Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0554–0592) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
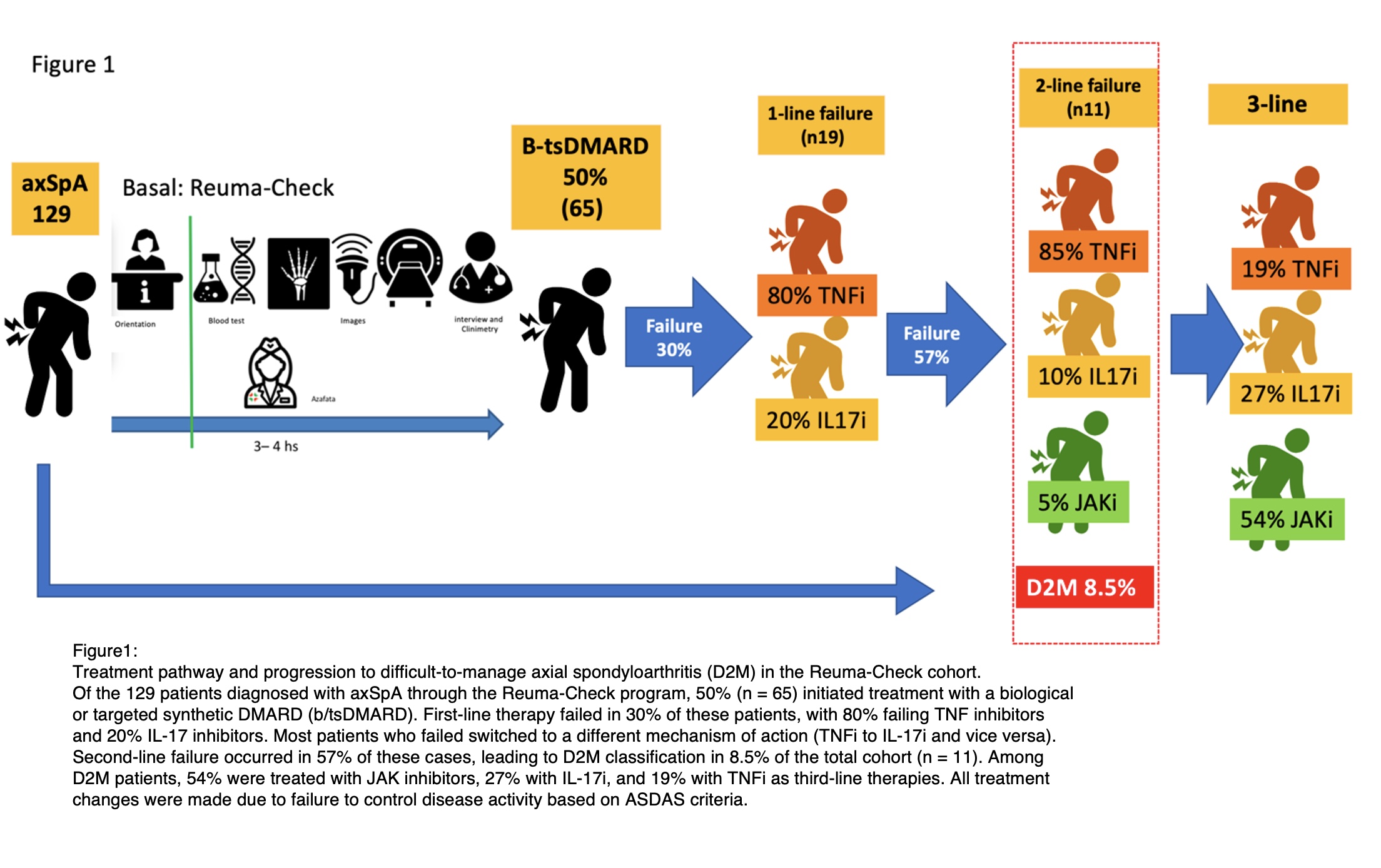
Background/Purpose: The concept of difficult-to-Manage axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA D2M), recently introduced by ASAS, describes patients who fail ≥2 lines of b-tsDMARDs treatment and remain active (amog others). Refractory patients are defined as those with D2M and objective signs of inflammation. This study aimed to estimate the frequency of D2M in the Argentinian Reuma-Check axSpA cohort, describe treatment trends, and analyze baseline characteristics associated with D2M during follow-up.
Methods: This prospective observational study (2017–2024) included axSpA patients aged ≥18 years. The Reuma-Check program conducted structured assessments, including blood tests (HLA-B27), sacroiliac X-rays, MRI (ASAS protocol), and enthesis ultrasound. Data collected included demographics, educational levels, back pain characteristics, diagnostic delay, NSAID response, VAS pain scores, morning stiffness, BASDAI, BASFI, MASES, and HAQ (figure 1). D2M was defined as the lack of response to ≥2 biological therapies with active disease. Descriptive statistics, comparative analyses, and logistic regression were performed to identify associated factors.
Results: A total of 129 axSpA patients were included, with a follow-up of 12 months (IQR: 3–36). The frequency of D2M was 8.53% (n=11; 95% CI: 4.83%-14.62%). The average time on the first biologic was 19 months (SD: 16) and the prevalence of use was 50%, 21 months (SD: 19) on the second before D2M definition. Among first-line therapies 30% failure: 8% failed TNFi, and 20% IL17, regardin second-line faiuler: 85% failed TNFi, 10% IL17, and 5% JAKi (figure1). Only four patients met criteria for refractory disease, two showing elevated CRP and two active MRI findings. Baseline variables associated with D2M included BASFI (4.16 ± 2.54 vs. 2.87 ± 2.15; p=0.04; 95% CI: 0.03–2.54), BASDAI (5.11 ± 2.87 vs. 3.54 ± 2.42; p=0.01; 95% CI: 0.32–2.82), and ASDAS (3.72 ± 1.45 vs. 2.84 ± 1.16; p=0.009; 95% CI: 0.23–1.53). Significant categorical variables included smoking (OR=6.347; 95% CI: 1.256–32.084; p=0.012), psoriasis (OR=3.771; 95% CI: 1.069–13.305; p=0.029), sacroiliac joint maneuvers (OR=3.71; 95% CI: 1.030–13.417; p=0.043), peripheral X-rays (OR=5; 95% CI: 1.3–6.487; p=0.01), and articular ultrasound (OR=10.65; 95% CI: 1.42–80.09; p=0.022). Multivariate analysis identified articular ultrasound as the only significant predictor (OR=10.651; 95% CI: 1.416–80.094). Among D2M patients, six received JAKi, three IL17, and two TNFi as third-line therapies.
Conclusion: The Reuma-Check cohort revealed a low prevalence of axSpA D2M. Clinical and imaging features, particularly articular ultrasound and disease activity scores (BASFI, BASDAI, ASDAS), were predictive of D2M. These findings underscore the importance of advanced diagnostic tools and a multidimensional approach to optimizing the management of this complex population
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
García Salinas R, Mejia N, Ruta S, Magri S. Difficult-to-Manage Axial Spondyloarthritis According to ASAS Criteria in Reuma-Check Cohort: Frequency, Predictive Factors, and Treatment Patterns. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/difficult-to-manage-axial-spondyloarthritis-according-to-asas-criteria-in-reuma-check-cohort-frequency-predictive-factors-and-treatment-patterns/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/difficult-to-manage-axial-spondyloarthritis-according-to-asas-criteria-in-reuma-check-cohort-frequency-predictive-factors-and-treatment-patterns/

.jpg)