Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: A recent study in German chronic back pain (CBP) patients (pts) with a suspicion of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) report on the performance of, among others, the ASAS inflammatory back pain (IBP) criteria and the individual IBP parameters. Pts were diagnosed by a rheumatologist blinded for all clinical features but IBP and by a rheumatologist with all diagnostic tests available as in daily practice (reference standard). Data show high sensitivity but low specificity of the ASAS IBP criteria and individual IBP parameters(1). Performance of IBP in other countries is less studied. Therefore our objective was to investigate what the diagnostic utility of IBP and the individual IBPpar according to the ASAS IBP criteria is in several rheumatology settings in West- and Northern-Europe?
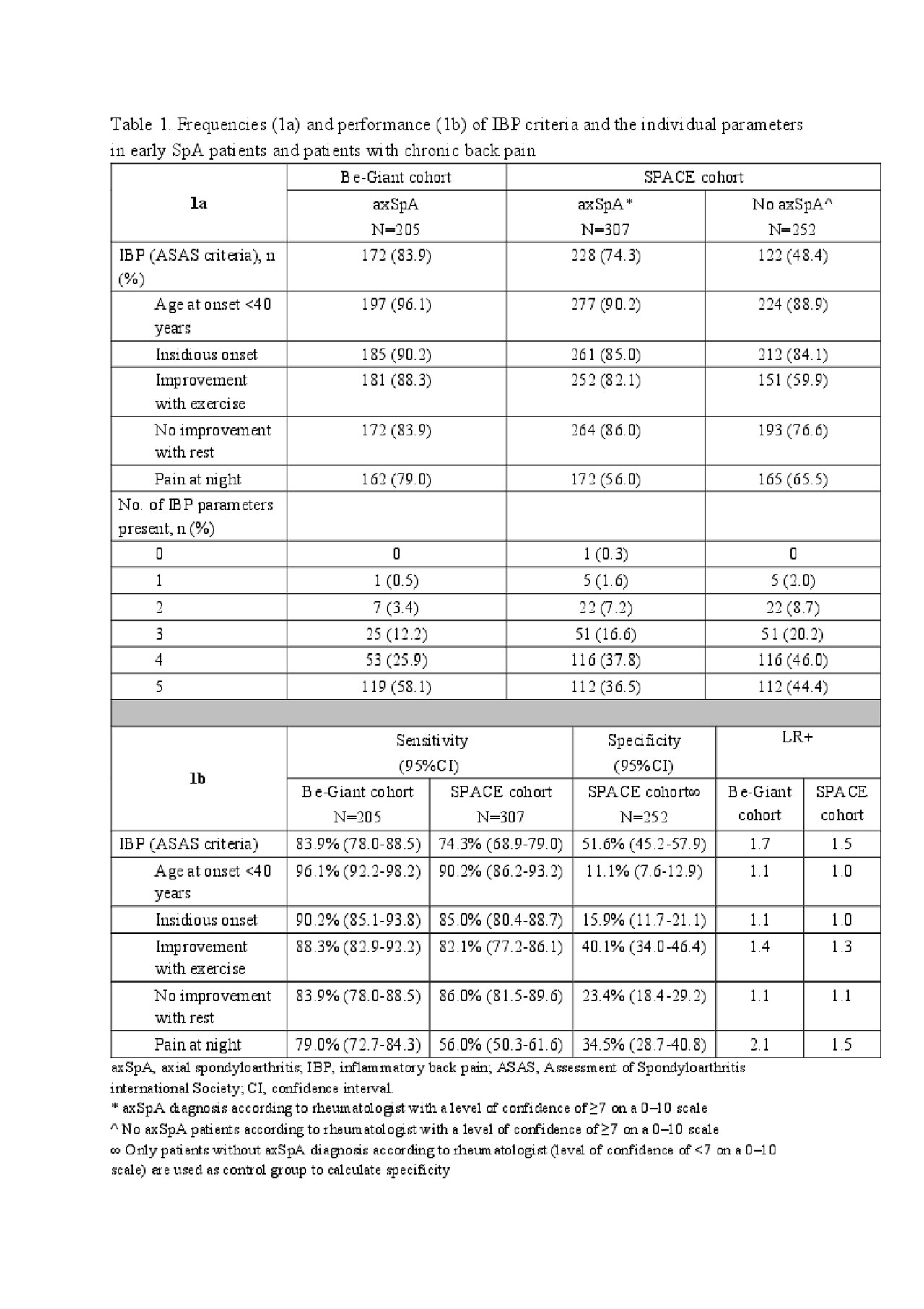
Methods: Data of the multicentre, observational BelGian inflammatory arthritis and spondylitis (Be-Giant) and international SPondyloArthritis Cause Early (SPACE) cohorts were used. The Be-Giant cohort included ≥18 years old, newly diagnosed axSpA patients who were diagnosed by a team of expert rheumatologists and fulfilled the ASAS axSpA criteria. The SPACE cohort included patients, ≥16 years, with (almost) daily chronic back pain for ≥3 months and ≤2 years, with a symptom onset < 45 years. All patients underwent a diagnostic workup according to a predefined protocol of the corresponding cohort, including data on the individual parameters of the ASAS IBP criteria. AxSpA patients from the SPACE cohort diagnosed by a rheumatologist with a level of confidence on the diagnosis (LOC) of ≥7 on a 0–10 scale were included as ‘axSpA’. All patients in SPACE without axSpA diagnosis (LOC ≥7 for no axSpA) were categorised as ‘no axSpA’. For patients with a LOC < 7, diagnosis was considered not sufficiently certain and these patients were excluded from primary analyses. Sensitivity, specificity and positive likelihood ratios (LR+) were calculated using axSpA patients from each cohort separately and no axSpA patients as control group.
Results: Information on IBP parameters was available in 228 patients (Be-Giant) and 559 patients (SPACE) of whom 49.6% and 39.5% were male and mean age was 34.7 (SD9.7) and 30.7 (SD8.0) years, respectively. Few axSpA patients had < 2 IBP parameters (table 1a; Be-Giant 3.9%, SPACE 9.1%). The individual IBP parameters show high sensitivity ( >80%) but low specificity (< 36%) with ‘pain at night’ as exception with slightly better specificity. LR+ of IBP were in both cohorts much lower (table 1b) than the LR+ for IBP of 3.1 previously reported as diagnostic estimate in routine practice.
Conclusion: This study shows that the diagnostic utility of IBP criteria in a rheumatology setting in several European countries is lower than previously assumed with a (very) low specificity and LR+. This suggests that the distinctive impact of IBP is almost fully expressed when physicians refer their patient to the rheumatologist.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
de Hooge M, van Gaalen F, van de Sande M, Ramonda R, Fagerli K, Jacobsson L, van der Heijde D, Elewaut D, Van den Bosch F. Diagnostic Utility of Individual Inflammatory Back Pain Parameters in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-utility-of-individual-inflammatory-back-pain-parameters-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-utility-of-individual-inflammatory-back-pain-parameters-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/