Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
.Background/Purpose:
The aim of this study was to investigate the performance of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in detecting high signal intensity areas (HSIA), as potential signs of bone inflammation, in wrist and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, in comparison with short tau inversion recovery (STIR) MRI images.
.Methods:
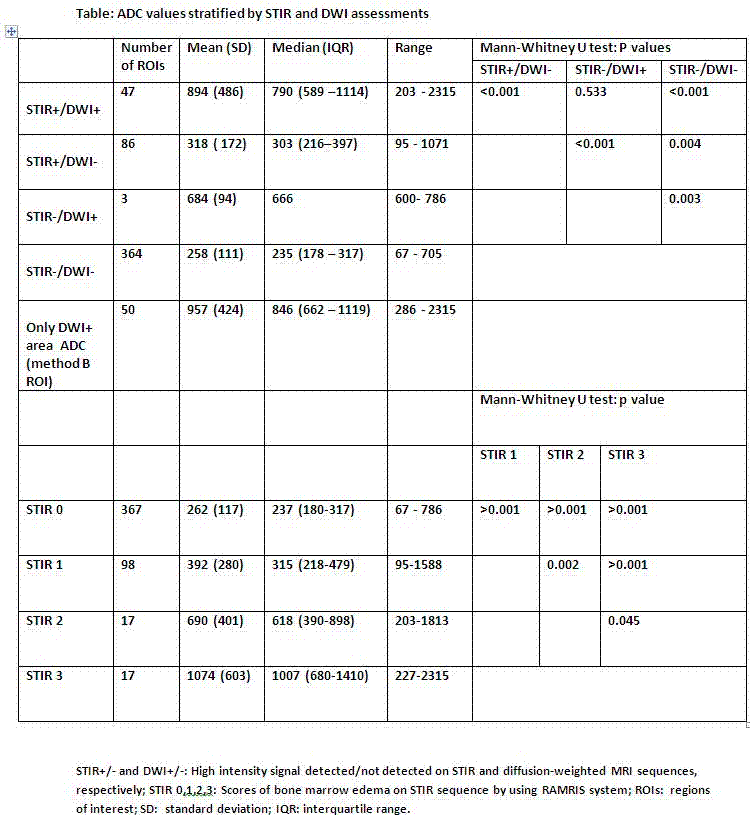
26 patients with RA in clinical remission underwent MRI including DWI (with apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps), T1-weighted (T1w) and STIR images. 13 were rescanned after 4 months. STIR scans were scored for bone marrow edema (BME) according to Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials (OMERACT) Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging scoring system (RAMRIS) and DWI scans were scored for absence (0) or presence (1) of HSIA in bone marrow. STIR and DWI images were reviewed separately by one reader and ADC values were calculated in each of 21 bones in the wrist and MCP joints. For calculation of ADC, regions of interest (ROIs) were drawn, which covered the maximal possible subcortical bone areas, including both areas with high and with normal signal, avoiding erosions (method A). Furthermore, in DWI positive areas, ROIs were also placed within the HSIA (method B). ADC values were divided into 4 groups based on STIR and DWI scores as seen in the table below and nonparametric tests were used to compare groups. The reproducibility of the scores was analyzed by kappa (k) values, intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC), and smallest detectable difference (SDD) and change (SDC).
.Results:
STIR showed more positive lesions (132 HSIA (=bone marrow edema)) than DWI (50 HSIA) (p<0.001 Fisher's exact test). Mean ADC of “STIR-only” (STIR+/DWI-) positive lesions (318±172x10-3 mm2 /s was significantly lower than lesions, where both STIR and DWI were positive (STIR+/DWI+; 894±486×10-3mm2/s) (p<0.001; Mann-Whitney U test). ADC-values increased with increasing STIR scores (see table).The median ADC, in DWI positive areas, with method A (759.5x10-3mm2/s) was slightly lower than the median ADC with method B (846×10-3mm2/s) (p-value 0.048; Wilcoxon signed rank test). There was no statistically significant difference between baseline and 4 months follow-up scans in any parameters (p=0.9, 0.8 and 0.2 for STIR, DWI and ADC respectively; Wilcoxon signed rank test).The intraobserver agreement was good to excellent using STIR (k=0.80) and DWI (k=0.76), respectively (baseline). The intraobserver ICC of ADC measurements was 0.85. Intraobserver SDD of ADC at baseline was 60×10-3mm2/s, whereas intraobserver SDC between baseline and 4 months follow up was 108×10-3mm2/s.
.Conclusion:
DWI, including ADC measurements, in bones of patients with RA were highly reproducible and may partially reflect BME on STIR MRI. Further studies are needed to investigate if the method is useful for monitoring treatment response and/or predicting disease progression.
Disclosure:
M. Khurram,
None;
J. M. Møller,
None;
M. Østergaard,
Abbott/Abbvie, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Eli-Lilly, Centocor, GSK, Janssen, Merck, Mundipharma, Novo, Pfizer, Schering-Plough, Roche UCB, and Wyeth.,
5,
Abbott/Abbvie, Centocor, Merck, Schering-Plough,
2;
H. Thomsen,
None;
B. J. Ejbjerg,
None;
M. L. Hetland,
None;
S. Møller-Bisgaard,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diffusion-weighted-magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri-of-wrist-and-hands-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-reproducibility-and-correlation-with-conventional-mri/