Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a recently recognized fibro-inflammatory disease with multi-organ system involvement, often but not always characterized by elevated serum IgG4 concentrations. The aim of this study was to determine the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of serum IgG4 levels for the diagnosis of IgG4-RD.
Methods: This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our hospital. We searched the Massachusetts General Hospital database using the Research Patient Data Registry tool. Since March, 2001, 193 serum samples from unique patients were found to have elevated serum IgG4 concentrations (normal < 135 mg/dL). We reviewed the electronic medical record to determine the reason for the serum IgG4 assay and the underlying diagnosis in every case. The diagnostic criteria of IgG4-RD were determined according to the IgG4-RD international symposium consensus guidelines. In addition, we randomly selected 193 separate patients with normal serum IgG4 concentrations (from a pool of 3360 patients with normal results) in order to evaluate the test characteristics of IgG4 measurement.
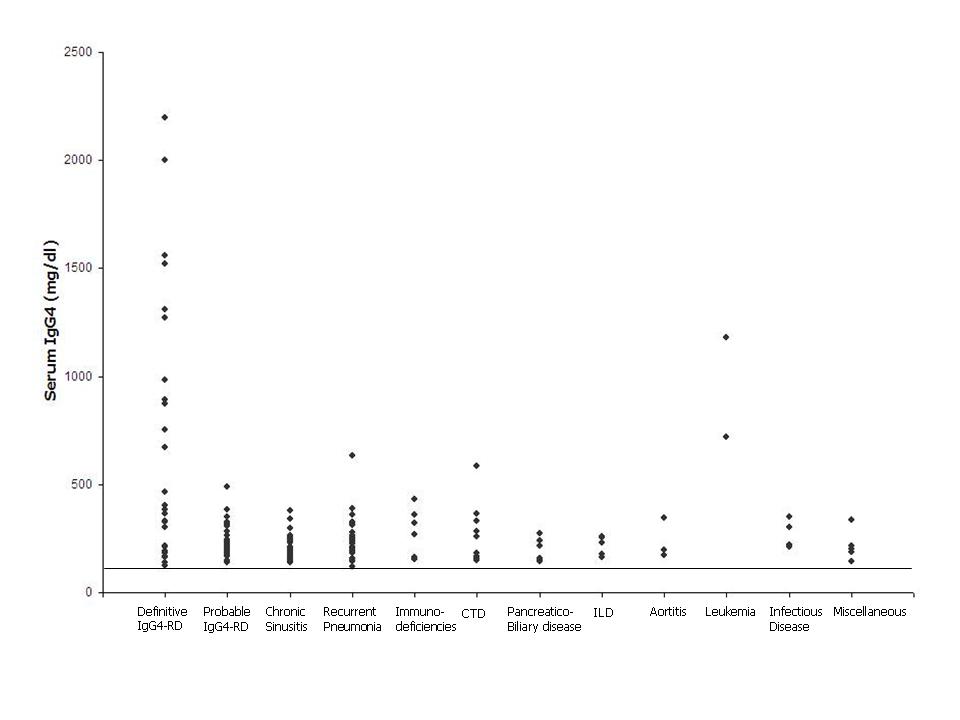
Results: Among the 386 patients analyzed, 73 had either probable or definitive diagnoses of IgG4-RD. Sixty-six of these 73 patients had elevated serum IgG4 concentrations (mean: 404 mg/dL), for a sensitivity of 90%. In contrast, 313 (82%) of the patients analyzed did not have IgG4-RD diagnoses. Among those, 127 had elevated IgG4 concentrations (mean: 232 mg/dL; p <0.0001), for a specificity of 59%. The non-IgG4-RD diagnoses associated with elevated serum IgG4 levels are shown in the Figure. Common causes of false-positive results were chronic sinusitis, recurrent pneumonia, and connective tissue diseases such as lupus, Sjögren’s, and vasculitides. The negative predictive value of a serum IgG4 assay was 96%, but the positive predictive value was only 34%.
Conclusion: With regard to the diagnosis of IgG4-RD, both the sensitivity and the negative predictive value of serum IgG4 assays are high. However, multiple non-IgG4-RD conditions can also be associated with elevated serum IgG4 concentrations, leading to poor specificity and a low positive predictive value for this test.
Figure: Diagnoses Associated with Elevated Serum IgG4 Concentrations
Disclosure:
M. Carruthers,
None;
T. Augustin,
None;
J. H. Stone,
Genentech,
5;
A. Khosroshahi,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-utility-of-serum-igg4-in-igg4-related-disease/