Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Numerous studies
have modeled whether biologic drugs are good value for money in the treatment
of RA, in terms of reducing health care use and work loss to a higher extent
than when using alternative therapeutic options. However, whereas several
studies have estimated costs in RA and in relation to therapies, few studies
have investigated cost trajectories in relation to the clinical response to
such therapies. The aim of this study was therefore to estimate the societal monthly costs related to work loss, health care use,
and prescription drug use over 2 years in relation to the level of disease
activity control achieved after start of biologic therapy.
Methods:
RA patients ≥18y with a treatment period of ≥3 months with a
first ever biologic drug between 2006 through 2010 were identified from the
Swedish Rheumatology Quality Register (including the Swedish Biologics Register
ARTIS). Based on start DAS28 and the lowest registered DAS28 during visits 3 to
12 months after biologic start, patients were categorized as EULAR good,
moderate and no responders.
Data on work loss, health care use, drug use, and mortality
were retrieved from nationwide registers. Patients were followed from 12 months
before the DAS28 evaluation until first of 24 months of follow-up, death,
emigration, or Dec 31, 2012. As a general population benchmark we used five
sex-, age-, and county-matched comparators per RA patient.
Results:
A total of 3788 patients with RA who started their
first biologic therapy in 2006 through 2010 were identified (mean age, 56.7y;
75% women; mean disease duration, 10.2y). Of these, 1950 (51%) patients achieved
and were categorized as EULAR good response (55.1y; 72%; 10.0y), 1208 (32%) achieved
moderate response (59.0y; 79%; 10.6y), and 630 (17%) patients never reached any
EULAR response (57.2y; 77%; 10.1y).
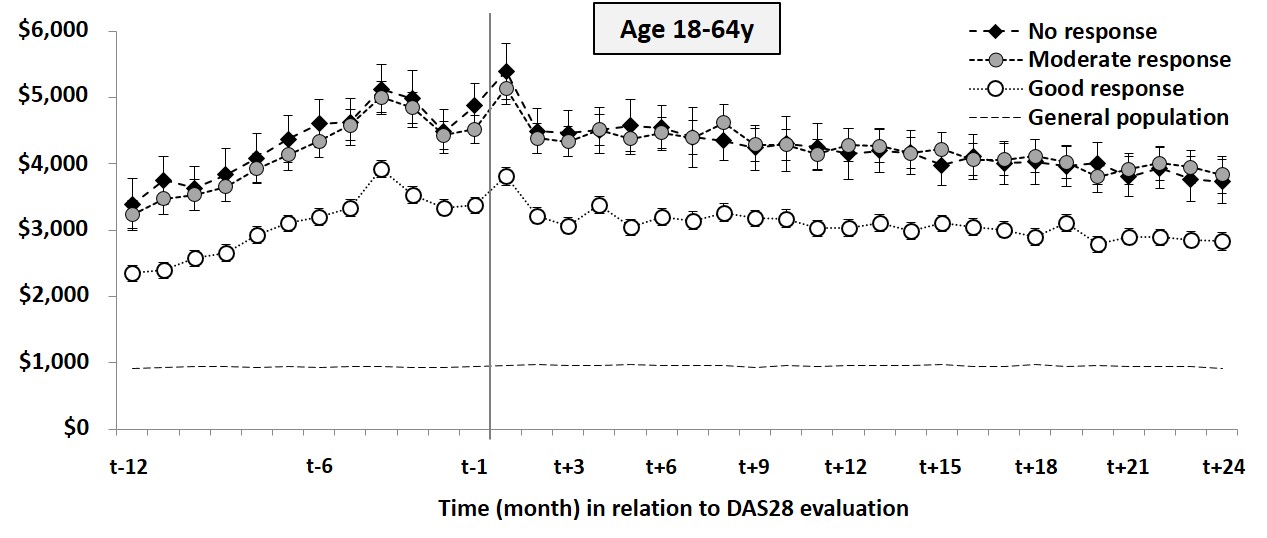
The mean monthly cost
at 24 months after DAS28 evaluation was lower
in working age patients with good response (n=1249) compared to patients with
moderate or no response (n=1052;
$2837 vs $3799; adjusted
mean difference [95% CI], -$242 [-503; -$15]; Figure). The lower monthly cost in
patients with good response was mainly driven by reduced work loss costs.
In patients
≥65y, the mean monthly health care cost was similar across the response
groups.
Conclusion:
Working age RA patients who achieve a good level of
disease control during the year after start of biologic therapy have lower
monthly costs as compared to patients with moderate or no response. However,
the monthly cost in those who achieved good disease control was still around 3
times higher compared to the general population 2 years after biologic therapy
initiation.
Figure Trajectories of costs for hospital care,
drugs and lost work days, stratified by EULAR good, moderate and no response in
working age patients with RA and their matched general population comparators
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eriksson JK, Neovius M, Askling J. Does the Level of Disease Control Achieved with Biologics Influence Overall Costs for Health Care and Work Loss in RA? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-the-level-of-disease-control-achieved-with-biologics-influence-overall-costs-for-health-care-and-work-loss-in-ra/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-the-level-of-disease-control-achieved-with-biologics-influence-overall-costs-for-health-care-and-work-loss-in-ra/