Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: RA patients are at about 50% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD)1. Despite this risk, numerous studies show inadequate cardiovascular risk assessment of these patients. Preventive cardiology focuses on reducing CVD risk factors through a multidimensional approach that uses nutrition, exercise, and pharmacologic intervention. This study assesses referral rates of RA patients seen in outpatient rheumatology clinic and referred to the preventive cardiology department through the use of an electronic health record (EHR) based best practice alert (BPA).
Methods: This retrospective cohort study compares referral rates to preventive cardiology with and without a BPA for RA patients with visits to rheumatology clinics on main and satellite campuses in a tertiary care system. The main campus uses a BPA that is triggered at least once a year for patients with a diagnosis code of RA, while the satellite campuses did not institute a BPA (usual care) for RA patients. Only patients with referral eligible visits (no referral in past 12 months) were included each year for analysis. Patients with a CVD diagnosis were excluded. The referral rate from when the BPA was implemented in 2009 to 2016 was determined for each year as the number of patients with referral divided by the number of patients with at least one referral eligible visit. A Poisson regression was conducted to examine the number of preventive cardiology referrals performed by campus locations with and without the BPA as a function of year.
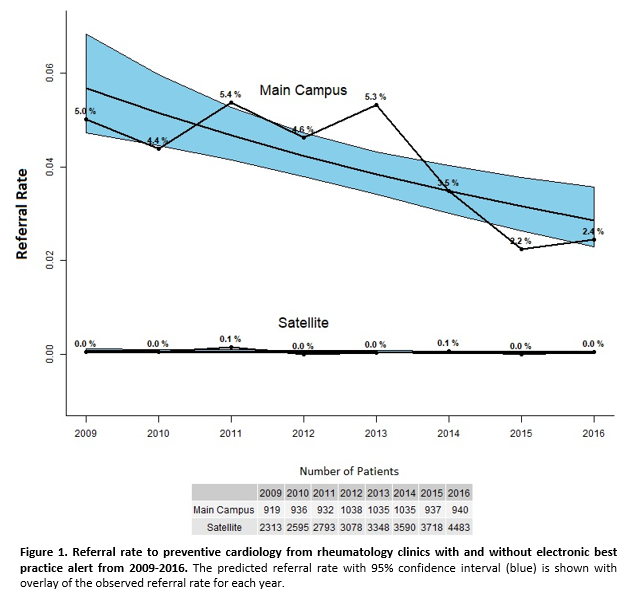
Results: Overall, 12,916 RA patients (age: 55.3 (SD=15.0); 77.2% female) were seen across 90,810 clinical visits from 2009-2016. There were 2,714 (21%) main campus patients and 10,202 (79%) satellite patients. The difference in referral rates between the main campus (with BPA) and satellite group (without BPA) was statistically significant (p<0.0001). The main campus rate ranged from 2.2% to 5.4% with an average of 4.1% (Figure 1). The satellite referral rate ranged from 0% to 0.1% (Figure 1).
Conclusion: The EHR-based BPA was modestly effective in improving referral rates for RA patients to preventive cardiology compared to usual care. A multimodality approach is needed to further improve CVD risk factor management for RA patients. Future interventions such as laboratory focused BPAs assessing lipid profiles, interdisciplinary clinics between rheumatology and cardiology, and increased education targeted to physicians and patients to promote CVD risk management in RA should be explored.
References
Avina-Zubieta JA, Thomas J, Sadatsafavi M, Lehman AJ, Lacaille D. Risk of incident cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(9):1524-1529. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200726.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smoker S, Romich E, Nowacki A, Husni ME. Does a Best Practice Alert Improve RA Patient Referral to Preventative Cardiology? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-a-best-practice-alert-improve-ra-patient-referral-to-preventative-cardiology/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-a-best-practice-alert-improve-ra-patient-referral-to-preventative-cardiology/