Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Biology and Pathology of Bone and Joint: Ostearthritis Pathogenesis
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose:
Wnt has a key role in the formation of bone, cartilage
and synovium. Increased Wnt signaling may contribute to initiation and
progression of osteoarthritis (OA) by inducing cartilage degradation and
reducing its thickness.1 Polymorphisms in Wnt signaling genes are
associated with increased susceptibility to OA.2 SM04690, a novel,
small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway was evaluated in preclinical
studies to determine its potential to treat OA.
Methods:
SM04690’s capacity to inhibit the Wnt pathway was
determined via a cellular screen using a luciferase reporter driven by a
Wnt-responsive promoter. SM04690’s ability to induce chondrogenesis was
established using differentiation of primary human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC)
to chondrocytes, as determined by Safranin-O staining and upregulation of
chondrogenic genes. Pharmacokinetics were evaluated by intra-articular (IA)
injection in Sprague Dawley rats and Beagle dogs, followed by evaluation of
compound concentration in joints and plasma. In vivo activity was
evaluated in the anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT) combined with
medial meniscal tear model in rats, in which SM04690 or vehicle control was
injected into the IA space of the damaged knee (N=8-12/group), followed by
histological evaluation using blinded Osteoarthritis Research Society
International (OARSI) scoring [0-24].3
Results:
In vitro, SM04690 inhibited Wnt pathway
activation with EC50≈3 nM. Consistent with Wnt’s role in
chondrogenesis, SM04690 induced hMSCs to differentiate to chondrocytes with EC50≈30
nM as measured by staining and expression of chondrogenic markers: SOX9,
collagen2A, aggrecan and TIMP1. In vivo, a single IA injection of
SM04690 into knees of Sprague Dawley rats or Beagle dogs resulted in a joint
concentration above target EC50 with a residence time of 60-90 days.
No compound was detectable in plasma immediately after IA injection or 30–180
days post-injection. In ACLT model, one injection of SM04690 2 weeks
post-injury improved cartilage health in a dose-dependent manner relative to
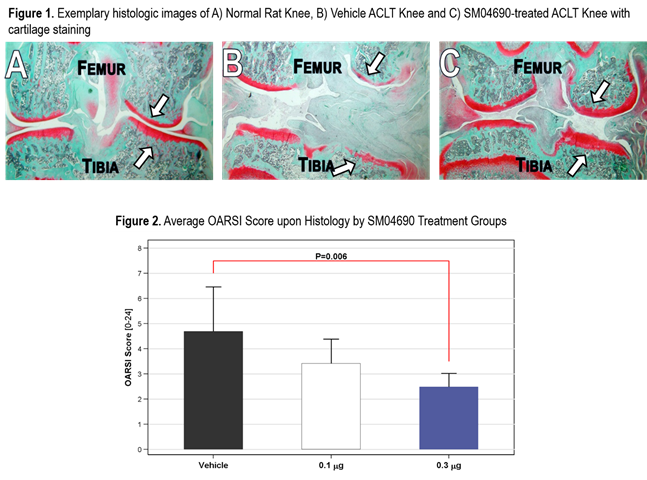
vehicle, with no observable toxicity. Histology in ACLT model shows marked
cartilage degradation in vehicle (Figure 1B), while SM04690 showed
cartilage thickness similar (1C) to normal (1A) non-ACLT knee. At
optimal IA dose of 0.3 ug/knee in rats, OARSI scores decreased significantly
from 4.7 to 2.5, P=0.006 (Figure 2).
Conclusion:
SM04690 was shown to inhibit the Wnt pathway, induce
chondrogenesis and improve cartilage health in rat models of OA after a single
IA injection. SM04690 was maintained in joint space for up to 90 days with no
detectable SM04690 in plasma, consistent with a low potential for systemic
toxicity. These data suggest that locally injected SM04690 may have potential
as a disease modifying therapy for OA.
References:
1. Gelse Osteoarthr Cartil
2012; 20(2):162-71
2. Wu Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18:3293
3. Bendele J
Musculoskeletal Neuronal Interact 2001; 1:363
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Barroga C, Hu Y, Deshmukh V, Hood J. Discovery of an Intra-Articular Injection Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM04690) As a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discovery-of-an-intra-articular-injection-small-molecule-inhibitor-of-the-wnt-pathway-sm04690-as-a-potential-disease-modifying-treatment-for-knee-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discovery-of-an-intra-articular-injection-small-molecule-inhibitor-of-the-wnt-pathway-sm04690-as-a-potential-disease-modifying-treatment-for-knee-osteoarthritis/