Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The primary objective was to report persistence at 24 months among patients who initiated a new b/tsDMARD. Secondary endpoints included descriptive and comparative effectiveness and survival data at 3, 12, and 24 months. The analysis aimed to report baseline characteristics and comparative effectiveness of PsA treatments at three (M3) and twelve (M12) months.
Methods: Descriptive (baseline characteristics) and baseline-adjusted comparative analyses were powered for evaluating treatment groups above 10% of the total sample: ixekizumab, other interleukin (IL)-17A inhibitors (IL-17Ai; secukinumab 150 mg or 300 mg), tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi), IL-12/23i, IL-23i, and Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi).
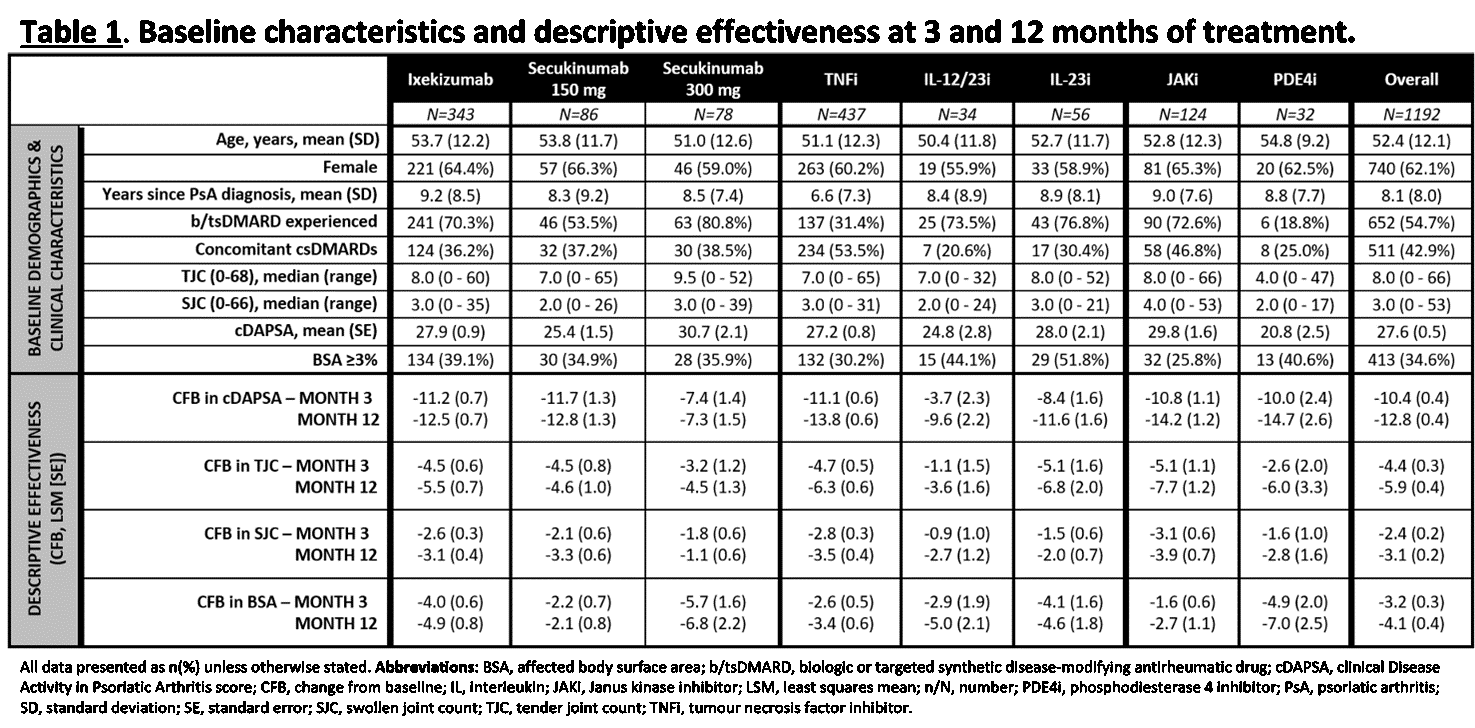
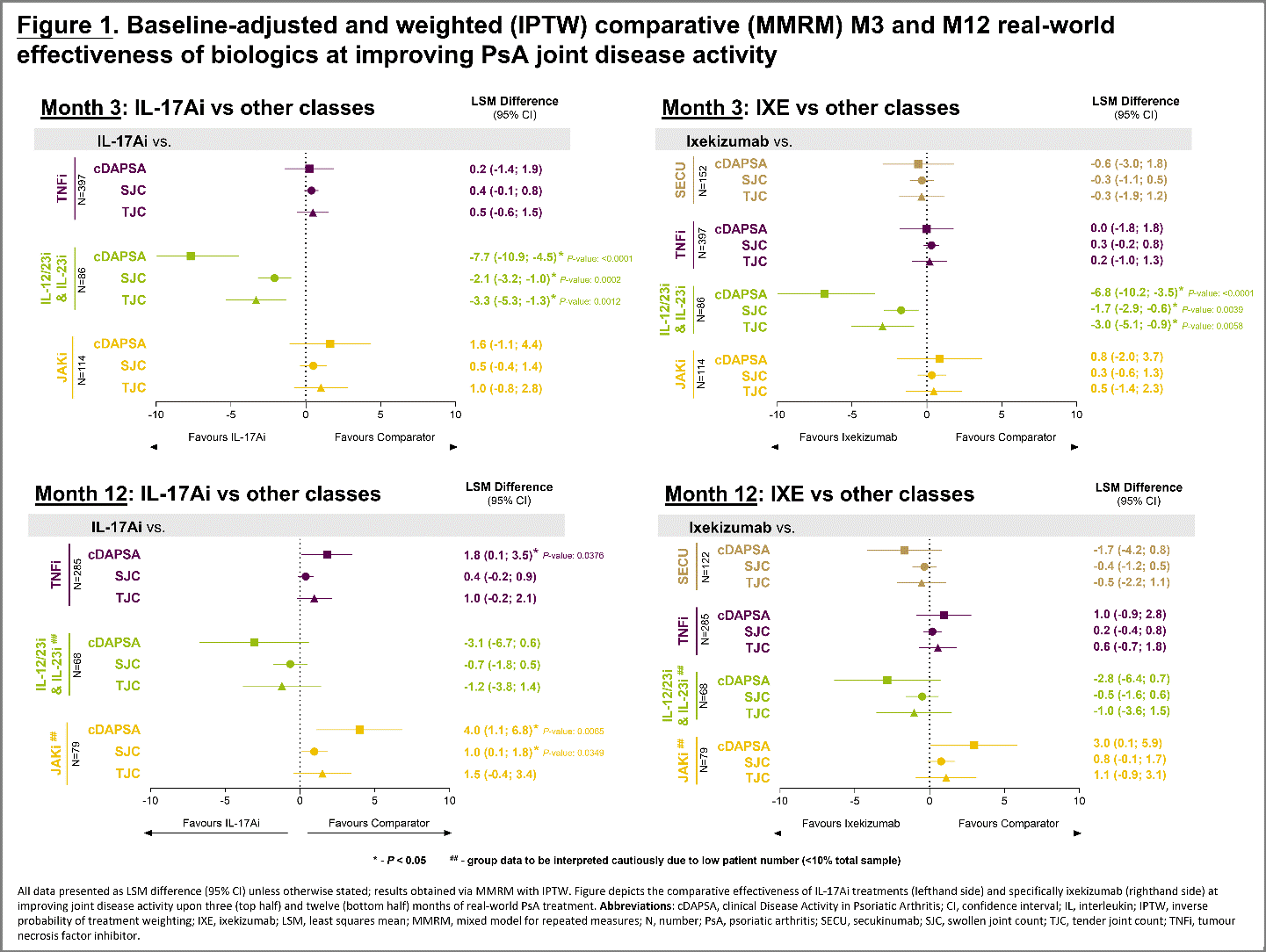
Results: In the 1192 treated patients, baseline characteristics and disease activity were similar, except for TNFi and SEC 150 mg patients who had shorter disease duration, less previous b/tsDMARD experience, and higher proportions of the TNFi (53.5%) and JAKi (46.8%) patients concomitantly using csDMARDs at baseline; a smaller proportion of the JAKi patients presented with affected body surface area (BSA) ≥3% at baseline (25.8%; Table 1). Comparative effectiveness analyses further confirmed that: for the joints, IXE was as effective as TNFi and JAKi at both M3 and M12 in the improvement of clinical Disease Activity in PsA (cDAPSA) scores as well as tender (TJC) and swollen joint counts (SJC). Higher concomitant use of csDMARDs at baseline plus improvements in TJC (M12; Table 1) might have contributed to the pattern of cDAPSA scores seen with JAKi (Figure 1); cDAPSA improvement was less prominent when comparing M12 TNFi and JAKi against the whole IL-17Ai class. At M3, both IXE and the IL-17Ai class were significantly better at improving cDAPSA, TJC, and SJC than IL-12/23i and IL-23i, indicating a faster response; in the skin, IXE showed significantly greater improvement in BSA than TNFi at both M3 (IXE: -4.1 [-4.8 – -3.4]; TNFi: -2.6 [-3.3 – -2.0]) and M12 (-4.4 [-4.9 – -3.8]; -3.5 [-4.0 – -3.0]).
Conclusion: PRO-SPIRIT captures a heterogeneous sample of patients across six countries and five classes of advanced therapies and confirms that IXE is as effective as TNFi and JAKi at improving joint disease activity in PsA patients, despite the IXE subpopulation having greater b/tsDMARD experience and longer disease duration than those receiving a TNFi as well as fewer patients on concomitant csDMARDs than both the TNFi and JAKi groups. The study also demonstrates that IXE and the IL-17Ai class provide faster improvement in cDAPSA scores than either an IL-12/23i or IL-23i, and a greater benefit in BSA than TNFi.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tillett W, Alten R, Lubrano E, Jing Ng K, Ngantcha M, de la Torre I, Kennedy D, Gullick N, McGonagle D. Early (3-Month) and Maintained (12-Month) Comparative Effectiveness of 5 Different Classes of Advanced Therapies in a Large Multinational Cohort of Real-World PsA Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-3-month-and-maintained-12-month-comparative-effectiveness-of-5-different-classes-of-advanced-therapies-in-a-large-multinational-cohort-of-real-world-psa-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-3-month-and-maintained-12-month-comparative-effectiveness-of-5-different-classes-of-advanced-therapies-in-a-large-multinational-cohort-of-real-world-psa-patients/