlight the importance of early response in these two domains on the trajectory of long-term pt outcome.
References:
1. Deodhar A et al. Lancet. 2020;395(10230) :1115-25
2. Mease PJ et al. Lancet. 2020;395(10230):1125-36
3. Coates LC et al. A893. EULAR 2022, Denmark
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates L, Ramírez J, McGonagle D, Aydin S, Zimmermann M, Nantel F, Shawi M, Rampakakis E, Nash P, Mease P. Early Skin and Early Enthesitis Responses in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Treated with Guselkumab Associate with Long-term Response: Post Hoc Analysis Through 2 Years of a Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-skin-and-early-enthesitis-responses-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-treated-with-guselkumab-associate-with-long-term-response-post-hoc-analysis-through-2-years-of-a-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-skin-and-early-enthesitis-responses-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-treated-with-guselkumab-associate-with-long-term-response-post-hoc-analysis-through-2-years-of-a-phase-3-study/