Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In general, drug
retention rate reflects the effectiveness and tolerability of the drug. TNF inhibitors
include fusion protein agent such as etanercept (ETN) and antibody agent such
as adalimumab(ADA),golimumab(GLM). There is few data comparing the retention rates between
these biological therapies without concomitant methotrexate(MTX) for RA
patients in daily clinical practice. The purpose of this study is to compare
the drug retention rates of biological therapies with different TNF inhibitors
that include fusion protein agent and antibody agent without MTX.
Methods: We collected the data
from the patients who started ETN, ADA, GLM as first-biologics without MTX
since 2008 and registered in the multicenter, large cohort of RA patients
(Tsurumai Biologics Communication Registry; TBCR). We devided patients into two
groups including ETN group and antibody group(ADA,GLM).We surveyed the
following information: demographic data, disease activity (DAS28-CRP) at the
baseline of each biological treatment. Drug retention rates were
calculated by the Kaplan-Meier analysis and compared using the log-rank test
among two groups.
We
investigated drug retention rates for discontinuation due to insufficient effectiveness
and adverse events.
Results: We analyzed 356 patients
of 2324 patients registered in TBCR until March 2013 (244 patients in the
ETN group, 112 patients in the antibody group including, 78 patients with ADA,34
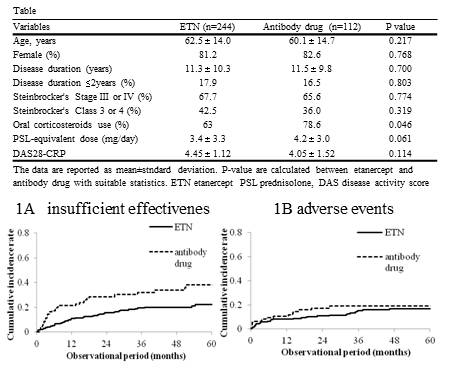
patients with GLM). The mean follow up time was 34.7 months. Table shows
baseline characteristics of the groups (Table). Cumulative incidence rate for discontinuation due to
insufficient effectiveness
was significantly lower in the ETN group (p=0.0017, Fig.1A). There was no
significant difference in cumulative incidence rate for discontinuation due to
adverse events
(p=0.342, Fig.1B).
Conclusion: We demonstrated that ETN
therapy without concomitant MTX had a lower discontinuation rate due to insufficient
efficacy compared with antibody agent without concomitant MTX.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Matsubara H, Hayashi M, Takahashi N, Kojima T, Funahashi K, Ishiguro N. Drug Retention Rates of Biologic Monotherapies for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving TNF Inhibiting Fusion Protein Agent and Antibody Agent; From Multicenter Registry in Japan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-rates-of-biologic-monotherapies-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-tnf-inhibiting-fusion-protein-agent-and-antibody-agent-from-multicenter-registry-in-japan/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-rates-of-biologic-monotherapies-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-tnf-inhibiting-fusion-protein-agent-and-antibody-agent-from-multicenter-registry-in-japan/