Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis (PsO) and multiple comorbidities.1 Approximately one-third of patients with PsO develop PsA during the course of their disease.2 As patient cohorts included in randomized clinical trials are not necessarily representative of the real world, registry data can complement information gained on patient characteristics and disease outcomes.1,3 The British Association of Dermatologists Biologic and Immunomodulators Register (BADBIR) is one such registry for patients with plaque PsO, with PsA being one of the comorbidities recorded at patient enrollment. The primary objective of this study was to evaluate baseline characteristics and comorbidities in patients with PsO with and without a PsA diagnosis using the BADBIR database. The hypothesis was that patients with both diseases have a higher likelihood of being diagnosed with additional comorbid conditions vs. those with PsO alone.
Methods: This was a retrospective observational study using two cohorts of BADBIR data (i.e. adult patients with PsO either receiving ustekinumab [UST] as their biologic treatment or receiving conventional systemic anti-psoriatic medication [conventional systemic]). Comparisons were made between comorbid PsA and PsO alone patients in each cohort at baseline, additionally stratifying by biologic experience in the UST treatment group. Baseline characteristics of interest were evaluated, including body mass index, smoking, and employment status, as well as comorbidities (i.e. diabetes, hypertension, myocardial infarction, and depression). Strength of association between variables was measured by odds ratio, and 95% confidence intervals were generated; two-sided p-values were obtained by Fisher’s exact test.
Results: Patient counts in each cohort were as follows: UST without PsA, n=2697; UST with PsA, n=590; conventional systemic without PsA, n=5105; conventional systemic with PsA, n=529. Patients with PsO and a PsA diagnosis had a higher prevalence of diabetes, obesity, and hypertension across both conventional systemic and UST cohorts vs. PsO alone (Table 1). Similarly, inability to work was notably higher in patients with PsO and comorbid PsA vs. PsO alone (Figure 1). Patients with PsO and comorbid PsA receiving UST were more likely to have a diagnosis of depression than those receiving conventional systemic treatment (Table 1).
Conclusion: These results indicate that the prevalence of obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and inability to work was higher in patients with PsO and comorbid PsA vs. PsO alone. Depression was also more prevalent in patients with PsO and comorbid PsA receiving biologic treatment vs. those receiving conventional systemics. These results potentially indicate a higher inflammatory and quality-of-life burden in patients with PsO and comorbid PsA, highlighting the need for adequate patient assessment and follow-up to ensure a best possible holistic patient management approach.
References: 1. Shah et al. RMD Open 2017;3:e000588; 2. Coates et al. Lancet 2015;386:2489–98; 3. Mason et al. JAMA Dermatol 2018;154:581–8.
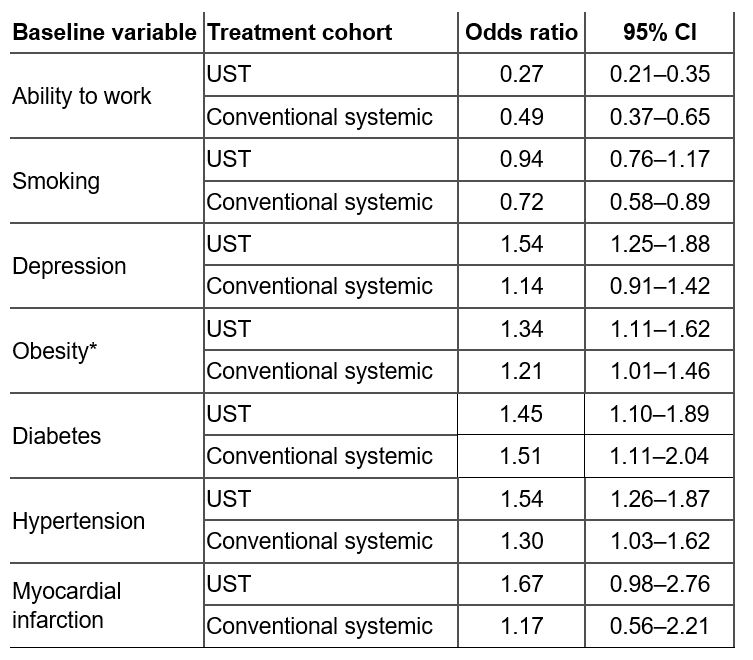 Table 1: Prevalence odds ratio of baseline characteristics of patients with PsO treated with either UST or a conventional systemic agent. Odds ratios and 95% CIs are shown for the prevalence of each patient baseline characteristic in the PsO with comorbid PsA group vs. the prevalence in the PsO alone group. *Obesity is defined as a BMI ≥30 kg/m2. BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; PsA, psoriatic arthritis; PsO, psoriasis; UST, ustekinumab.
Table 1: Prevalence odds ratio of baseline characteristics of patients with PsO treated with either UST or a conventional systemic agent. Odds ratios and 95% CIs are shown for the prevalence of each patient baseline characteristic in the PsO with comorbid PsA group vs. the prevalence in the PsO alone group. *Obesity is defined as a BMI ≥30 kg/m2. BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; PsA, psoriatic arthritis; PsO, psoriasis; UST, ustekinumab.
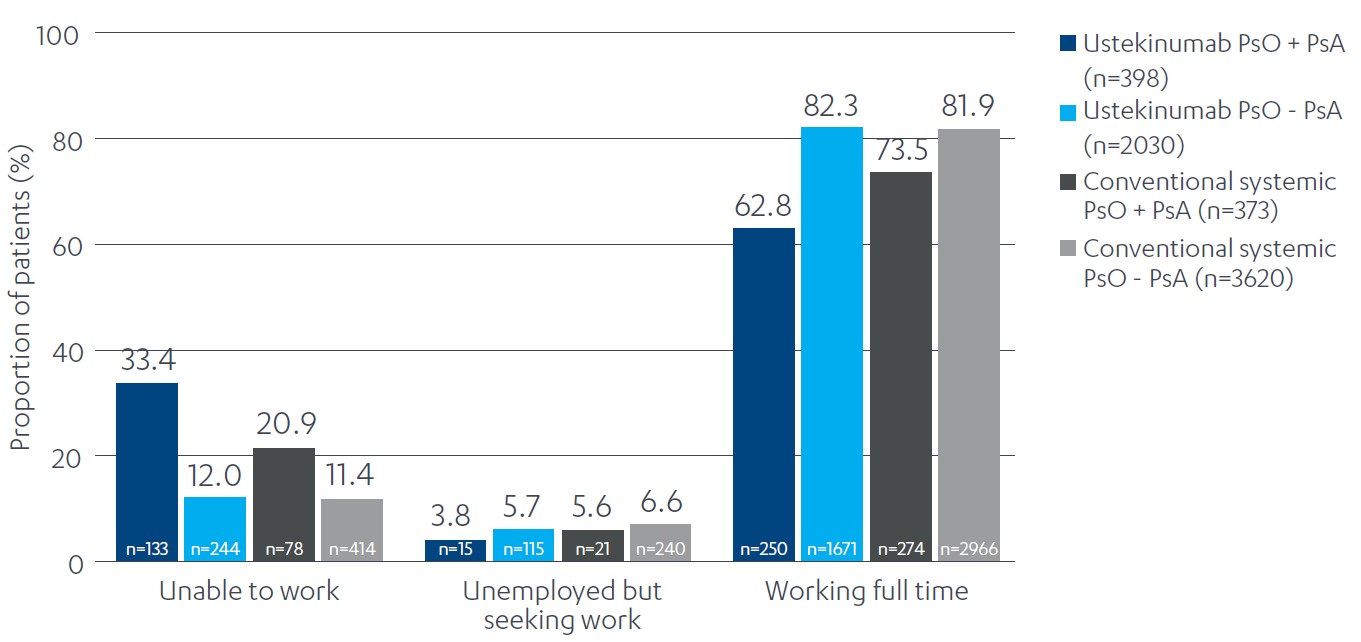 Figure 1: Employment status of patients with PsO by presence of comorbid PsA and treatment type. PsA, psoriatic arthritis; PsO, psoriasis.
Figure 1: Employment status of patients with PsO by presence of comorbid PsA and treatment type. PsA, psoriatic arthritis; PsO, psoriasis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tillett W, Ogdie A, Gorecki P, Passey A. Differences in Real-World Patient Characteristics of 8921 Patients with Psoriasis with and Without Comorbid Psoriatic Arthritis Using the UK BADBIR Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differences-in-real-world-patient-characteristics-of-8921-patients-with-psoriasis-with-and-without-comorbid-psoriatic-arthritis-using-the-uk-badbir-database/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differences-in-real-world-patient-characteristics-of-8921-patients-with-psoriasis-with-and-without-comorbid-psoriatic-arthritis-using-the-uk-badbir-database/
