Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster III: Therapy
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: ABILITY-2
has demonstrated the efficacy of adalimumab (ADA) vs. placebo (PBO) over 12
weeks (wk) in patients (pt) with peripheral spondyloarthritis (pSpA)1
and sustained response following up to 2 years (yr) of ADA. The purpose
of this study is to determine predictors of long-term remission in pts with
pSpA.
Methods: In ABILITY-2 pts
were randomized to receive ADA 40 mg every other wk or PBO during a 12-wk
double-blind period, followed by an open-label period of up to 3 yrs of
treatment. PSpARC1 remission was defined as SJC ≤1 plus 4/5 of the
following: Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) of Disease Activity ≤20 mm
(visual analog scale, VAS); PGA-pain ≤20 mm VAS, TJC ≤1, enthesitis
count ≤1, dactylitis count ≤1. ASDAS inactive disease (ASDAS ID)
was ASDAS score <1.3. Possible predictors for remission at 1 and 3 yrs of
ADA treatment were selected a priori. Categorical variables included symptom
duration, abnormal baseline (BL) hs-CRP, HLA-B27+, and response at wk 12 for
BASDAI50, PSpARC, and ASDAS categories. Continuous variables included BL values
for TJC, SJC, enthesitis count, BASDAI, ASDAS, Patient Global Assessment of
disease activity (PtGA), PGA, and hs-CRP. Univariate logistic regression was
used to evaluate predictors for remission variables at yrs 1 and 3.
Multivariate analysis was done to determine predictors of achieving sustained
(≥ 3 consecutive visits) remission at any time during the study.
Results: 165 pts (ADA
84/PBO 81) were randomized. Among pts completing both yr 1 and 3, 48.2%
(54/112) of pts achieved PSpARC remission and 58.9% (63/107) were in ASDAS ID
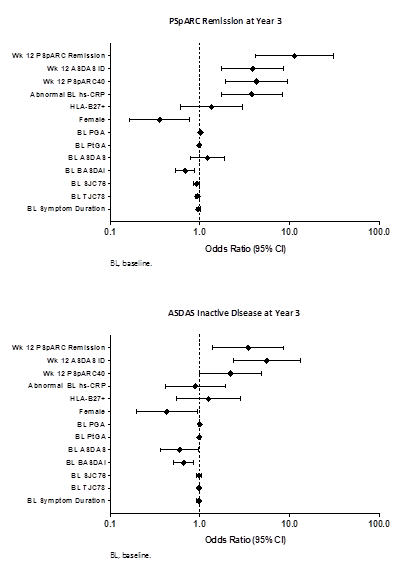
at yr 3. Univariate analysis showed that wk 12 responses were more consistent
predictors of remission at yr 1 or 3 (Figure) than most BL disease
characteristics. Abnormal BL hs-CRP was a predictor of PSpARC remission at yr
3, but not at yr 1. Furthermore, abnormal BL hs-CRP was not a predictor of
ASDAS ID at yr 1 or 3. 44.9% (74/165) and 57.6% (95/165) achieved sustained
PSpARC remission and ASDAS ID, respectively, during the 3-yr study.
Multivariate analysis demonstrated that PSpARC remission at wk 12 predicted
sustained PSpARC remission (Odds ratio (OR) 95.96, P=0.0023) and ASDAS
ID at wk 12 predicted sustained ASDAS ID (OR 46.29, P=0.0084).
Conclusion: Early response
to ADA in pSpA patients is a better predictor of long-term remission for up to
3 years, whether at a single point in time or sustained over time, than
baseline disease characteristics.
Reference
1. Mease
P et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014;Accepted Dec 29. DOI 10.1002/art.39008.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Den Bosch F, Mease PJ, Sieper J, Baeten D, Varothai NA, Pangan AL, Song IH. Early Clinical Response Is a Better Predictor of Long-Term Remission Than Baseline Disease Characteristics Following Adalimumab Treatment in Peripheral Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-clinical-response-is-a-better-predictor-of-long-term-remission-than-baseline-disease-characteristics-following-adalimumab-treatment-in-peripheral-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-clinical-response-is-a-better-predictor-of-long-term-remission-than-baseline-disease-characteristics-following-adalimumab-treatment-in-peripheral-spondyloarthritis/