Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: While the associations of baseline characteristics with drug effectiveness have often been studied in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), little is known about how the evolution of disease characteristics influences drug retention, a measure integrating both drug’s effectiveness and tolerance. Aim: To examine the association of time-varying disease characteristics with drug retention of abatacept (ABA).
Methods: This is a pooled analysis of nine RA registries (ARTIS, ATTRA, RHEUMA DATA, DANBIO, GISEA, NOR-DMARD, ORA, SCQM, Reuma.pt). Inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of RA, initiation of ABA treatment and information on date of visit. Each time-varying variable was divided into baseline assessments and changes from baseline at subsequent visits. The baseline values capture the inter-individual differences at drug initiation, while the changes over time inform on the intra-individual differences. We used time-varying Cox regression models to examine the association of baseline and time-varying characteristics with drug discontinuation, adjusting for age, sex, seropositivity, disease duration, number of previous conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD), and biologics (bDMARDs), presence of a comorbidity, calendar year of drug initiation, and stratifying by registry.
Results: 5440 patients initiated ABA, contributing 9715.4 patient-years, and 2920 stopped ABA during follow-up. Patients had a mean age of 57.8 years (SD: 13.1), mean RA duration at ABA initiation of 12.5 years (SD: 10.0), and most patients had failed several previous DMARDs (median csDMARD: 2, median bDMARDs: 1).
Median time to ABA discontinuation was 1.40 years. Seropositivity was associated with a lower chance of discontinuing ABA (Table). Previous failure of bDMARDs was associated with ABA discontinuation, whereas there was no such association for previous csDMARDs failure.
For most time-varying characteristics, the change over time (intraindividual evolution) was a stronger predictor of discontinuation than the baseline values (interindividual differences). Overall, ABA discontinuation was most strongly associated with a poor evolution of physician global assessment (HR: 1.62, 95% CI: 1.52-1.72). It was further independently associated with an inadequate progression of DAS28 and patient global assessments. In contrast, only the changes in physician global and patient global assessments were associated with discontinuing ABA for AEs.
Conclusion: The decision to discontinue ABA appears to be mostly influenced by the physician judgment and in particular its evolution over time. The evolution of the patient’s appraisal and disease activity over time also play a role above and beyond the impact of the physician’s assessment. Table: Multivariable Cox models of discontinuing ABA treatment due to any reason, to ineffectiveness and to adverse event. 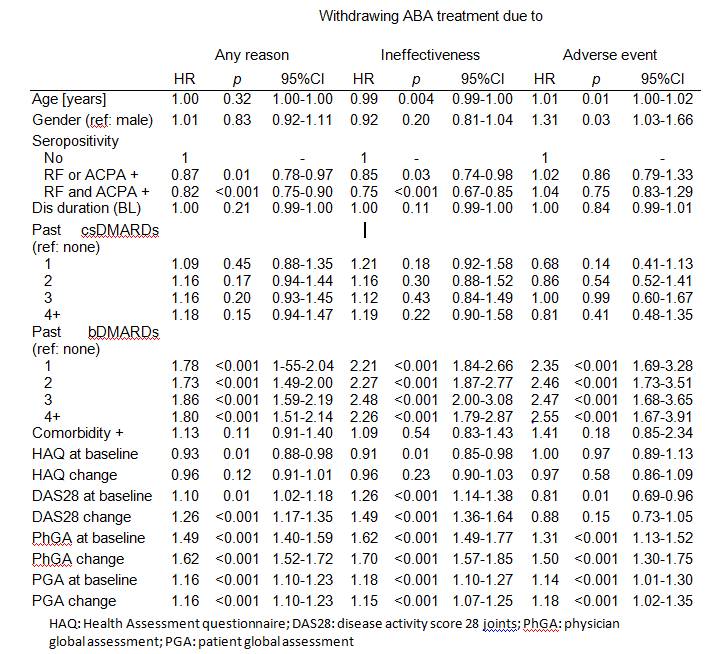
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Courvoisier D, Alpizar Rodriguez D, Gottenberg JE, Iannone F, Lie E, Santos MJ, Pavelka K, Lund Hetland M, Turesson C, Mariette X, Choquette D, Finckh A. Drug Retention of Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: The Role of Baseline Characteristics and Impact of Time-Varying Factors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-of-biologics-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-the-role-of-baseline-characteristics-and-impact-of-time-varying-factors/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-of-biologics-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-the-role-of-baseline-characteristics-and-impact-of-time-varying-factors/
