Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting global functioning and health (GH). GH, a concept linked to health-related quality of life, is multifactorial in axSpA. On top of the disease itself, chronic widespread pain, comorbidities, and patient-related factors seem to play a role in GH [1]. Our objective was to assess the relative importance of factors associated with GH in axSpA.
Methods: This was a post-hoc cross-sectional analysis of 4 databases, for patients fulfilling ASAS criteria for axSpA, and with available GH scores: COMOSPA (N= 2756 patients analysed) and PERSPA (N= 2651) international cross-sectional studies; DESIR at 7 years (N= 284), a French inception cohort, and COMEDSPA (N= 373) at baseline, a French randomized control trial. GH was assessed through the ASAS Health Index (ASAS-HI), range 0-17; in COMOSPA we used the EuroQoL-5D-3L (EQ-5D) since ASAS-HI was not available. Altered GH was defined by ASAS-HI ≥ 10 according to its graphical distribution and quartiles distribution in the datasets; a ROC curve of EQ-5D corresponding to this cut-off was obtained, and the Youden index that maximizes sensitivity and specificity was computed: thus, altered GH was defined by EQ-5D< 0.597. Disease-related factors included (a) disease activity: ASDAS, CRP, current psoriasis, current arthritis, current enthesitis; (b) other disease-related factors: disease duration, diagnostic delay, structural damage (bamboo spine), and bDMARD use. Non-disease-related factors included (a) sociodemographic data (sex, age, employment status and educational level), (b) comorbidities (Rheumatic Disease Comorbidity Index RDCI, obesity and depression) and (c) the construct of chronic widespread pain. Bivariate and multivariate logistic and linear regression were performed in each dataset. Partial R2 explored the proportion of variance explained by groups of variables, relative to the total explained variance, in each dataset.
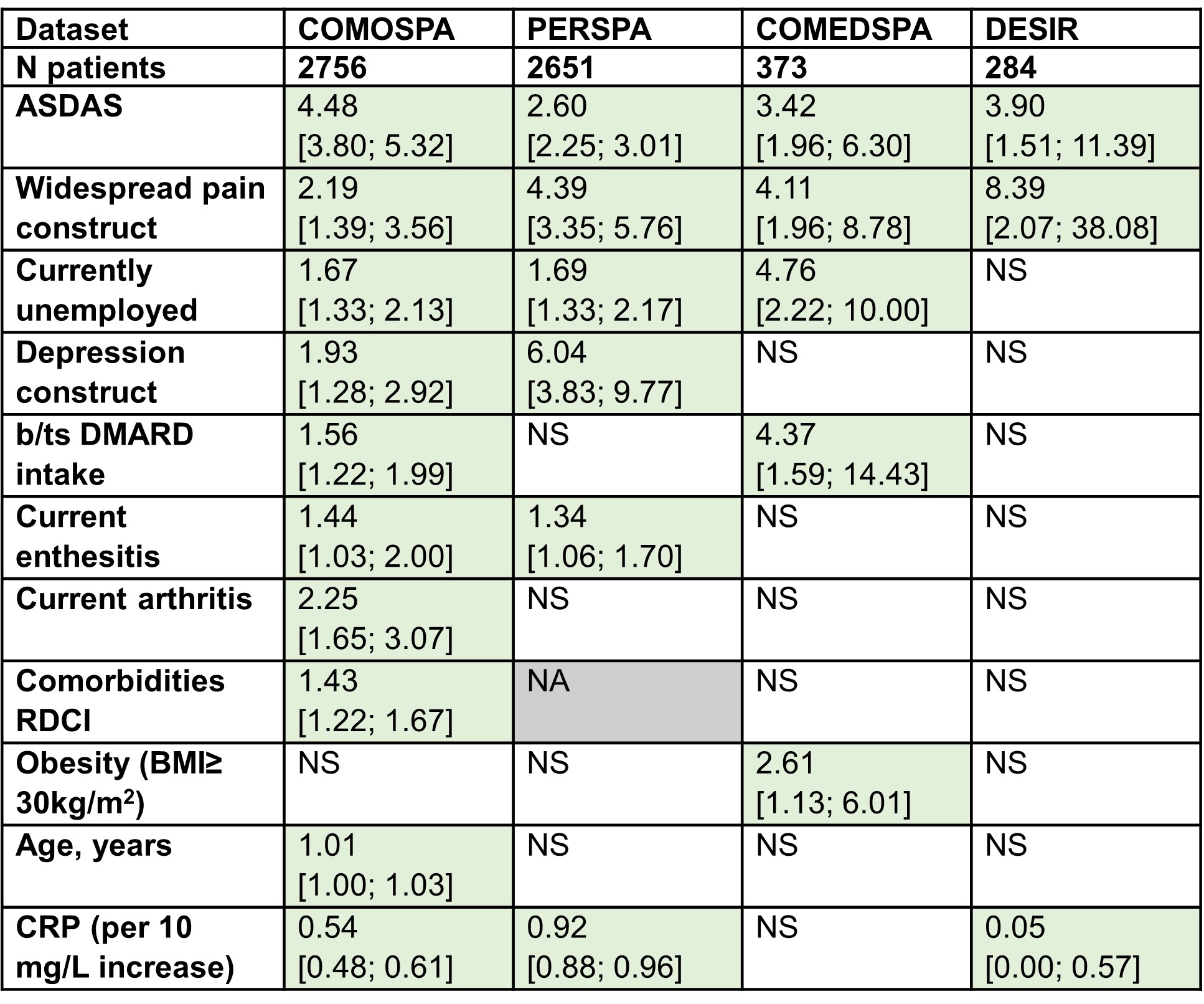
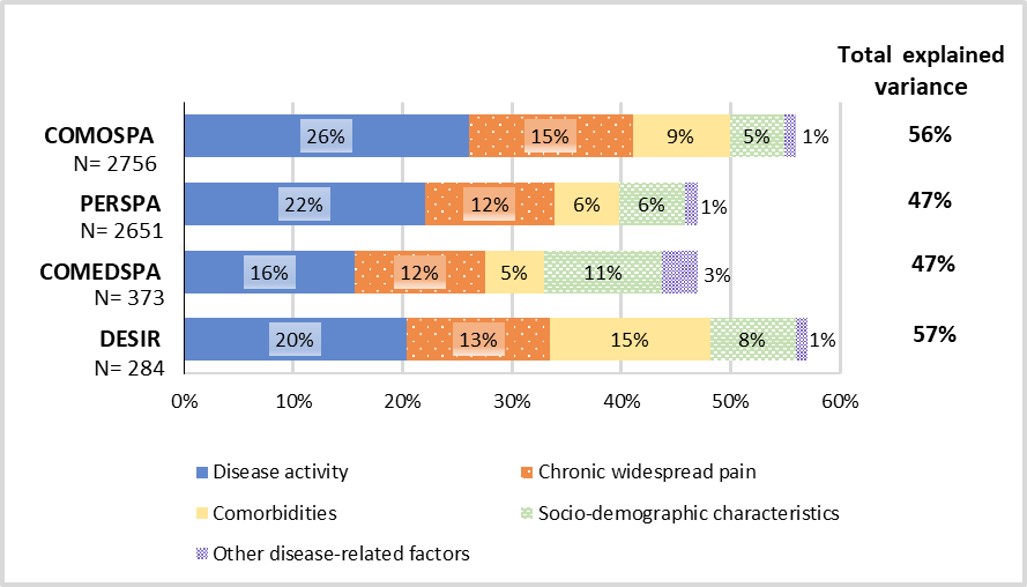
Results: In 6064 patients, mean age ranged from 38.9 to 45.8 years, 51.1%- 67.7% were male, 42.0%- 66.1% were in high disease activity, and 14.2%- 24.2% were screened positively for chronic widespread pain. GH was generally moderate to good: median ASAS-HI ranged from 5.0 to 7.0. In all, 47.0%, 29.1%, 23.1% and 16.5% patients had altered GH in COMOSPA, PERSPA, COMEDSPA and DESIR respectively. Altered GH was explained in all databases (multivariable logistic regression) by: ASDAS (odds ratio, OR, ranging 2.60-4.48) and chronic widespread pain (OR 2.19-8.39) (Table1), and 47%-57% of GH was explained by the models (total variance of GH, linear regression). Disease activity (partial R2, 16%- 26%) and chronic widespread pain (partial R2 12%- 15%) were the key variables explaining GH (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Overall, 16 to 47% axSpA patients reported altered GH in this large population. Two elements were consistently associated to altered GH and together were the key variables explaining GH: higher ASDAS and chronic widespread pain. Our results allow to attribute a relative role to groups of variables to explain GH in axSpA. These results may be helpful for patient-physician communication and shared decision-making. (1) MacFarlane et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2020 ;79 :202-8
RDCI was not available in PERSPA, diagnostic delay was not available in COMEDSPA and bamboo spine was not included in DESIR. Percentages are the proportion of the partial variance explained by each group of variables, relative to the total explained variance.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Drouet J, López Medina C, Granger B, Fautrel B, Molto A, Gaujoux Viala C, Kiltz U, Dougados M, Gossec L. Disease Activity and Widespread Pain Are the 2 Key Drivers of Global Health in Axial Spondyloarthritis, with Similar Findings in Different Patient Populations: An Analysis of 4 Databases and 6064 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-and-widespread-pain-are-the-2-key-drivers-of-global-health-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-with-similar-findings-in-different-patient-populations-an-analysis-of-4-databases-and-6064-pati/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-and-widespread-pain-are-the-2-key-drivers-of-global-health-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-with-similar-findings-in-different-patient-populations-an-analysis-of-4-databases-and-6064-pati/