Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I: Diagnosis and Testing
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In order to follow subclinical inflammation and adjust the therapy for an optimal disease control, clinicians seek for readily accessible, affordable and reproducible markers. C reactive protein (CRP) is widely used for this purpose. Some suggest that CRP measures are not conclusive in all cases, especially in initial stages of inflammation. It is suggested that Serum Amyloid A (SAA) may be more reliable and sensitive in predicting an ongoing inflammation.
Methods: In order to evaluate and to compare the sensitivity of SAA and CRP, 153 measurements from 28 patients M694V homozygous mutation and 31 measurements from 15 patients with M694V heterozygous mutation were obtained during a mean follow-up of 1 year. For the analysis, the folds of normal CRP and SAA values were used for correlation. Serum levels of the given markers were measured with nephelometric kits (normal CRP levels < 5 mg/L and SAA levels < 6,8 mg/L). More than one and half fold increasement of CRP and SAA was defined as an active inflammation.
Results: Except a patient, all patients in whole cohort were on prophylactic colchicine. Among 28 patients with M694V homozygous mutation, a patient with adalimumab, 12 patients with anti-IL-1 regimens. Of 15 patients with M694V heterozygous mutation, 4 were under anti-IL-1 treatment. There was a total of 183 measurements of CRP and SAA from 43 patients. Twenty-three measurements were obtained during the attack period in M694V homozygous group and the remaining 160 measurements were collected in attack free period. Figure demonstrates the correlation between CRP and SAA results (r=0.745, p< 0.001). Both acute phase reactants were increased in 69 measurements, while in 13 CRP was high but SAA was normal and in 31 SAA was high however CRP was within normal limits. The mean increase in CRP of the whole cohort was 2,37 ± 3,22-fold, whereas mean increase in SAA was 6,77 ± 13,23-fold of the normal.
Conclusion: According to these results, serial testing of SAA does not provide any additional advantages over CRP. Readily accessible and affordable bio-marker CRP seems to be sufficient for follow-up of patients with FMF
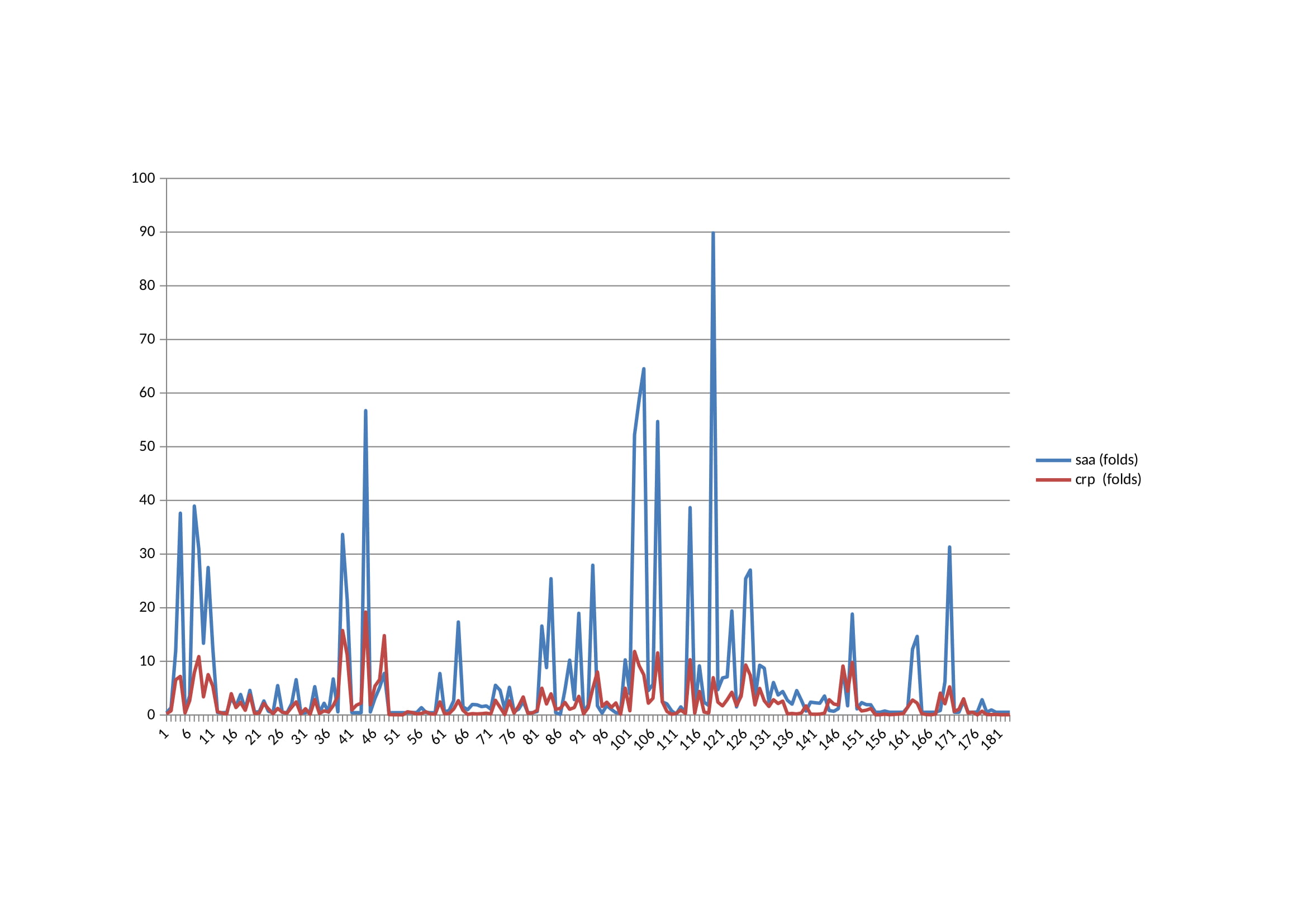 The folds of the CRP and SAA in whole M694V homozygous and heterozygous mutant population
The folds of the CRP and SAA in whole M694V homozygous and heterozygous mutant population
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oztas M, Ugurlu S, Selvi O, Ergezen B, Ozdogan H. Does Testing for SAA Is More Beneficial Than CRP for the Follow-up of Patients with FMF? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-testing-for-saa-is-more-beneficial-than-crp-for-the-follow-up-of-patients-with-fmf/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-testing-for-saa-is-more-beneficial-than-crp-for-the-follow-up-of-patients-with-fmf/
