Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoporosis (OP) is a problem in the aging population. Patients with autoimmune disease are at increased risk for OP given their history of steroid use.
Methods: As part of a QI project on bone health, we reviewed female patients age >50 and male patients age >60. If the last DEXA scan was done prior to 2 years ago, a recommendation was made to order a new study. We collected data on risk factors for secondary OP and steroid doses within the past year, including most recent dose and average dose over one year. FRAX scores were calculated for all patients regardless of DEXA score, accounting for all of the standard risks for OP. We adjusted FRAX scores for steroid use based on the NEJM article recommendation to multiply the FRAX score by 15% for major OP fractures and by 20% for risk of hip fractures in patients who currently take >7.5mg of prednisone daily (1).
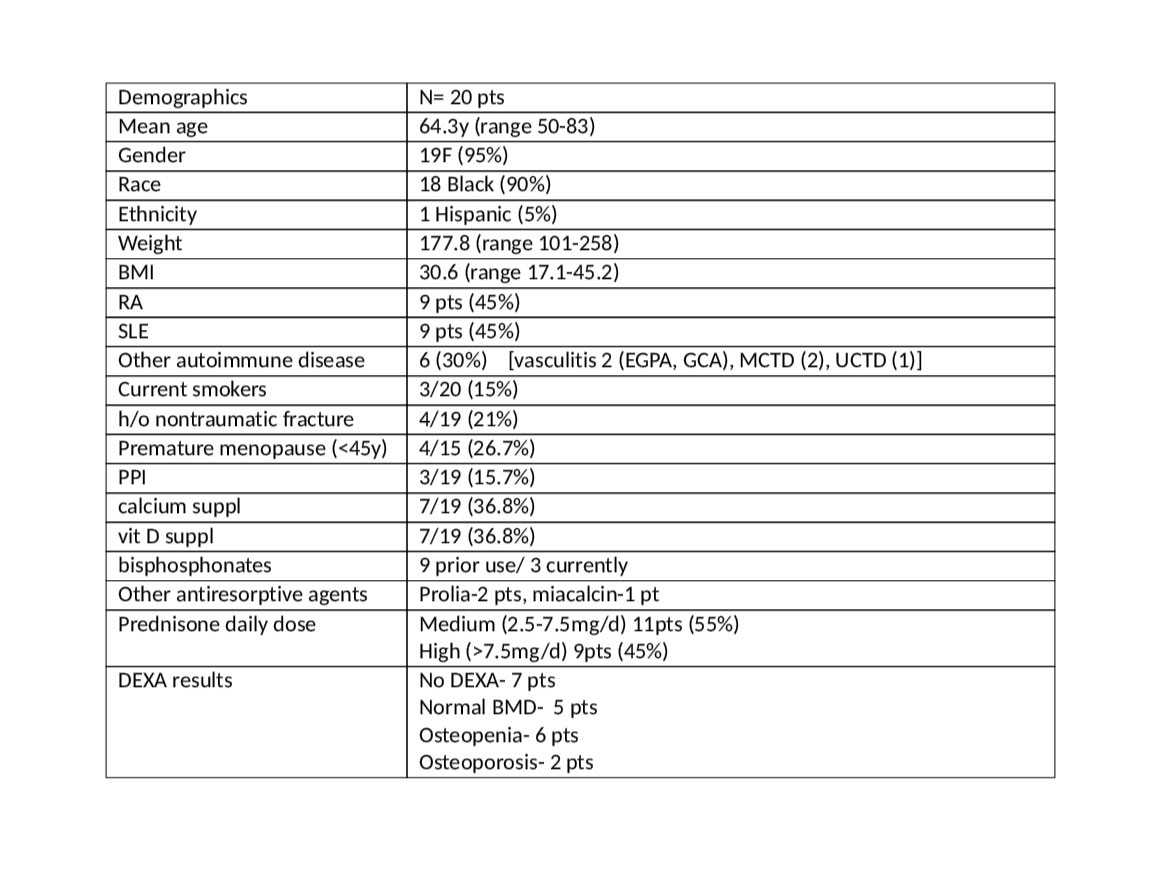
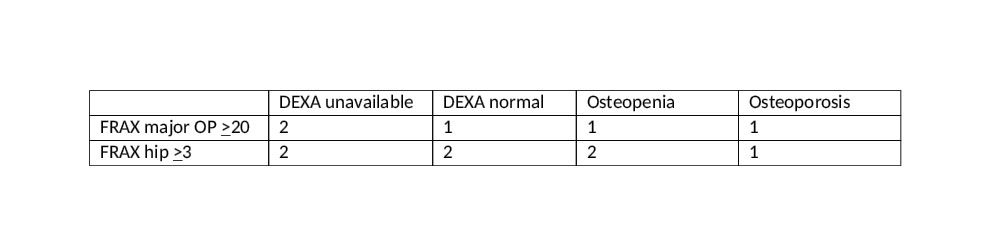
Results: 55 patients with autoimmune disease were studied, of whom 48 received prednisone at some time. 20/55 were on prednisone during the past year, average dose 14.6mg/d (range 2.8-30mg/d), 18/55 are currently on prednisone. Of the 20 patients on prednisone over the past year, mean age was 64.3y (range 50-83), 19 female (95%), 18 Black (90%), (full demographics in Table 1). Prednisone use was classified as low (< 2.5mg/d) n=0, medium (2.5-7.5mg/d) n=11, high ( >7.5mg/d) n=9. DEXA results were not available in 7 patients. 5 patients had normal bone density, 6 were classified as osteopenia, and 2 were osteoporotic. Calculated FRAX scores were different from those anticipated by DEXA score (Table 2). FRAX > 20% risk for major OP fractures was found in 5/20pts; of those, 2 had no DEXA available, 1 had normal BMD on DEXA, 1 was osteopenic and one had osteoporosis. Calculated FRAX of >3% risk for hip fractures was found in 7/20 pts, of whom 2 had no DEXA avail, 2 had normal BMD on DEXA, 2 were osteopenic and 1 was osteoporotic. Further adjustment for high dose prednisone use resulted in 2 additional patients at risk, 1 with FRAX > 20% risk for major OP fractures and 1 with FRAX > 3% risk for hip fracture.
Conclusion: There is a discordance between DEXA measured osteopenia/osteoporosis and FRAX risk. This is of particular concern in our demographically unique, largely Afro-Caribbean population with a high proportion of obesity, calcium-poor diets and comorbidities that can impact bone health. We recommend that FRAX scores be calculated on all patients even if no DEXA is available. We encourage smoking cessation and calcium/vitamin D supplementation for all. Just as weight gives only a partial glimpse of a patient’s burden of adiposity and BMI is needed to fully understand the issue, so too DEXA parameters only provide a partial glimpse of bone health.
(1) Buckley L, Humphrey MB. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 2018;379:2547-56
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Terebelo S, Abduraimova M, Freeman-Beman L, Kabani N, Pathiparampil J, Dvorkina O, Ginzler E. DEXA Does Not Accurately Reflect FRAX Score in Patients with Autoimmune Disease on Corticosteroids [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dexa-does-not-accurately-reflect-frax-score-in-patients-with-autoimmune-disease-on-corticosteroids/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dexa-does-not-accurately-reflect-frax-score-in-patients-with-autoimmune-disease-on-corticosteroids/