Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Recent studies evaluated the prevalence of Fibromyalgia (FM) in Spondyloarthritis (SpA) and its impact on disease activity scores, but none meta-analysis exists yet. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of fibromyalgia on activity scores in SpA.
Methods: We performed a systematic review of the literature until May 2019 using database including: MEDLINE (via PUBMED), EMBASE and abstracts from the ACR and EULAR congresses 2016-2019. We selected observational studies comparing characteristics of SpA patients (defined by ASAS, NY modified or CASPAR criteria) with or without fibromyalgia (defined by ACR 1990, 2011 fibromyalgia criteria or FiRST survey).
Two readers extracted the prevalence of FM in SpA, female ratio, HLAB27 status, disease duration, radiographic sacroiliitis, C-reactive protein (CRP), BASDAI, BASFI, ASDAS-CRP and Quality of Life (QoL).
Statistical analysis determined in each study theeffect size. Data was analyzed using the inverse variance approach.
Results: The literature search identified 433 articles. Finally, 15 studies met the inclusion criteria.
The prevalence of FM in SpA was 17% IC95% [0.12, 0.23] with a significant female ratio of 5.13 IC95%[3.02, 8.70]in SpA with FM.
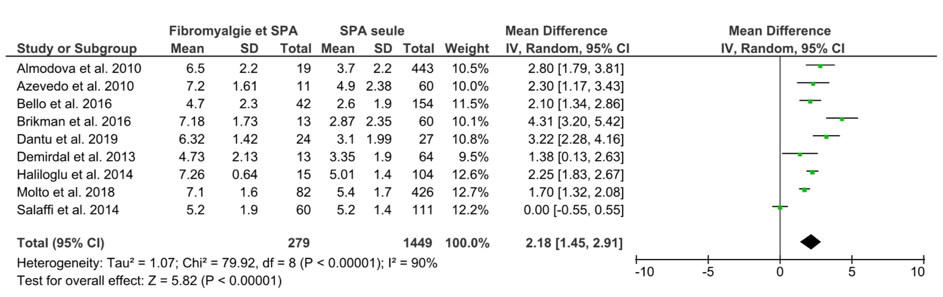
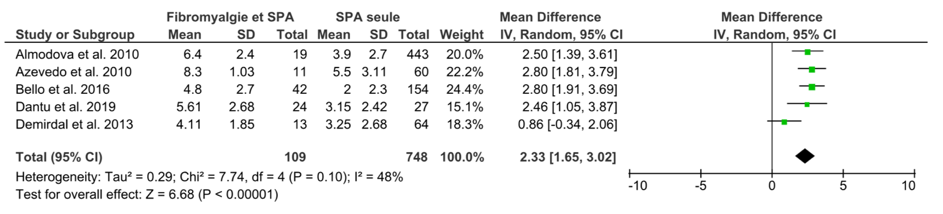
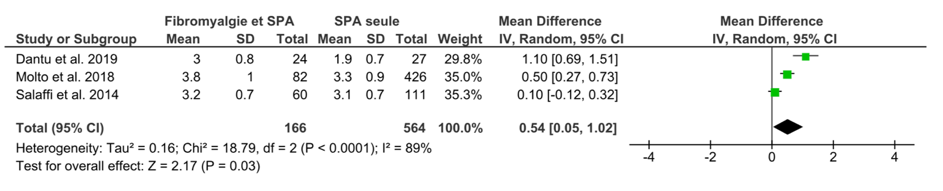
FM impacted significantly all the activity scores of SpA: BASDAI: OR= 2.18 IC95%[1.45, 2.91]; BASFI: OR= 2.33 IC95%[1.65, 3.02]; ASDAS-CRP: OR= 0.54 IC95%[0.05, 1.02]; AsQoL: OR=5.50 IC95%[4.28, 6.71]
No statistical difference was found concerning HLAB27 status, disease duration and CRP level.
Conclusion: In this meta-analysis, the prevalence of FM in SpA was 17%, whereas 2-8% in general population. The coexistence of FM with SpA led to higher activity scores, including ASDAS-CRP, although CRP trends to be lower in the FM group.
Rheumatologist have to be aware of the association of FM and SpA, activity scores may be biased.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Beck A, SOLE L, Barnetche T, Vergne-Salle P. Does Fibromyalgia Change the Evaluation of Spondyloarthritis Activity? A Meta-analysis of Observational Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-fibromyalgia-change-the-evaluation-of-spondyloarthritis-activity-a-meta-analysis-of-observational-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-fibromyalgia-change-the-evaluation-of-spondyloarthritis-activity-a-meta-analysis-of-observational-studies/