Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0252–0282) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The combination treatment of golimumab (GOL), a tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) antagonist, and guselkumab (GUS), an interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitor was shown to induce higher rates of clinical remission, endoscopic improvement, and histologic remission than each monotherapy in a randomized Phase 2 induction study in TNFα-naïve patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (VEGA; NCT03662542). Here, we investigated the underlying mechanism of action of GOL, GUS, and the combination (GUS+GOL).
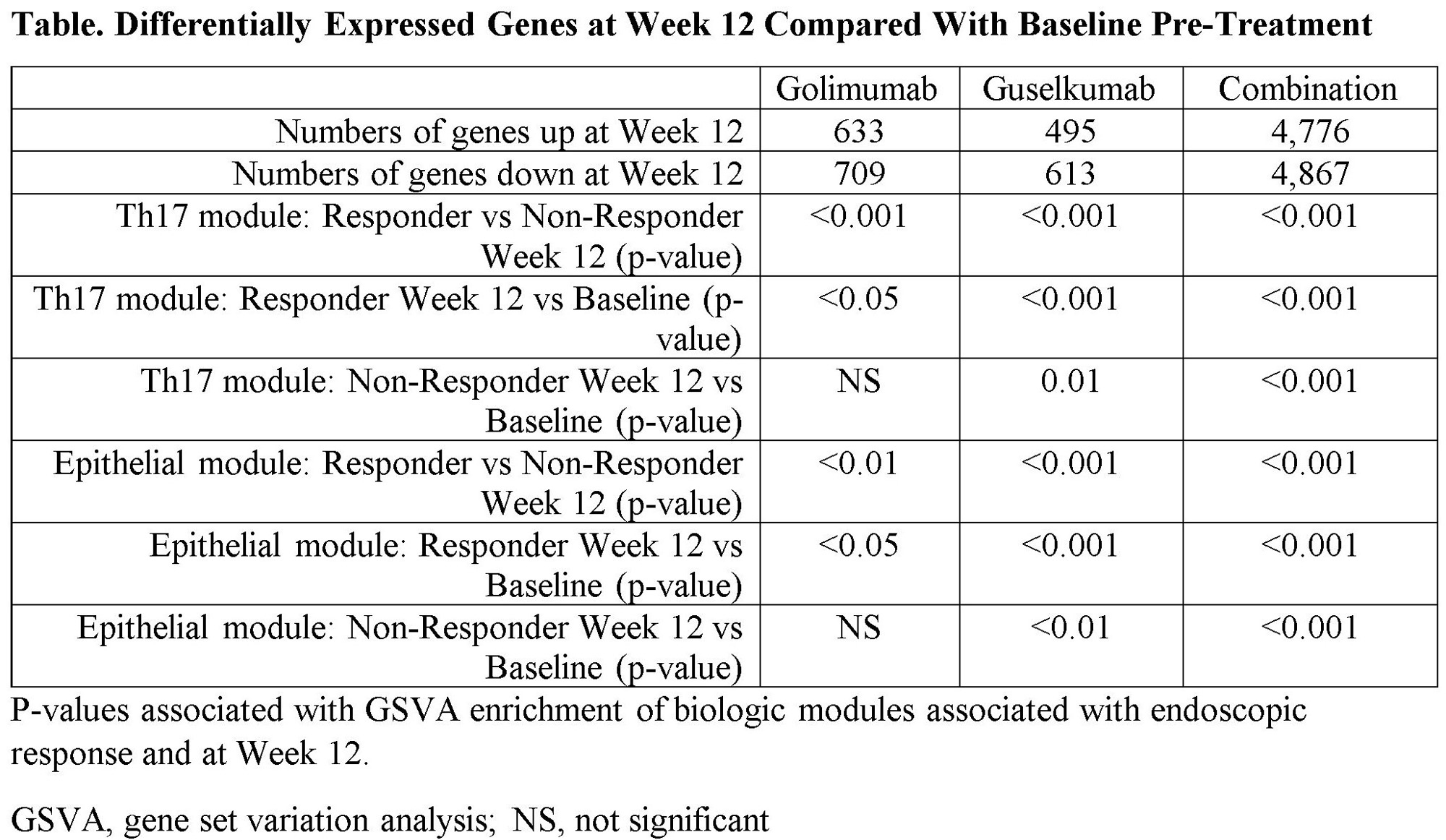
Methods: Colon biopsies were obtained at screening and at Week 12 in patients who received GOL (n=48), GUS (n=52), or GUS+GOL (n=50). Tissue transcriptional profiles were determined with RNA sequencing. Differentially expressed genes were analyzed in the context of cell-type specific transcriptional modules by first defining a gene correlation network and unsupervised network clustering. We then developed a method to create a single-cell-derived co-expression network using published ulcerative colitis single-cell data to provide high resolution gene modules associated with specific cell types and pathways. Gene set variation analysis (GSVA) was used to quantitatively assess changes in specific biologic modules in the context of responder and non-responder analyses.
Results: By Week 12, combination therapy induced a greater magnitude of transcriptional changes in the colon compared with each monotherapy (Table). These genes were associated with IL-23/Th17/myeloid-related processes, inflammation, and epithelial homeostasis. Significant changes were observed in Th17 cell and inflammatory epithelial cell modules in patients who achieved endoscopic improvement (subscore 0 or 1) at Week 12 compared with non-responders (Table). The magnitude of change relative to baseline was greater in the GUS monotherapy and GUS+GOL arms compared with GOL alone. These changes were consistent with a decrease in crypt destruction in responders at Week 12 as observed by histologic changes in the Geboes score. Genes modulated by GUS+GOL were indicative of greater suppression of inflammation, particularly myeloid cell activation and inflammatory fibroblast development. In contrast, genes modulated by either GUS or GUS+GOL were associated with increased epithelial normalization and decreased Th17 activity compared to GOL alone.
Conclusion: Combination induction with GOL+GUS for 12 weeks drove a greater reduction in inflammation and improvement in epithelial homeostasis compared to each monotherapy, demonstrating differential and complementary mechanisms of action of TNFα and IL-23 blockade. Combination therapy drives a significant increase in the overall magnitude of response with marked improvement in the restoration of normal epithelium.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Desai P, Branigan P, Richards D, McGonagle D, Vetter M, Cua D, Freeman T. Differential and Combinatorial Mechanism of Action of Golimumab and Guselkumab in Ulcerative Colitis Induction Therapy: IL-23 Blockade Drives Restoration of Normal Epithelium and Mucosal Healing [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-and-combinatorial-mechanism-of-action-of-golimumab-and-guselkumab-in-ulcerative-colitis-induction-therapy-il-23-blockade-drives-restoration-of-normal-epithelium-and-mucosal-healing/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-and-combinatorial-mechanism-of-action-of-golimumab-and-guselkumab-in-ulcerative-colitis-induction-therapy-il-23-blockade-drives-restoration-of-normal-epithelium-and-mucosal-healing/