Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: IL-16 is a chemoattractant factor that evokes massive infiltration of mononuclear cells in the synovial tissue in patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). IL-16 concentrations are elevated in RA synovial fluid and also sera. However, the effect of current pharmacological intervention on this key cytokine and its association with clinical outcome are not fully understood. The purpose of this study was to clarify the effects of various treatments on IL-16 and the role in RA pts.
Methods: The study enrolled consecutive RA p
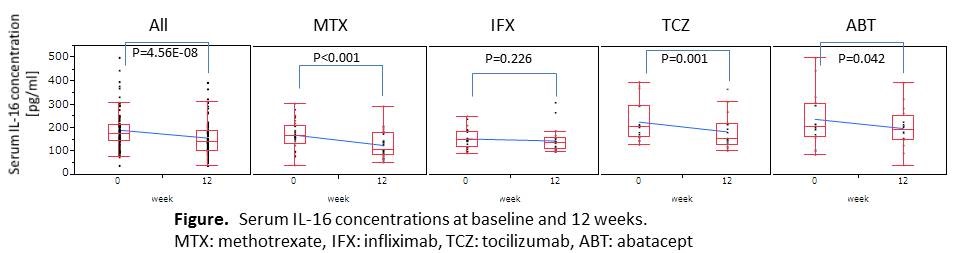
Results: Serum IL-16 concentration was significantly increased in pts with untreated active RA (n=28) compared to the HC (n=30, p<0.0001) and pSS (n=30, p<0.0001) groups. IL-16 was a positively and most correlated cytokine with serum MMP-3 (R=0.70, P=3.5E-05) in pts with untreated RA, but only weakly and negatively correlated with MMP-3 in pts with pSS (R=-0.31, p=0.095). IL-16 was significantly decreased during treatment for RA for 12 weeks in all 86 RA pts (Figure). On stratification, IL-16 was decreased in the MTX- (n=31), TCZ- (n=17) and ABT-treated (n=16) groups, but did not change in the IFX-treated group (n=22). Regarding clinical disease activity, the decrease in IL-16 was positively associated with DAS28-CRP in the MTX (R=0.48, p=0.007), ABT (R=0.60, p=0.01), TCZ (R=0.52, p=0.06) groups. Furthermore, the decrease in IL-16 was positively correlated with a decrease in serum CRP in the MTX (R=0.48, p=0.007) and ABT (R=0.54, p=0.03) groups, which indicates a stronger association with CRP in the composite measure, except for the TCZ group. MMP-3 in the MTX, IFX and TCZ groups was also significantly decreased at 12 weeks. In contrast, the decrease in IL-16 with treatment was not correlated with that of MMP-3, unlike the case with untreated RA at baseline.
Conclusion: Treatment with MTX, TCZ and ABT for active RA ameliorated the dysregulation of serum IL-16. This correction was correlated with decreases of clinical disease activity and CRP, except for TCZ, but not correlated with MMP-3. The directional change in serum IL-16 with different interventions, especially with TCZ, may indicate the need to revise molecular abnormalities in RA.
Disclosure:
A. Murota,
None;
K. Suzuki,
None;
Y. Kassai,
Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited,
3;
T. Miyazaki,
Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited,
3;
R. Morita,
None;
A. Yoshimura,
None;
T. Takeuchi,
Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma, Bristol–Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Pfizer Japan Inc., Sanofi–Aventis K.K., Santen Pharmaceutica,
2,
Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Bristol–Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co,. Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Pfizer Japan Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma, Diaichi Sankyo Co.,Ltd.,
8,
Astra Zeneca K.K., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Novartis Pharma K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Asahi Kasei Medical K.K., Abbivie GK, Daiichi Sankyo Co.,Ltd.,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dysregulated-serum-interleukin-16-concentration-associated-with-clinical-disease-activity-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-efficiently-corrected-by-immunological-intervention/