Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease – Clinical Aspects and Pathogenesis - Poster
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: As rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a well-established risk factor for osteoporosis and compression fracture, non-adherence to bisphosphonate (BP) therapy in patients with RA can adversely affect clinical outcome. Our study aimed to investigate the drug retention rate of oral BP and analyze the associated factor for this rate in RA patients under routine care.
Methods: In this retrospective longitudinal study, 410 RA patients in whom the first oral BP such as ibandronate (150 mg/month), risedronate (35 mg/week) and alendronate (70 mg/week) initiated from April 2003 to September 2015 at a university-affiliated rheumatology center in South Korea were included. Seropositve RA was defined as having for a positive test result for presence of either rheumatoid factor or anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody. The drug retention rate was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the predictors of this rate were identified by Cox-regression analyses.
Results: The mean age was 65.9 ¡¾ 11.3 years and 399 (96.6%) and 332 (81%) patients were female and seropositive RA, respectively. During the study period, 283 (69%) patient discontinued oral BP. The cause of BP discontinuation was as follows: treatment failure, 35.7%; adverse events, 6.4%; patients¡¯ decision, 43.1%; drug holidays, 2.8%; cost, 12%. The 2-year drug continuation rate was 65.8, 40 and 42.1% and the median retention was 39.2, 13.1 and 18.8 months for ibandronate, risedronate and alendronate, respectively. The drug retention rate significantly differed among the 3 oral BP (p<0.001, Fig. 1). In multivariable Cox regression models, risedronate demonstrated a worse retention rate than ibandronate (HR=2.34, 95% CI=1.79-3.06, p<0.001, Table 1). Additionally, seropositve RA patients showed a better BP retention rate than those without this feature (HR=0.59, 95% CI=0.42-0.84, p=0.004).
Conclusion: Persistence of BP treatments was suboptimal in RA patients under routine care. Monthly ibandronate showed better retention rate than weekly risedronate, suggesting that a longer dosing interval may improve the adherence of BP treatment in RA patients. 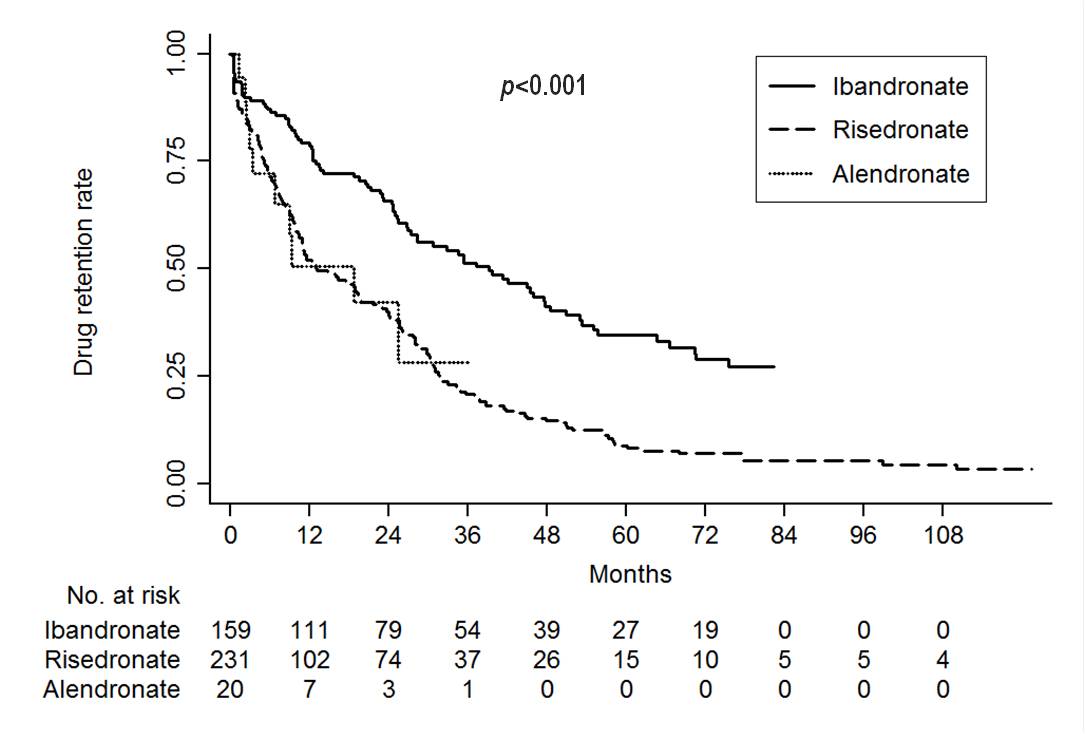
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier survival curve of oral bisphosphonate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Table 1. Cox-proportional hazard regression analyses with backward model selection for tacrolimus discontinuation according to causes.
| Variables |
Univariable |
|
Multivariable |
||
|
HR (95% CI) |
p |
|
aHR (95% CI) |
p |
|
| Age, years | 0.99 (0.98-1.01) | 0.58 | – | – | |
| Male | 1.34 (0.67-2.61) | 0.39 | – | – | |
| Glucocorticoids use | 1.06 (0.72-1.55) | 0.755 | |||
| Previous compression fracture | 1.43 (0.97-2.1) | 0.07 | – | – | |
| Seropositive RA | 0.66 (0.48-0.92) | 0.014 | 0.59 (0.42-0.84) | 0.004 | |
| Disease duration > 24 months | 0.68 (0.53-0.87) | 0.002 | – | – | |
| BP | 1.08 (0.41-2.87) | 0.87 | |||
| Ibandronate | ref. | ||||
| Risedronate | 2.23 (1.72-2.88) | <0.001 | 2.34 (1.79-3.06) | <0.001 | |
| Alendronate | 2.22 (0.14-4.3) | 0.018 | 1.66 (0.76-3.62) | 0.205 | |
a Estimated using multivariable Cox regression model with backward selection including age, gender, previous compression fracture, seropositive RA, disease duration and the type of BP
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Park JH, Lee SG, Park EK, Tag HS, Kim GT. Drug Retention Rate of Oral Bisphosphonate in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-rate-of-oral-bisphosphonate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-rate-of-oral-bisphosphonate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/
