Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: 5T106 ACR Abstract: Measures of Healthcare Quality I: QI in RA (2856–2861)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients have around 50% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Both traditional and RA-specific cardiovascular (CV) risk factors contribute to the excess risk. Although RA is an independent risk factor for CVD, management of traditional CV risk factors is inadequate in this population. In order to improve risk factor management, we implemented a best practice alert (BPA) in the electronic health record (EHR) to prompt referral to preventive cardiology. We then investigated the impact of preventive cardiology on CV risk factor assessment and management in RA patients compared to usual care.
Methods: This retrospective cohort included adult RA subjects without CVD who were seen by a board-certified rheumatologist from 2009-2015 and exposed to the BPA, which prompted referral to preventive cardiology. The date that the BPA triggered was the baseline date. The main analysis included intervention subjects (referred and attended cardiology) and primary control subjects (referred but did not attend). A secondary analysis combined additional control subjects (not referred at all) with the primary control group. The primary outcome was CV risk factor assessment, defined as 4 of 5 traditional risk factors measured within one year. The secondary outcome was risk factor management, including starting or adjusting cardiac medications and providing lifestyle management counseling.
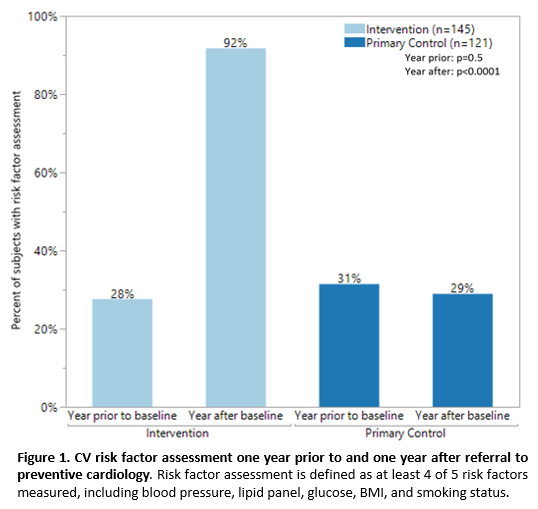
Results: 1,979 RA subjects (mean ± standard deviation age: 56 ± 14 years, 80% female, 74% white) were included. Overall, 266 (13%) subjects were referred to preventive cardiology; 145 (55%) subjects attended at least one preventive cardiology appointment (intervention), and 121 (45%) subjects were referred but did not attend (primary control). The remaining 1,713 subjects (not referred at all) were included in the combined control group (n=1834). One-third of subjects had risk factor assessment in the year prior to baseline. In the year after baseline, risk factor assessment occurred in 133 (92%) intervention vs. 35 (29%) primary control subjects (p<0.0001; Figure 1). The intervention group had higher frequency of lipid-lowering medication management (intervention 36% vs. primary control 12%, p<0.0001) and lifestyle management counseling (intervention 46% vs. 3% primary control, p<0.0001). Additionally, the intervention group experienced significant decreases in total cholesterol (-14.6 ± 32.2 mg/dl, p=0.03) and low-density lipoprotein (-13.8 ± 23.8 mg/dl, p=0.002) at one year. Results were similar using the combined control group.
Conclusion: RA patients who attended preventive cardiology visits prompted by an EMR-based technology had increased CV risk factor assessment, pharmacologic and lifestyle management, and improved lipid profiles compared to usual care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Romich E, Ahmed H, Nowacki A, Husni ME. Do Preventive Cardiology Consults Versus Usual Care Improve Cardiovascular Risk Factor Assessment and Management in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/do-preventive-cardiology-consults-versus-usual-care-improve-cardiovascular-risk-factor-assessment-and-management-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/do-preventive-cardiology-consults-versus-usual-care-improve-cardiovascular-risk-factor-assessment-and-management-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/