Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Dose escalation is a common strategy for patients (pts) on infliximab (IFX). This study examined the trend in disease activity across dose escalations to determine if dose escalation resulted in progressive lowering of disease activity.
Methods: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pts enrolled in the US Corrona registry initiating IFX on or after 1/1/2007 with an initial dose of 3mg/kg/Q8 weeks were identified. Eligible patients had at least 1 dose escalation and at least one follow-up visit after 1st dose escalation. Dose escalation was defined as an increase of >1mg/kg in dose and/or an increase in the frequency of dosing by ≥1 week. Trends in disease activity (CDAI) and functionality (HAQ) were summarized over time and scaled to number of dose escalations (CDAI at visits between escalations scaled to proportion of time between escalations). Locally weighted scatterplot smoothing (Lowess curve) were used to estimate trends over time.
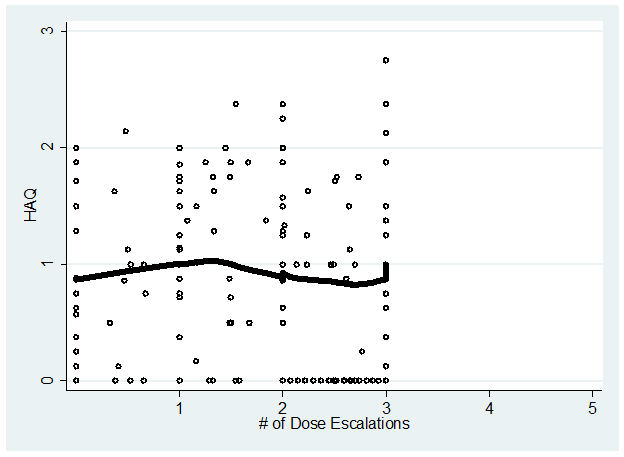
Results: Eligible pts (N=185) had a mean 7.5 years duration of RA and 72.4% were female; mean CDAI (SD) was 19.6 (13.2) at time of initiation and 16.6 (12.0) at 1st dose escalation. Figure 1 shows the estimated mean CDAI over time for pts with 3 dose escalations and Figure 2 shows estimated CDAI for pts with 4 dose escalations. In pts with 3 dose escalations (n=30), there is a progressive decrease in mean CDAI from initiation until the 2nd dose escalation, and then the mean CDAI remains at a plateau. In pts with 4 dose escalations (n=12), the decrease in mean CDAI is less and the overall level of disease is higher; trends in HAQ are flat across 3 dose escalations (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Initial dose escalations (i.e. the first two) provide reduction in mean CDAI, while later dose escalations are related to maintaining disease activity levels. Pts with ≥3 dose escalations had higher levels of initial disease activity, smaller initial response, and little subsequent reduction in disease activity after the first two dose escalations. These results have potentially important clinical implications since these data suggest there may be diminishing clinical benefit in at least a subset of patients beyond the initial 2 dose escalations and that an assessment of the risk-benefit of further dose escalations should be considered.
Figure 1. Lowess curve of CDAI in patients with 3 dose escalations
Figure 2. Lowess curve of CDAI in patients with at least 4 dose escalations
Figure 3. Lowess curve of HAQ in patients with 3 dose escalations
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Parenti D, Reed GW, Shan Y, Dandreo K, Kremer JM, DeHoratius RJ. Disease Activity Trends after Dose Escalation of Infliximab (Remicade) – Results from United States Consortium of Rheumatology Researchers of North America Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-trends-after-dose-escalation-of-infliximab-remicade-results-from-united-states-consortium-of-rheumatology-researchers-of-north-america-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-trends-after-dose-escalation-of-infliximab-remicade-results-from-united-states-consortium-of-rheumatology-researchers-of-north-america-registry/