Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Biological agents inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines, especially IL-6 and TNFa, have brought a great impact in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In addition, CTLA4-Ig has been shown to have beneficial effects in the treatment of RA. Although several studies have disclosed the in vitro effects of biological agents on the immune competent cells, the precise mechanisms of action in RA remain unclear. On the other hand, abnormalities in monocytes have been shown to play an important role in the pathogenesis of RA. The current study was undertaken to explore the effects of etanercept, infliximab, tocilizumab and abatacept on human monocytes.
Methods: Monocytes, which were highly purified from peripheral blood from healthy donors using magnetic beads, were cultured in the presence of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) with pharmacologically attainable concentrations of various biological agents, control IgG (control for etanercept, infliximab, tocilizumab) or IgG Fc (control for abatacept). The induction of apoptosis of monocytes was evaluated by staining with annexin V and propidium iodide, followed by analysis on flow cytometry. The expression of CD80, CD86 and HLA-DR were also measured on flow cytometry. The concentrations of IL-6 and TNFa in the culture supernatants were measured using ELISA.
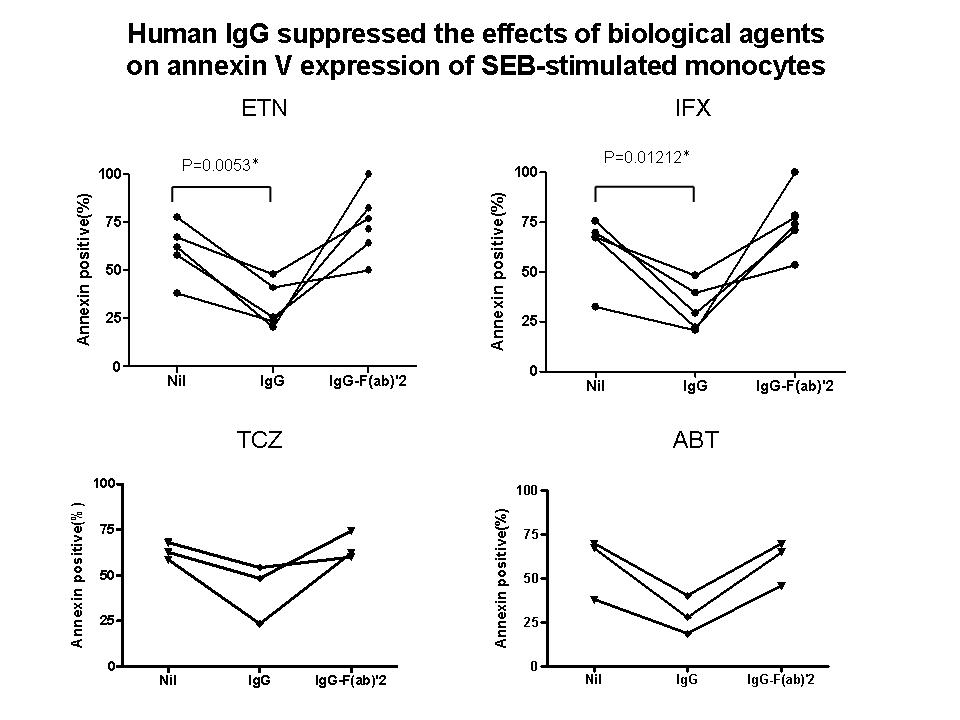
Results: All of etanercept, infliximab, abatacept and tocilizumab promoted apoptosis of SEB-stimulated monocytes. The induction of apoptosis of monocytes by these biological agents were reversed by addition of normal human IgG, but not by IgG F(ab)’2 fragments (Figure). Of note, etanercept as well as infliximab significantly suppressed the expression of CD80, CD86 and HLA-DR on SEB-stimulated monocytes. By contrast, tocilizumab and abatacept suppressed only the expression of CD80, but neither CD86 nor HLA-DR. Finally, etanercept, infliximab, abatacept but not tocilizumab, suppressed the production of IL-6 and TNFa of SEB-stimulated monocytes.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that all the biological agents, including TNF inhibitors, anti-IL-6 receptor antibody and CTLA4-Ig, have direct action on human monocytes, leading to the induction of apoptosis thereof, which involves interaction with Fc receptor on monocytes. Moreover, the data also indicate that these biological compounds display differential influences on various functions of monocytes, including the expression of costimulation molecules, HLA-DR and proinflammatory cytokines, depending on their interactions with different molecules on monocytes.
Disclosure:
T. Tono,
None;
Y. Arinuma,
None;
T. Nagai,
None;
S. Tanaka,
None;
S. Hirohata,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-effects-of-tnf-inhibitors-anti-il-6-receptor-antibody-and-ctla4-ig-on-human-monocytes/