Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1412–1441) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II: SpA
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: PsA is a heterogeneous disease, and identifying clinical phenotypes may assist clinical decision making. Patients (pts) treated with advanced therapies demonstrate varying treatment responses. Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of PsA. In this post hoc analysis, we aimed to capture these variations by identifying pt groups with distinct disease activity trajectories; comparisons of associated baseline (BL) variables across groups were used to describe clinical phenotypes in pts with PsA treated with tofacitinib.
Methods: Data were pooled from two Phase 3 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in pts with PsA who were conventional synthetic DMARD-inadequate responders (IR)/TNF inhibitor (TNFi)-naïve (OPAL Broaden; 12 months (M); NCT01877668) or TNFi‑IR (OPAL Beyond; 6M; NCT01882439); pts randomized to tofacitinib 5/10 mg twice daily (BID) were included and analyzed separately. PsA Disease Activity Score (PASDAS) to M6 was used in group-based trajectory modeling (a special case of finite mixture modeling) to identify distinct trajectory groups for each tofacitinib dose. Groups were compared by BL characteristics using t‑tests (2‑sided) or chi-squared tests, applying a Bonferroni correction for pairwise comparisons for each variable. Safety to M6 across groups was assessed descriptively.
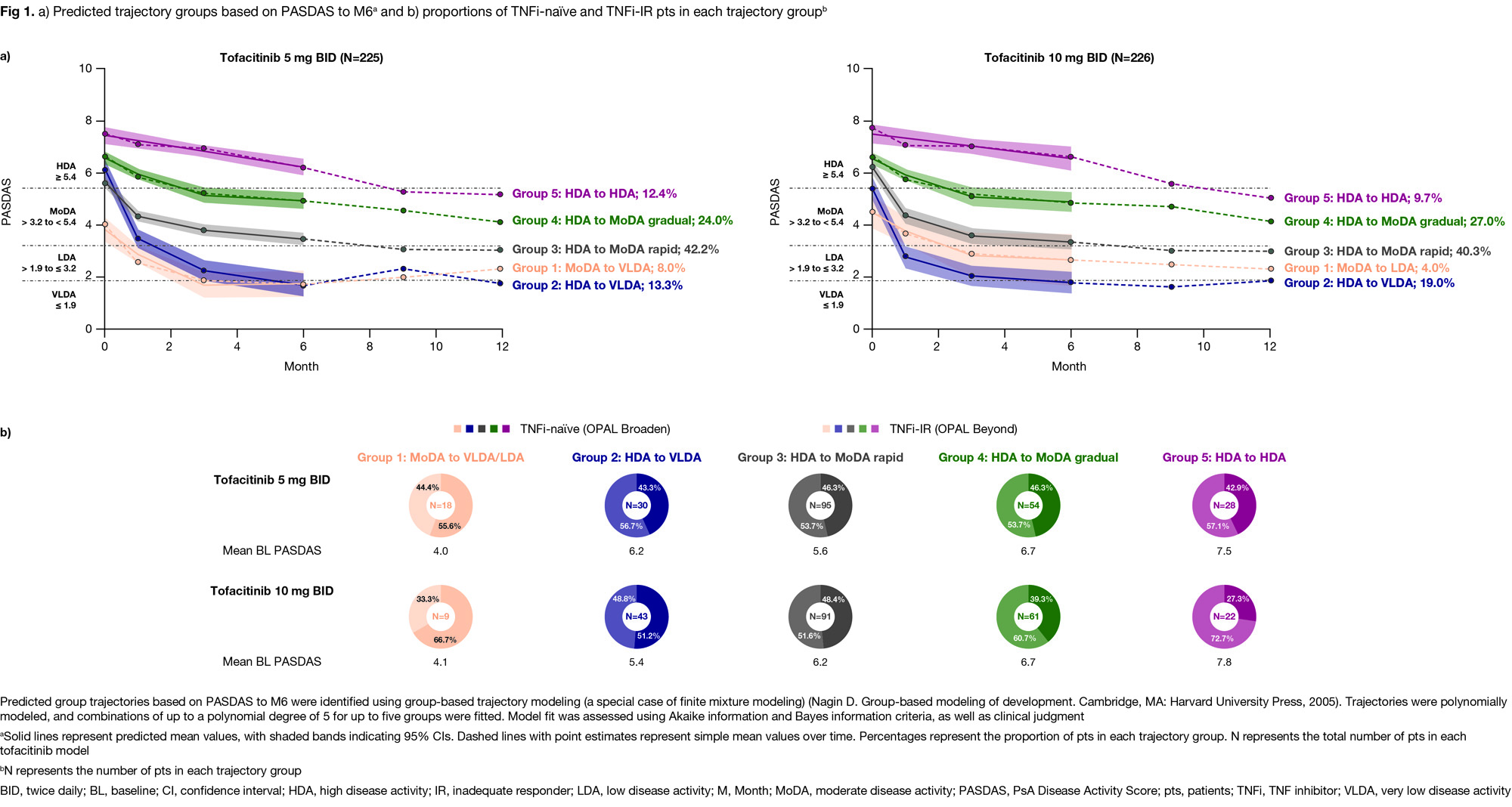
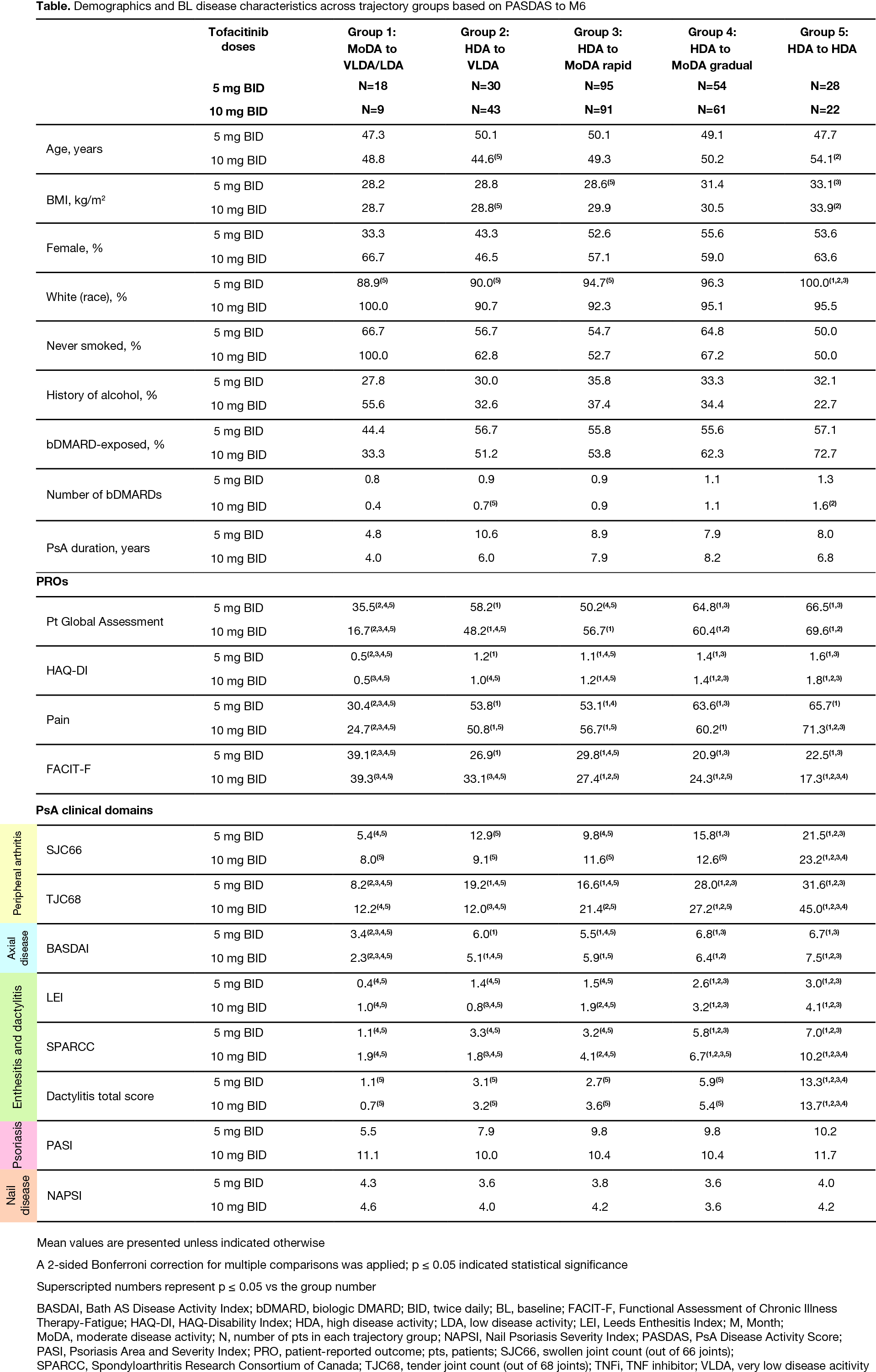
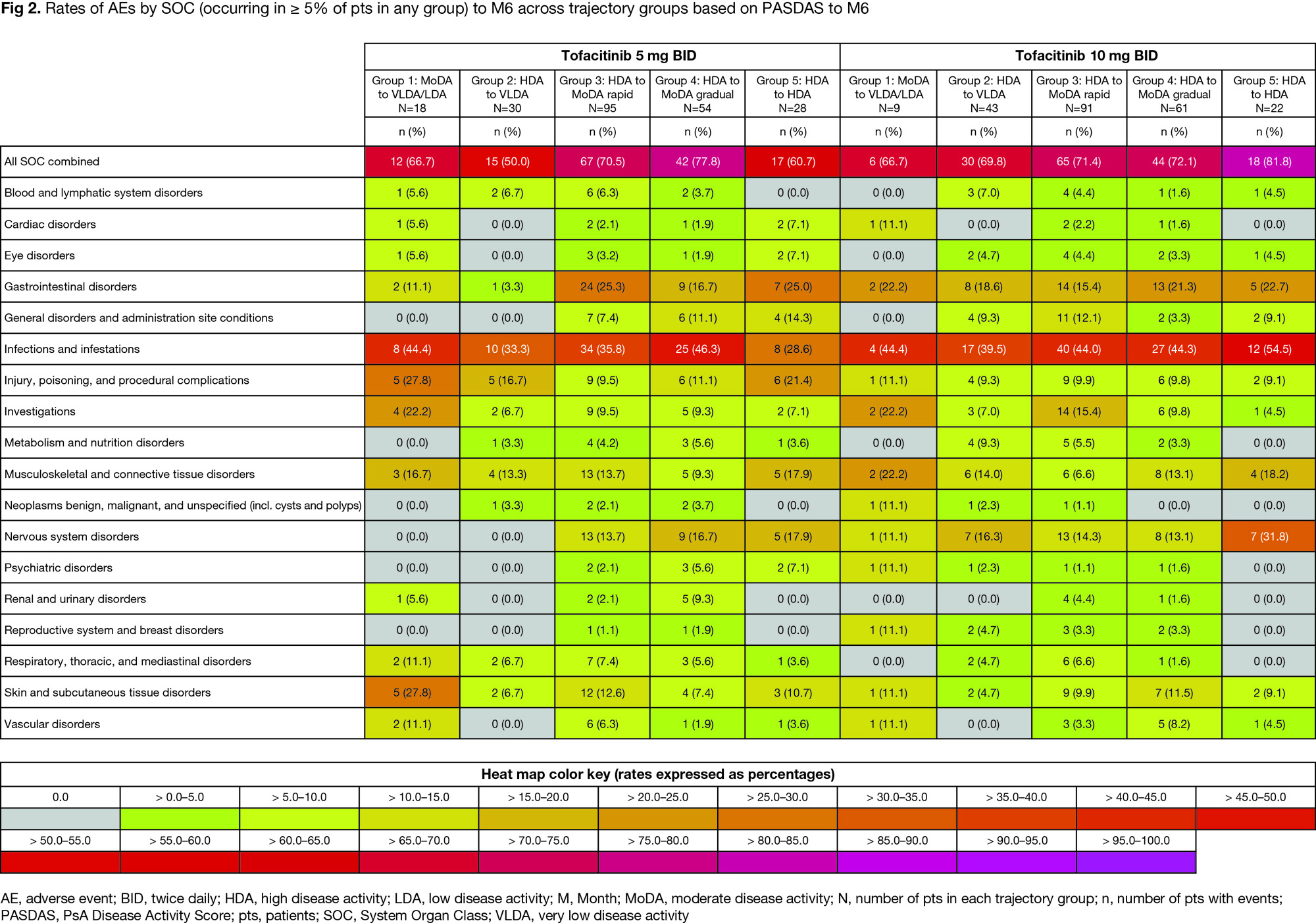
Results: From 225/226 pts with PsA who received tofacitinib 5/10 mg BID, respectively, five disease trajectory groups were identified by PASDAS from BL to M6 for each dose separately; resulting models for either dose were of similar shape with the same polynomial degree and clinical interpretation. Groups progressed from moderate disease activity (MoDA) to very low disease activity (VLDA)/LDA (Group 1), high disease activity (HDA) to VLDA (Group 2), HDA to MoDA rapidly/gradually (Groups 3/4), or remained in HDA (Group 5; Fig 1a). In the tofacitinib 10 mg BID model, proportions of TNFi-naïve and TNFi‑IR pts were numerically higher in Groups 1 and 4/5, respectively, vs other groups (Fig 1b). Groups 4/5 vs 1/2/3 had generally significantly higher BL PsA clinical domain scores, but no significant differences in psoriasis/nail disease scores were seen across groups (Table). In Groups 4 vs 2, which had HDA at BL but distinct responses to M6, significant BL characteristic differences included higher enthesitis scores and tender joint counts (TJC; Table). Across groups, adverse event (AE) rates were generally comparable; most common AEs were infections/infestations (Fig 2).
Conclusion: In pts with PsA treated with tofacitinib, PASDAS response analysis by group-based trajectory modeling identified distinct clinical phenotypes at BL. As expected, higher BL disease burden was associated with poorer responses and differences in BL enthesitis and TJC may impact response to tofacitinib; phenotypes affecting treatment responses were consistent across doses. Trajectory groups showed comparable safety. Limitations included small pt numbers and restricted extrapolation of used RCT data to routine care. Identification of clinical phenotypes may be used to develop personalized treatment algorithms.
Study sponsored by Pfizer. Medical writing support provided by J Juana, CMC Connect; funded by Pfizer.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gladman D, Tillett W, Gruben D, Coates L, Hahne S, Volkov M. Distinct Treatment Response Trajectories in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Receiving Tofacitinib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/distinct-treatment-response-trajectories-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-receiving-tofacitinib/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/distinct-treatment-response-trajectories-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-receiving-tofacitinib/