Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Disease and Treatment Characteristics that Might
Influence Long-term Retention with Biologics in the Real-world Clinical
Setting: Experience from the Rhumadata Clinical Database and Registry
Background/Purpose: Patient adherence and
sustainability of the regimen plays an important role in the long term
outcomes. Biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) have
revolutionized the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), yet drug
discontinuation is common. We aim to investigate factors that might influence long-term
retention with biologics in a population-based of real-life unselected RA
cohort.
Methods: RA patients (pts) treated with abatacept
(ABA) or an anti-TNF inhibitor, adalimumab (ADA), etanercept (ETA), or
infliximab (INF) were grouped according to their experience with biologics. Patient
characteristics were compared using ANOVA with Bonferroni correction.
Kaplan-Meier methods were used to compute the cumulative incidence of drug discontinuation.
Results: The first cohort included 403 pts receiving
1st line biologic (62 ABA, 111 ADA, 195 ETA, 35 INF) and the second
cohort included 189 pts on their 2nd biologic (76 ABA, 47 ADA, 47
ETA, 19 INF). 11.9% of pts in the first (14.5% ABA, 8.1% ADA, 14.4% ETA, 5.7%
INF) and 25.9% of pts (26.3% ABA, 27.7% ADA, 29.8% ETA, 10.5% INF) in the
second cohort were on biologic monotherapy. Approximately 66% (66.7% first;
66.1% second cohort) of pts were rheumatoid factor (RF) positive. Anti-cyclic
citrullinated peptide antibodies (anti-CCP) were detected in 62.0% and 55.4% of
pts in the first and second cohort, respectively. Neither the RF status nor
the use of biologics as monotherapy vs in combination with non-bDMARDs had a
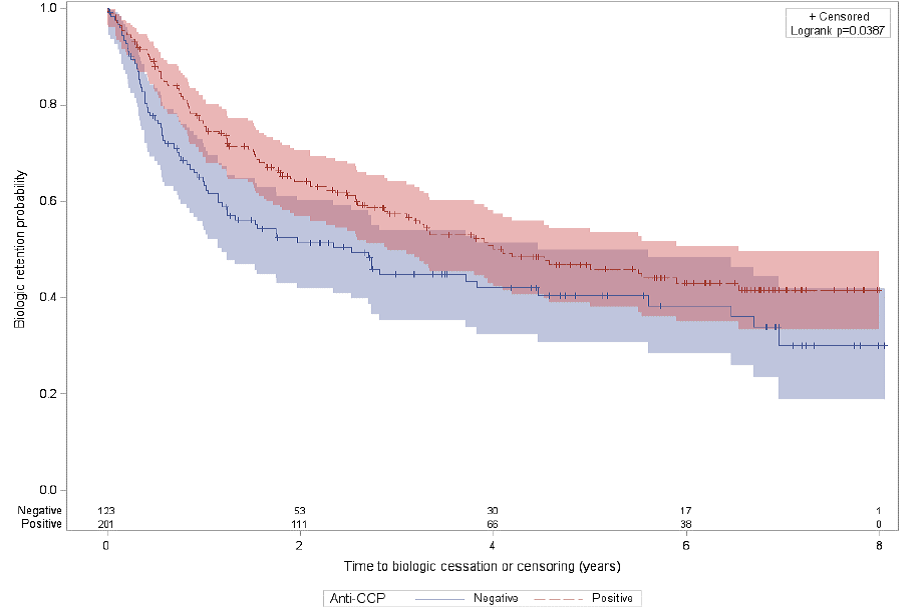
significant impact on long term retention. However, retention probability was
significantly higher in the first cohort in anti-CCP positive vs negative
patients, Figure 1. The anti-CCP positivity did not affect retention in the
second cohort. In the second cohort treatment with ABA was associated with
significantly higher retention compared to anti-TNFs, Figure 2.
Conclusion: The anti-CCP positivity was associated
with significantly higher retention when biologics were used first line. This
is important as anti-CCP antibodies are predictors of an aggressive disease. These
results are compatible with other registries that indicate that anti-CCP might
have an impact on retention rates. There were no significant differences in the
retention rates in the first cohort. In the second cohort treatment with ABA
was associated with significantly higher retention compared to anti-TNFs.
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Choquette D, Bessette L, Haraoui B, Raynauld JP, Sauvageau D, Turcotte A, Villeneuve , Coupal L. Disease and Treatment Characteristics That Might Influence Long-Term Retention with Biologics in the Real-World Clinical Setting: Experience from the Rhumadata Clinical Database and Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-and-treatment-characteristics-that-might-influence-long-term-retention-with-biologics-in-the-real-world-clinical-setting-experience-from-the-rhumadata-clinical-database-and-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-and-treatment-characteristics-that-might-influence-long-term-retention-with-biologics-in-the-real-world-clinical-setting-experience-from-the-rhumadata-clinical-database-and-registry/